Week 9 lecture 3 Doppler Artifacts Summary
.
Doppler Artifacts
Spectral Doppler Artifacts
Frequency aliasing
Range ambiguity (high PRF)
Spectral broadening
Spectral mirror artifact
Colour Doppler Artifacts
Colour aliasing
Colour dropout
Colour bleed
Angle effects
Mirror image
Spectral Doppler Artifacts
1. Frequency Aliasing
Spectral Doppler flow information appears above and below the baseline.
Doppler shift frequencies are greater than 1/2 the PRF (Pulse Repetition Frequency).
The Nyquist limit is exceeded, leading to aliasing.
PRF is also referred to as the scale.
Correcting Spectral Aliasing
Adjust the PRF/scale: Increase the velocity scale.
Decrease the baseline: This is called baseline shifting.
Increase the Doppler angle: But not beyond 60 degrees.
Use a lower operating frequency: A lower operating frequency results in a lower Doppler shift.
Doppler Equation:
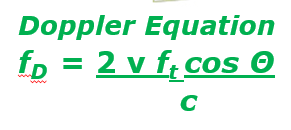
Where:
f_D is the Doppler shift frequency
v is the velocity of blood flow,
f_t is the transmitted frequency,
\Theta is the Doppler angle,
c is the speed of sound in the medium.
Use continuous wave (CW) Doppler: Continuous wave Doppler does not have the same aliasing limitations as pulsed wave Doppler.
2. Range Ambiguity Artifact
In PW Doppler, the ultrasound system sends another pulse before all echoes from the previous pulse are received.
This leads to the range ambiguity artifact.
3. Intrinsic Spectral Broadening
The spectral window is filled in (vertical thickening).
This is seen with turbulent flow conditions.
4. Spectral Mirror Artifact
Flow is seen on opposite sides of the baseline.
Often seen when flow is perpendicular to the beam.
Colour Doppler Artifacts
1. Colour Aliasing
Colour Doppler has a reduced PRF compared to spectral Doppler, therefore aliasing is more commonly seen.
Wrapping around of colour map.
Opposite flow direction to Doppler shift.
2. Colour Dropout
Colour is not displayed when it should be.
Causes:
Doppler shift signal is too weak.
Colour Doppler settings are not optimized.
Solutions:
Reduce Doppler angle.
Use Power Doppler.
Adjust Colour Doppler settings.
Avoid having Wall Filters set to Max and Gains lowered!
3. Colour Bleed
Colour pixels appear outside of the vessel wall.
Most likely caused by tissue movement.
4. Colour Angle Effects
Different hues and direction are displayed for blood flowing at the same velocity and direction.
It's important to understand the different Doppler angles to interpret what is going on.
5. Mirror Image
Duplication of a vessel or colour Doppler shift on the opposite side of a strong reflector.
The mirror vessel will demonstrate colour flow.
Decreasing colour gain may reduce or eliminate this artifact.