Chapter 11: Atoms and Radioactivity
Inside Atoms
Atom is made up off:
- Central nucleus made up of protons and neutrons. Protons and neutrons are called nucleons.
- ==number of particles depend on the type of atom.==
- Protons have a (+) charge. Electrons have a (-ve) charge.
- An electron has same number of protons and electrons so charge is zero.
- Electrons re held in orbit by he force of attraction between opposite charges.
- ==Protons and neutrons and held tightly together in the nucleus by a different kind of force, called== ==strong nuclear force.==
Isotopes and Mass number
==Isotopes are elements/atoms/atomic number which have same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons.==
For example;
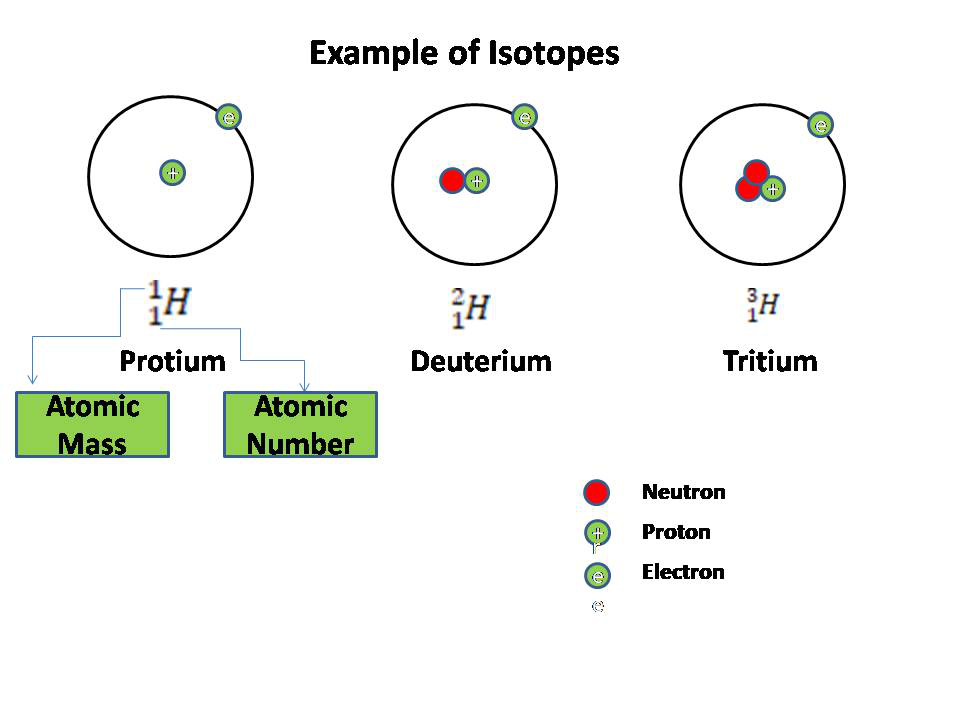
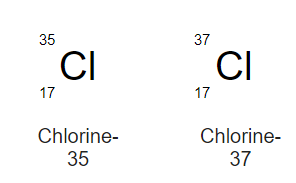
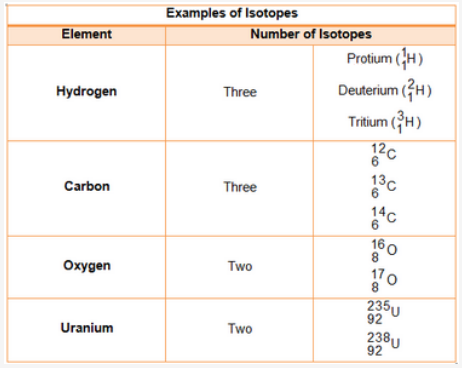
Nuclear Radiation
- The particles and waves radiate from the nucleus which is called nuclear radiation.
- ==Materials which emit nuclear radiation are== ==radioactive materials.==
- ==The disintegration of nucleus is called== ==radioactive decay.==
Ionizing Radiation
Atoms become ions when they lose (or gain) electrons.
