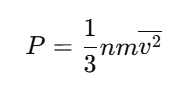Kinetic Theory(PRESSURE EXERTED BY GAS)
PRESSURE EXERTED BY GAS
An ideal gas is enclosed in a cubical box of side length lll.
A molecule of gas is moving with a random velocity v, which can be resolved into components:
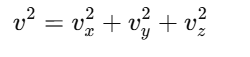
Momentum along the x-axis for a molecule is px=mvx, where m is the mass of the molecule.
Change in Momentum During a Collision
When a molecule collides with a wall parallel to the y-z plane, its velocity component vx is reversed, so:
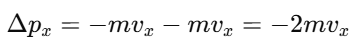
This is the total change in momentum along the x-axis.
Number of Collisions in Time ΔT
Consider the number density n, which is the number of molecules per unit volume.
Molecules that can collide with the wall in time ΔT are those within a distance vxΔT of the wall.
The number of such molecules is:

The factor 1/2 accounts for only those molecules moving toward the wall.
Momentum Transferred to the Wall
For each collision, the momentum transfer is 2mvx.
Total momentum transferred in time ΔT is:
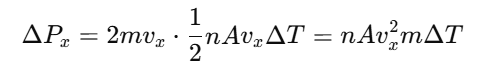
Force on the Wall
Force is the rate of change of momentum:
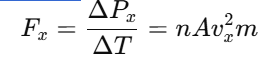
Pressure on the Wall
Pressure is force per unit area:
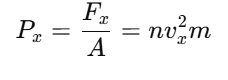
Velocity Averaging
Since molecules have different velocities, we use the average of v²x
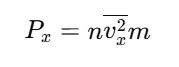
From symmetry of the cube, pressure is the same along all three axes (Px=Py=Pz):
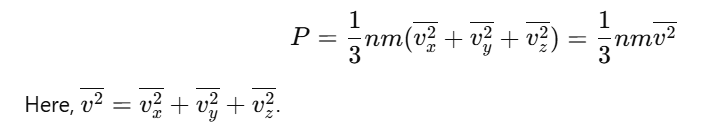
The pressure of the gas is: