GENBIO (copy)
Steps in Scientific Method
problem statement
Literature review
hypothesis formulation
experimentation
data collection & analysis
conclusion
2 types of hypothesis
Ho - null hypothesis
Ha- alternative hypothesis
2 Types of conclusion
Accept
Reject
Anti- bacterial
Reject - Ho Accept - Ha
W/o Antibacterial
Reject - Ha Accept - Ho
ml = microliter
1ml = 1000pql
OBJECTIVE LENS
Scanner (Red) = 4x
Low Power Objective | LPO (Yellow) = 10x
High Power Objective | HPO (Blue) = 40x
Oil Immersion Objective | OIO (White) = 100x
Total Magnification:
4x * 10x = 40x
Cells
Cell Theory
3 Postulates
All living things are composed of one / more cells
The cell is the basic unit of life
All cells arise from pre- existing cells.
Cell Structure And Functions
Cell membrane
Outer covering
Supports & Protects
Also Calle as plasma membrane
made with phospholipids
Cytoplasm
Thick, Clear liquid Jelly substance where organelles are suspended in.
Fluid (Cytosol)
Nucleus
Center of control in the cell, contains the DNA
Send signals to the cells to grow, mature, & die
Inside DNA, Creates Ribosomes’
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Rough ER - Has attached ribosomes
Smooth ER - No Ribosomes
Transports substances, has a role in metabolism.
Molecules
Golgi Apparatus/ Complex/ Body
Cells “Post Office”
Packages molecules processed by ER
Protein
Mitochondria | Singular = Mitochondrion
Powerhouse of the Cell
Makes ATP, Energy from food → Oxygen + Glucose
Made through Cellular Respiration
ATP = Adenosine Triphosphate
Lysosomes & Peroxisomes
Recycling Center = Recycle worn - out cell
Digest old foreign cells / Bacteria in the cell
Animal Cells
Rid of toxic Substance
Ribosomes
Protein Synthesizers ( Creates Proteins using cell genetic material)
Can be found floating around cytoplasm or stick - around ER
Cell Wall
Only in Plant Cell
Outermost layer of plant cell + Protects and maintaining plant formation
Chloroplast
Only in plant cell : Organelles for photosynthesis
Contains the chlorophyll
Yellow
Green
Red
Vacuoles
Stores food, water & other wastes in the cell.
TYPES OF CELLS
Eukaryotic Cells | Prokaryotic Cells |
Present Nucleus Ex: Animal Cells | Nucleus is not present (Singular cellular) Ex: Bacteria |
Division Thru mitosis | Division thru cell fission |
Plastids
Color pigments in the cells
Prokaryote
The organism Itself
Works for all types of cell
Prokaryotic
The cell
Works for all types of cell
Types of Cells
Epithelial Cells
Organ Lining
Connective tissue cells
Secretes Rigid extracellular matrix
Muscle cells
Has muscle fibers allowing in/voluntary movement
Collagen &
Nerve Cells
Sends electric signals
Modifications
Apical
Cilia - Hair like projections moving bacteria
Flagella/ Flagellum (Singular) - Whiplike tail used for locomotion
Formed form microtubules
Villi - Fingerlike projections, epithelial layer in organs
Microvilli - present in intestines + absorbs nutrients
smaller projections that arise from cell’s surface
Pseudopods - irregular lobes formed by amoebas
“walks” to catch its prey
ECM | Extracellular Matrix - Glycoprotein is the main ingredient in animal cells
Basal
Desmosomes | Hemidesmosomes
Primary made of keratin, integrin, cadherin
Lateral
Tight Junctions
Acts a barriers, Regulating the movement of water & solutes
Gap Junctions
Allows direct exchange of chemicals between cytoplasm of 2 cells
Adhering Junctions
Fastens cells to each other
Cell Cycle
Interphase
Longest phase , Preparation stage
G0 - Resting state ; No act
G1 - Grows in size, nutrients, development
S - Synthesis phase, copying DNA (Genetic Material)
G2 - Double checking cell size, DNA replication
If error occurs → Apoptosis (Cell death)
Mitotic phase
P -Prophase
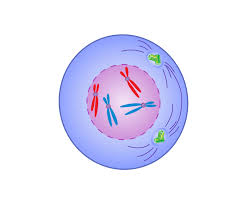
Metaphase

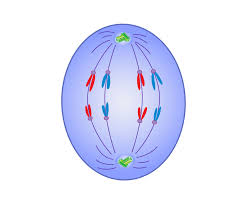
Anaphase
Telophase
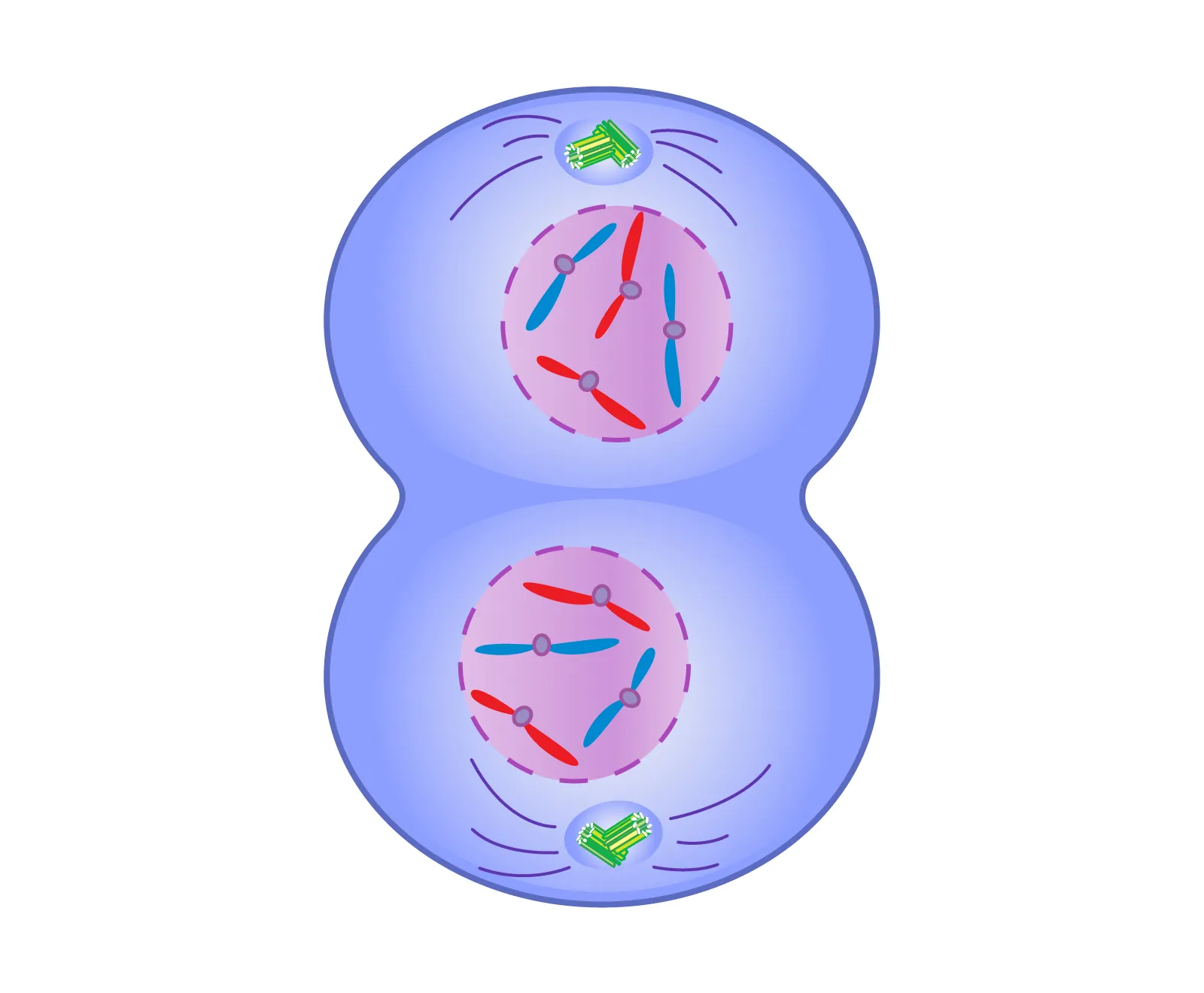
→ Cleavage
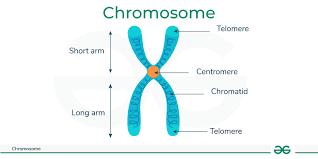
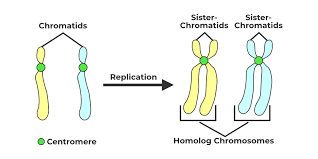
23 - Homolysis Chromosomes
2n = 46 → Diploid
n = 23 - Haploid
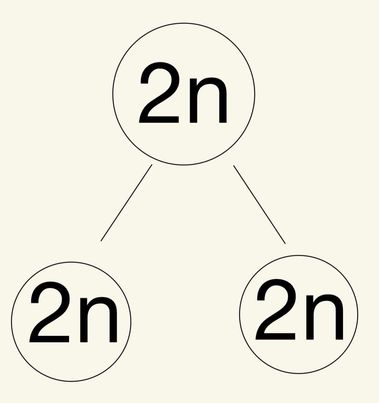
Mitosis - 2 Identical daughter cell
ONLY Somatic cells, Body cells
Animal → A.C - Cleavage furrow
Plant → P.C - Cell plate
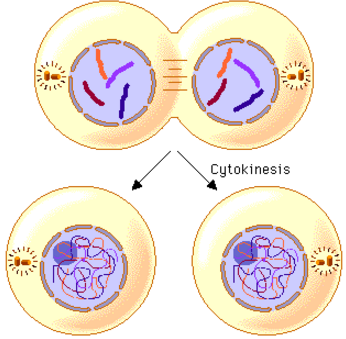
Cytokinesis
Division of Cytoplasm
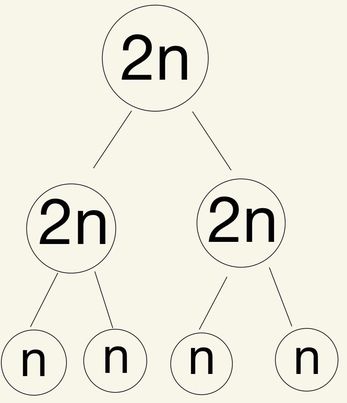
Meiosis
4 Haploid cells
Reduction Division
Gametes (Sex Cells)
SC.23
Spermatogenesis
Oogenesis - Haploids
47- 3 (start of cell)
With disorder
Down Syndrome
Results from a 3rd chromosome on the 21st pair
when there’s too little chromosomes
TRANSPORT MECHANISM
Structure of Cell Membrane / Plasma
Phospholipids
Bilayered
Hydrophilic
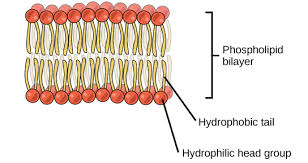
Hydrophilic
Water Loving
Hydrophobic
Water fearing
SJ Singer & Garth L. Nicolson 1972 FLUID MOSAIC MODEL
Cell Membrane
Thin layer Surrounding Cytoplasm of pro & eukaryotic cells
