Measuring Stars
Masses of (Binary) Stars
Key equation: 𝐷^3 = (𝑀1 + 𝑀2)𝑃^2
Luminosity Relation: 𝐿 ~ 𝑀^4
Diameters of The Sun
The Sun’s angular diameter (apparent size on the sky): Approximately 1/2 °
Linear diameter comparison:
109 times the diameter of Earth
1.39 million km
It’s difficult to measure distances for far stars.
Measuring Star Diameters
Method: Observe the dimming of a star’s light when the Moon passes in front of it.
The technique involves precise measurement of how long it takes for brightness to drop to 0.
We know the speed of the moon.
You must know the distance to the star.
Analyzing Eclipsing Binary Stars
Four contact points are observed during eclipses.
Time intervals provide information on the diameters of the stars involved:
Interval 1-2: measures the diameter of the smaller star.
Interval 1-3: measures the diameter of the larger star.
Spectra analysis via the Doppler effect gives relative speeds, which lets us calculate the diameter.
Radiation Law Application for Diameter Measurement
Hotter temperatures result in increased energy emission (photons) across all wavelengths.
Stefan-Boltzmann Law
This law mathematically describes the observation concerning hotter objects. Hotter objects radiate more energy at all wavelengths.
Total energy from a blackbody is summed over the electromagnetic spectrum.
Key formula: F = σ ∙ T^4
Where σ = constant = 5.67 x 10^{-8}
Radiation Law for Diameter (Stefan-Boltzmann)
Focus on constant temperature and energy flux applications.
Reinforces the equation: F = σ ∙ T^4
Stellar Diameters
Measurements indicate most nearby stars are similar in size to the Sun; with faint stars generally being smaller than luminous ones.
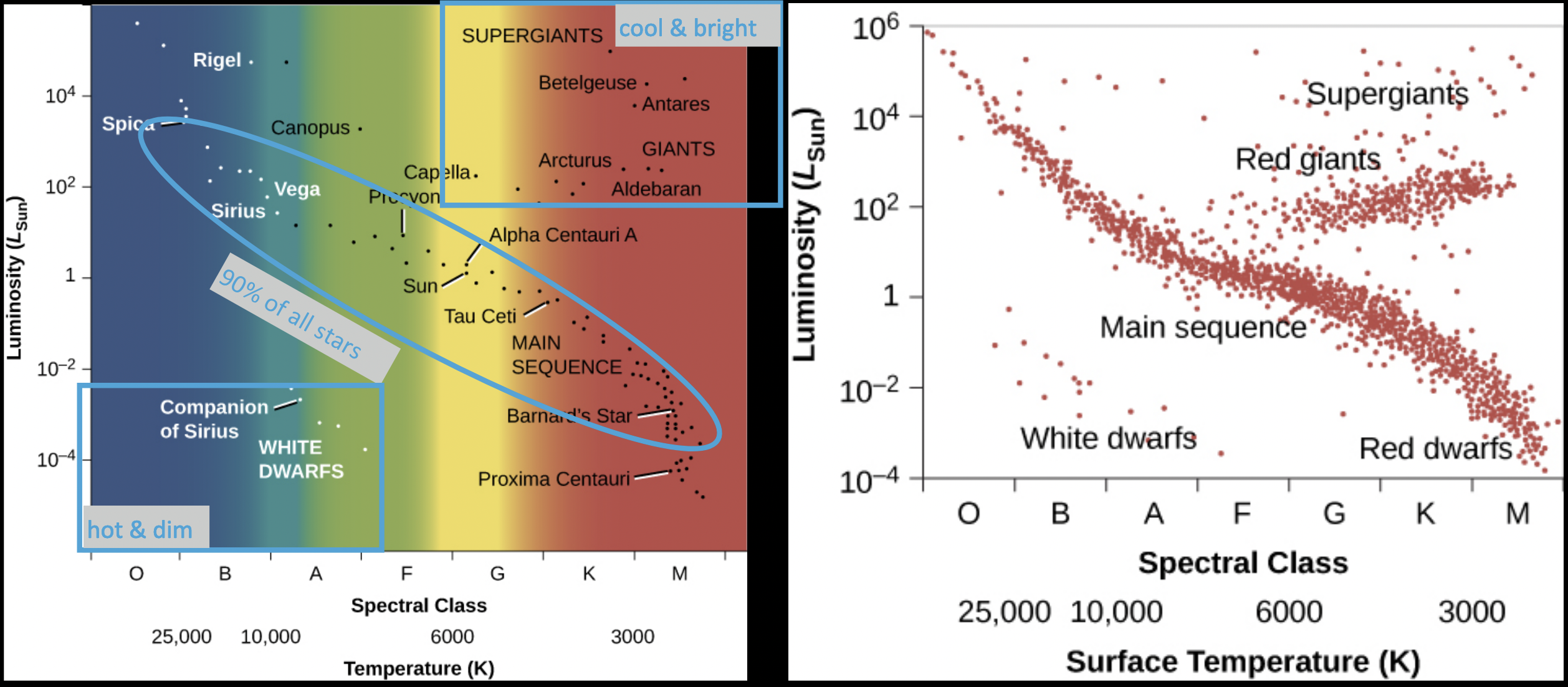
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
Purpose: Useful in characterizing star life cycles.
For the main sequence stars, the more luminous they are, the hotter they are.