Key Elements of Information Security Programs
Information Security Program Components

Controls: Derived from policies aligned with goals and objectives.
Types include standards, procedures, baselines, guidelines.
Categories: technical, administrative (procedural), and physical controls.
Types of controls: deterrent, preventive, detective, corrective.
Monitoring and Metrics:
Essential for evaluating if controls provide adequate security.
Involves functional and assurance-related monitoring for validation.
Program Management Knowledge:
Security manager's responsibility to manage security controls effectively.
Ensuring controls are effective and cost-efficient.
Technology Awareness:
Understand available technologies and assess them against organizational goals.
Decisions should align with business expectations and budget constraints.
Constraints in Security Programs
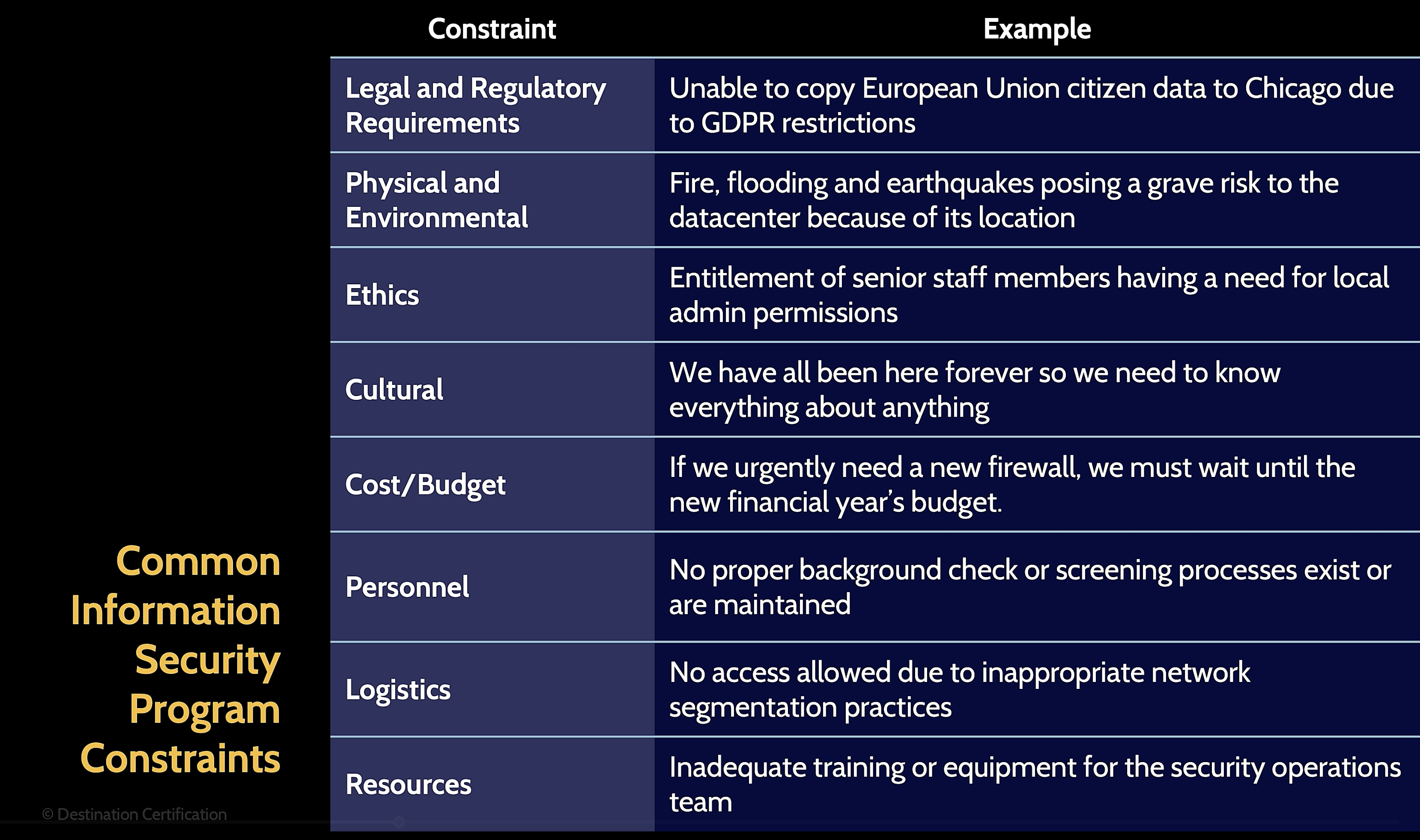
Compliance Requirements: Must align controls with legal and regulatory mandates.
