AQA GCSE Chemistry Trilogy: Hydrocarbons and Alkanes
Crude Oil:
- Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain hydrogen and carbon atoms only.
- Crude oil is a finite resource that is found in the Earth’s crust.
- It is the remains of organisms that lived and died millions of years ago - mainly plankton, which was buried in mud.
- Crude oil is a complex mixture of hydrocarbons.
- Used as -
- Fuels such as petrol, diesel, kerosene, heavy fuel oil and liquefied petroleum gases
- Feedstock for the petrochemical industry
- Solvents
- Lubricants
- Detergents
- A feedstock is a raw material used to provide reactants for an industrial reaction.
- A petrochemical is a substance made from crude oil using chemical reactions.
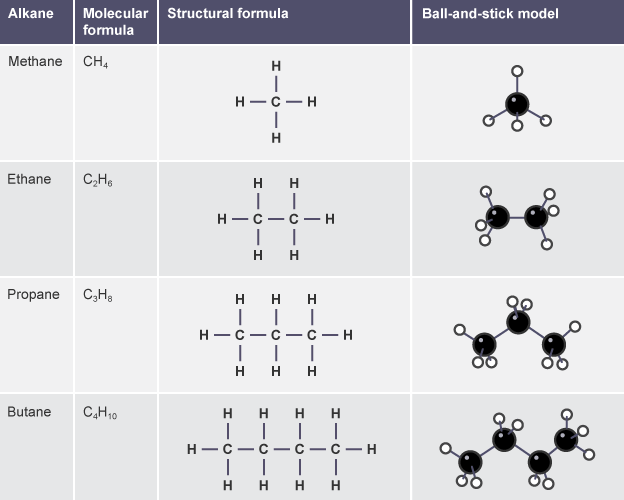
Alkanes:
Form a homologous series - A 'family' of organic compounds that have the same functional group and similar chemical properties. Alkanes:
- have the same general formula
- differ by CH2 in molecular formulae from neighbouring compounds
- show a gradual variation in physical properties, such as their boiling points
- have similar chemical properties
The general formula for the alkanes is CnH(2n+2), where n is the number of carbon atoms in the molecule.
Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons:
- Hydrocarbons, because they are compounds containing hydrogen and carbon only
- Saturated, because their carbon atoms are joined by C-C single bonds