Lesson 15: Environmental problems/Environmental Justice
Lecture Outline:
What is an environmental problem?
Environmental problems in historical context
The scale of environmental problems
Global environmental problems reveal global environmental injustice
The politics of environmental justice: social movements and law
3: The Scale of the environmental problems:
Local scale:
Regional scale:
For example:
Imports of Eucalyptus and Eucalyptus plantations → Very flammable → Fires release harmful particle for human breathing → Winds storms etc. will then carry this through the rest of the region or multiple regions
4: Global environmental problems reveal global environmental injustice
5. Environmental injustice:
Environmental justice is a social movement that addresses injustice that occurs when poor or marginalized communities are harmed by hazardous waste, resource extraction and other land uses without benefit. The exposure to environmental harm is inequitably distributed.
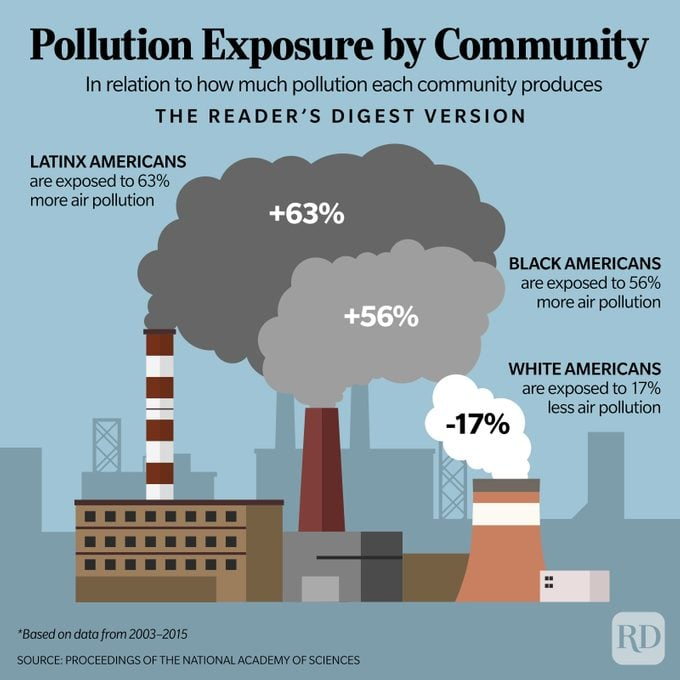
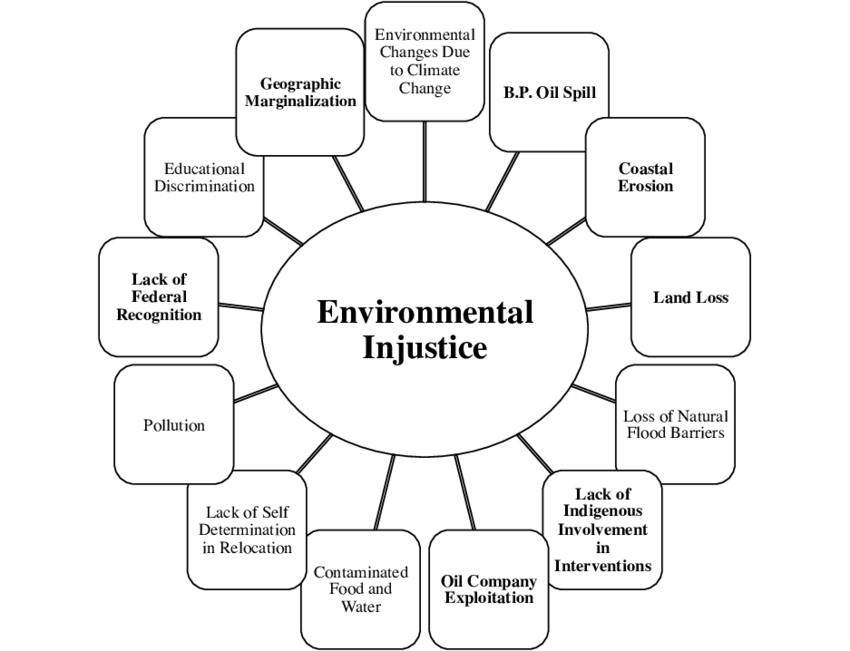
Externality: A cost or benefit caused by an economic actor that is not suffered or enjoyed by that same actor.
6: The politics of environmental justice: Social movements and law:
Legal Recognition of Nature’s rights