Physical Security: Essential to protect systems from physical threats (e.g., unauthorized access).
Cultural Implications:
Importance of cultural change and ethics in implementation.
Organizational tone set by leadership regarding security responsibility.
Cost and Budget:
Security investments must return value and align with organization goals.
Proportional expenditure on security measures is critical.
Staff Skills:
Importance of having skilled personnel, possibly CISM certified.
Logistics: Need alignment of resources with operational requirements.
Challenges in Security Program Implementation
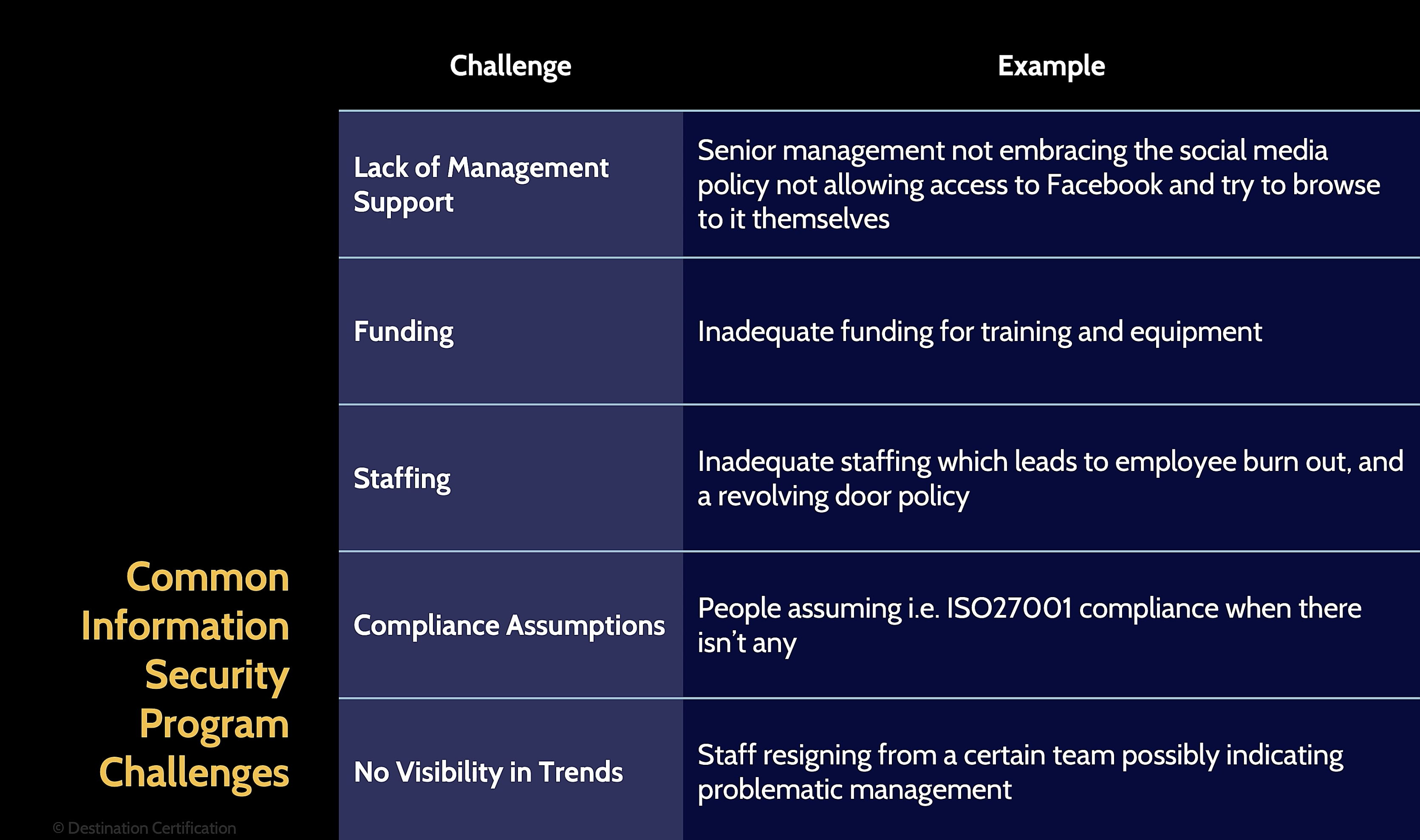
Management Support:
Critical for success; lack leads to reactive security functions.
Management involvement ensures alignment with organizational objectives.
Funding and Staffing:
Directly linked to the level of management support.
Compliance Assumptions:
Regular assessment of compliance obligations required; avoid assumptions.
Visibility and Trending:
Continuous monitoring of environment trends and employee turnover as key risk indicators.