- ==Nuclear radiation== ==can remove electrons from atoms in its path, so it has an ionizing effect.==
- *If a gas becomes ionized, it will conduct an electric current.
Alpha, Beta and Gamma radiation
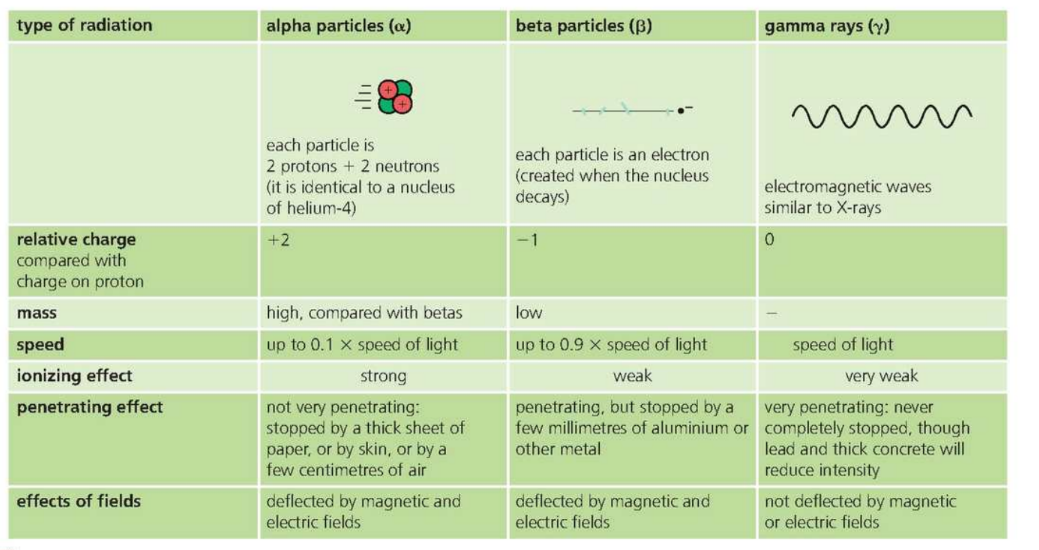
- ==Alpha Particle== ==are more ionizing than== ==Beta Particles.==
- They have a greater charge, so exert more forces on electrons.
- They are slower, so spend more time close to any electrons they pass.
- ==Gamma rays== ==are least ionizing because they are uncharged.==
Radiation Dangers
- ==Nuclear radiation can damage or destroy living cells, and stop organs in the body working==
- It can also affect chemical reactions in cells.
- If radioactive gases are absorbed in the body, they are difficult to remove, and their radiation can cause damage to cells.
- Beta and gamma rays are most harmful because they can penetrate to internal organs.
Background Radiation
==Background radiation is a measure of the level of ionizing radiation present in the environment at a particular location which is not due to deliberate introduction of radiation sources.==
GM Tube
It is used to detect alpha, beta and gamma radiation.
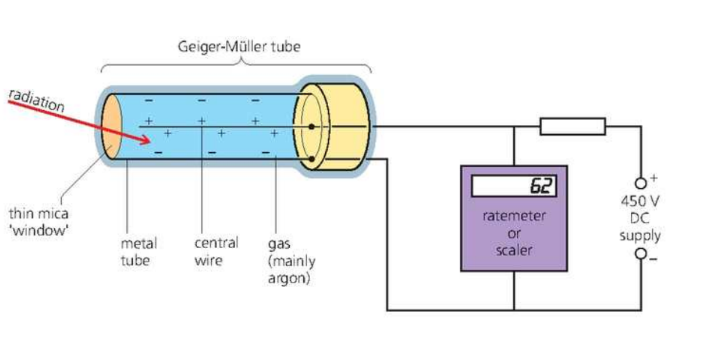
The GM tube can be connected to the following:
- A ratemeter gives reading in counts per second.
- A scalar counts the total number of particles detected by the tube.
- An amplifier and loudspeaker - loudspeaker makes a click when each particle or burst of gamma particle is received.