Semi selective permeable, allows only specific things in.
Attachment site for cytoskeletal shaping & Supporting
Cytoskeletal | Organelle
Maintains Shape / structure
Microfilaments
Microtubules
Intermediate Filaments
Aquaporin
Water moves rapidly into & out of cells
Water channels in bacteria
Since tails are hydrophobic
Conformational Change
Protein changes shape
Membrane proteins
Embedded / attached in cell membrane
a. Receptor - Binds to chemical messengers fitting into it.
b. Enzyme - Breaks down chem messengers
c. Ion channel - Constantly open for exist
d. Gated Ion Channel - Open/ Closes to allow ions at specific times
e. Cell identity marker -Glycoprotein acting, Distinguishing the body’s own cell from foreign cells.
f. Cell adhesion molecule | CAM - Binds one another (Physically)
Types of Membrane proteins
Integral Protein - Embedded fully/ partially
Peripheral Protein - Loosely attached to the cell’s membrane
Transport Mechanism
Various ways molecules move around membranes for homeostasis function
To maintain homeostasis, Membranes need to oversee what goes in and out of the cell
→ Homeostasis
Process of keeping stable internal / external environment
→ Diffusion
Higher to Lower Concentration
Universe tends toward disorder
Aquaporin classifies under facilitated diffusion
Types of cellular transport
Passive
Movement w/out energy
Active
Movement w/ energy & Proteins
Facilitated Diffusion
w/ assistance (Protein)
Simple Diffusion
Direct transport | Uniport = 1 way
Osmosis
Diffusion of water
Concentration of water
Determines osmosis direction
Hypertonic
More solute, Less water
Ex: Salt water
Hypotonic
Less solute, more water
Ex: Melted ice in ice tea
Isotonic
Equal solute. Equal water
Ex: Normal water
Managing water balance
Where cell survival depends
Active transport | Details
energy is harvested by hydrolysis → Water breakdown
ATP - ADP (bisphosphate)
Low to high concentration
Ex: Sodium potassium pump
Symport
Same direction
Antiport
Opposite direction
Primary Active Transport
Uses the energy found in ATP, Photons & Electrochemical gradients
Photo energy
Basic unit of light
Secondary - Active Transport
Maybe symport or antiport
Bulk Transport
Phagocytosis - Cell eating
Pinocytosis - Cell drinking | Extracellular Fluid → Nutrients
Receptor - Mediated Endocytosis
Receptor used to capture specific target molecules
Exocytosis
disposes leftovers “Kiss n Run” touches membrane & diffuses out.