Radioactive Decay
- The emission of an alpha or beta particle makes unstable nuclei, stable; but alters the number of protons and neutrons in it. So it becomes nucleus of a different element.
- The original nucleus is called the parent nucleus. The nucleons formed is the daughter nucleus.
- The daughter nucleus and any emitted particles are the decay products.
Alpha Decay
}}Radium-226 (atomic number 88) decays by alpha emission. The loss of the alpha particle leaves the nucleus with 2 protons and 2 neutrons less than before. So the mass number drops to 222 and the atomic number to 86. Radon has an atomic number of 86, so radon is the new element formed as shown below:}}
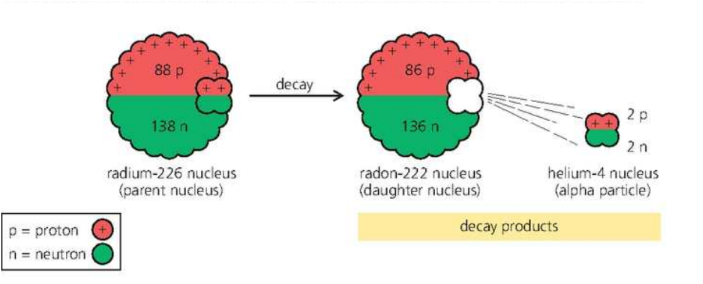
It can be written as:
- Equation
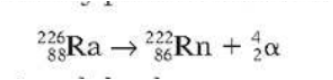
- ]]During alpha decay:]]
- the top numbers balance on both sides of the equation (226 = 222 + 4), so the mass number is conserved (unchanged).
- the bottom numbers balance on both sides of the equation (88 = 86 + 2), so charge is conserved.
- a new element is formed, with an atomic number 2 less than before. The mass number is 4 less than before.
Beta Decay
Iodine-131 (atomic number 53) decays by beta emission. When this happens, a neutron changes into a proton, an election, and an uncharged, almost massless relative of the electron called an antineutrino. The electron and antineutrino leave the nucleus at high speed. As a proton has replaced a neutron in the nucleus, the atomic number rises to 54. This means that a nucleus of xenon-131 has been formed:
\n 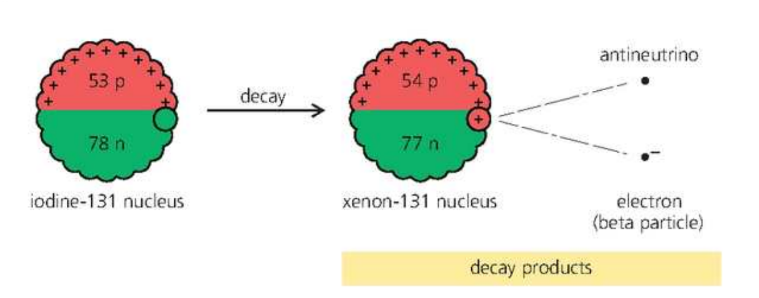
It can be written as:

]]During beta decay]]
- the top numbers balance on both sides of the equation (131=131 + 0 + 0), so the mass number is conserved.
- the bottom numbers balance on both sides of the equation (53=54-1+0), so charge is conserved.
- a new element is formed, with an atomic number 1 more than before. The mass number is unchanged.
Gamma Emission
With some isotopes, the emission of an alpha or beta particle from a nucleus leaves the protons and neutrons in an 'excited' arrangement. As the protons and neutrons rearrange to become more stable, they lose energy. emitted as a burst of gamma radiation. This is emitted as a burst of gamma radiation.
- ==Gamma emission by itself causes no change in mass number or atomic number.==
Rate of half decay and Half life
The half life of a radioactive isotope is the time taken for half the nuclei present in any given sample to decay.
For example:
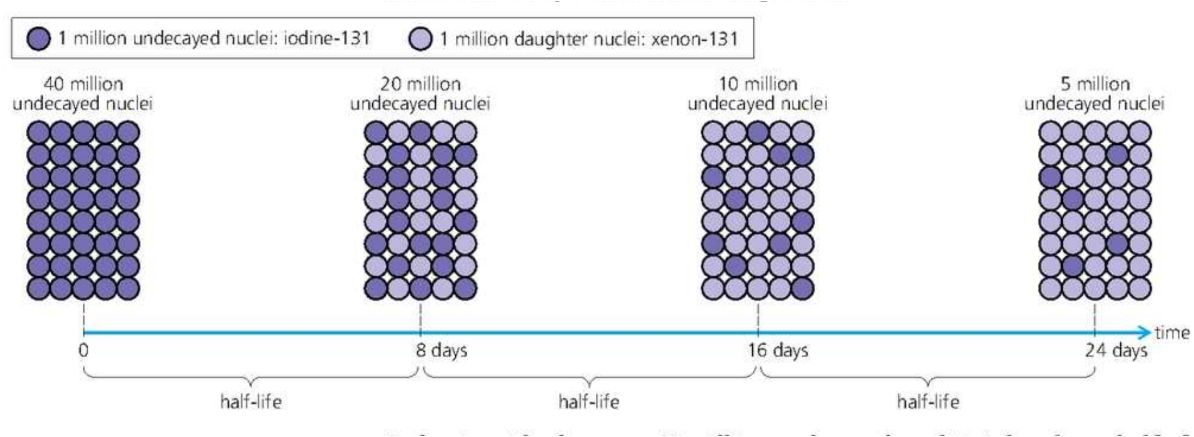
Activity and Half life
]]The half life of a radioactive isotope is the time taken for the activity of any given sample to fall to its original value.]]
Nuclear Energy
Nuclear Fission
- It is the process of splitting a nucleus.
- Uranium-235 is a commonly used isotope as the fuel in nuclear reactors.
- When a Uranium-235 nucleus absorbs a neutron, it splits into two daughter nuclei and 2 or 3 neutrons, releasing energy in the process.
- The neutrons then can induce further fission events in a chain reaction.
Nuclear Fission
- ==It is the process of fusing two nuclei to form a larger nucleus.==
- Energy is released during this process.
- Nuclear fusion is how the sun and other stars release energy.
Using Radioactivity
Tracers
- Checking the function of body organs.
- For example, to check thyroid function, a patient drinks a liquid containing iodine-123, a gamma emitter. Over the next 24 hours, a detector measures the activity of the tracer to find out how quickly it becomes concentrated in the thyroid gland.
- Tracking a plant's uptake of fertilizer from roots to leaves by adding a tracer to the soil water.
- Detecting leaks in underground pipes by adding a tracer to the fluid in the pipe.
Testing Cracks
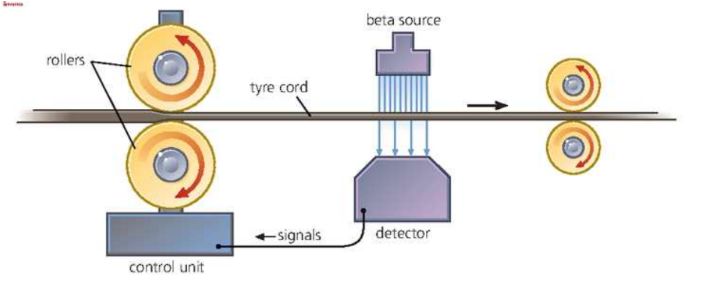
Thickness Monitoring
Following diagram shows one of the way to do this,
Carbon Dating
{{Through carbon dating we can determine the age or date of organic matter from the relative proportions of the carbon isotopes carbon-12 and carbon-14 that it contains. The ratio between them changes as radioactive carbon-14 decays and is not replaced by exchange with the atmosphere.{{
Atoms and Particles
Thompson’s “plum pudding” model
- J.J Thompson identified in 1987 identified that ==electron has a negative (-ve) electric charge, so an atom with electrons in it must also contain positive (+ve) charge to make it electrically neutral.==
- Thompson suggested that an atom might be a sphere of positive charge with electrons dotted inside it like raisins in a pudding.
- This made it name plum pudding model.
Rutherford Nuclear model
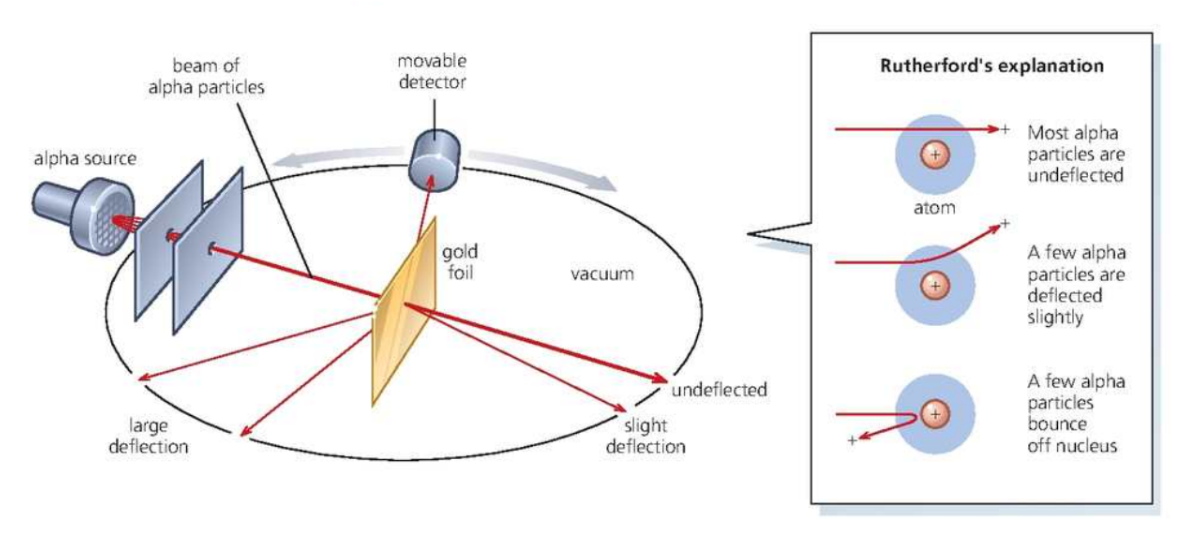
- Above experiment was ==carried out in 1911 by Geiger and Marsden== under the ==supervision of Ernest Rutherford==.
- It produced results which could not be explained by the plum pudding model.
- Thin gold foil was bombarded with alpha particles, which are positively charged. Most passed straight through the gold atoms, but a few were repelled so strongly that they bounced back or were deflected through large angles.
- Rutherford concluded that the atom must be largely empty space, with its positive charge and most of its mass concentrated in a tiny nucleus at the center.
- In his model, the much lighter electrons orbited the nucleus rather like the planets around the Sun.
Rutherford - Bohr model
- In 1913, Neils Bohr modified Rutherford's model by applying the quantum theory devised by Max Planck in 1900.
- According to this theory, energy cannot be divided into ever smaller amounts. It is only emitted (or absorbed) in tiny 'packets', each called a quantum.
- Bohr reasoned that electrons in higher orbits have more energy than those in lower ones. So, if only quantum energy changes are possible, only certain electron orbits are allowed. This modified model is known as the Rutherford-Bohr model.
Fundamental particles
It is a particle which is ^^not made up of other particles^^.
Quark changes in beta decay
In the most common form of beta decay, a neutron decays to form a proton, an electron (the beta particle), and an antineutrino:
- neutron ----→ proton + antineutrino
If this is rewritten to show the quarks:
up quark up quarkdown quark ------→ up quark + electron + antineutrino down quark down quarkFrom the above, you can see that this type of beta decay occurs when a down quark changes into an up quark, as follows:
down quark ------→ up quark + electron + antineutrino(-1/3) (+2/3) (-1) (0)The relative charges underneath the equation show that there is no change in total charge. In other words, charge is conserved.
In the less common form of beta decay, a proton decays to form a neutron, a positron (the beta particle), and a neutrino. This happens when an up quark in the proton changes into a down quark.