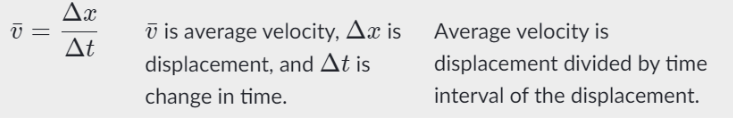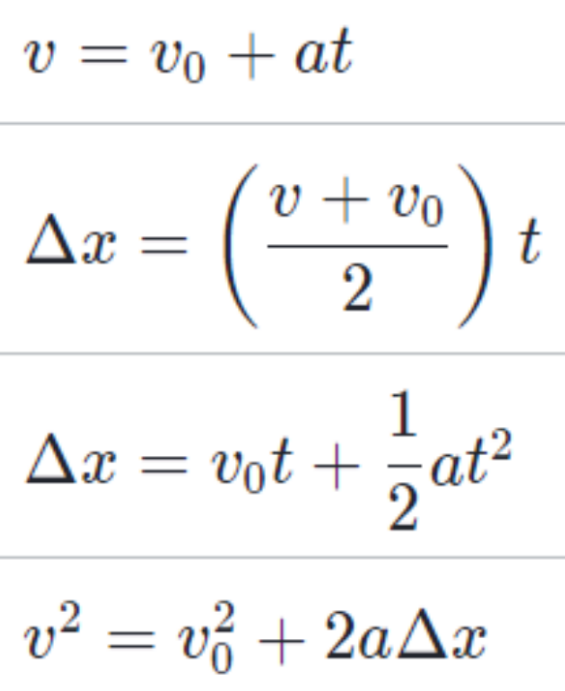Unit 1: One-dimensional Motion
Physics Foundations:
vectors- magnitude/size AND DIRECTION is specified

scalars- magnitude/size

Distance, Displacement, and Coordinate System:
distance- total length of your path
- always absolute value (can never be negative)
- is a scalar quantity with units of distance
displacement- net change in position
- mentions change + direction
- vector quantity with units of distance
formula for displacement:
position time graph- time is on horizontal axis & position is on vertical axis
- ex of position time graph:
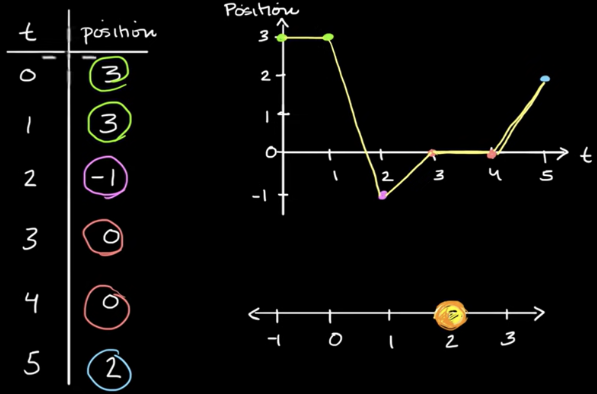
coordinate system- what we use to describe position
- origin = 0
- defines directions with positive & negative numbers
position- location of the object based on origin (0)
- represented by x when referring to the position
reference frame: point of view from which measurements can be made where all frames of reference are equally valid
Average Velocity and Average Speed:
- average velocity- is a vector
formula for average velocity:
- average speed- is a scalar
formula for average speed:
Velocity and Speed from Graphs:
instantaneous speed- speed of an object at a particular moment in time
- always absolute value (can never be negative)
instantaneous velocity- velocity at a particular moment
- can be positive (+) or negative (-)

to be more exact you can choose a smaller displacement and shortter time interval
case where velocity of object does not change: average velocity
- in that case average velocity = instantaneous velocity
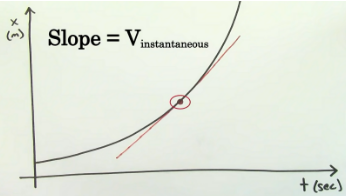
case where velocity of object is changing: motion on x-verses t-graph
- slope at any particular point = instantaneous velocity
- get instantaneous rate of when x is changing with respect to time (find slope using closest unit of time before and after)
3. case where acceleration is constant
-kinematic formulas (explained further on)
-area under the velocity vs time curve = displacement
- Instantaneous vs average (in general)
- average = over time
- instantaneous = a given moment
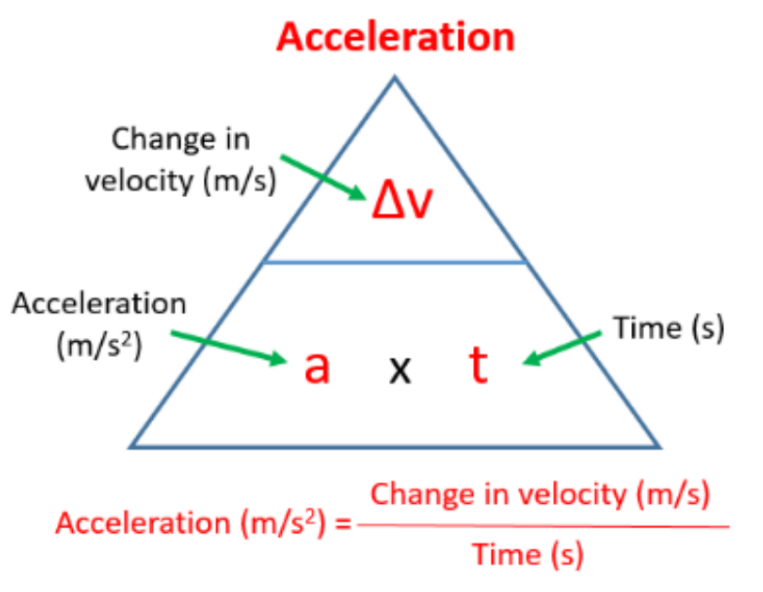
Average and Instantaneous Acceleration:
- acceleration- change in velocity over time (is a vector quantity)
formula for acceleration:
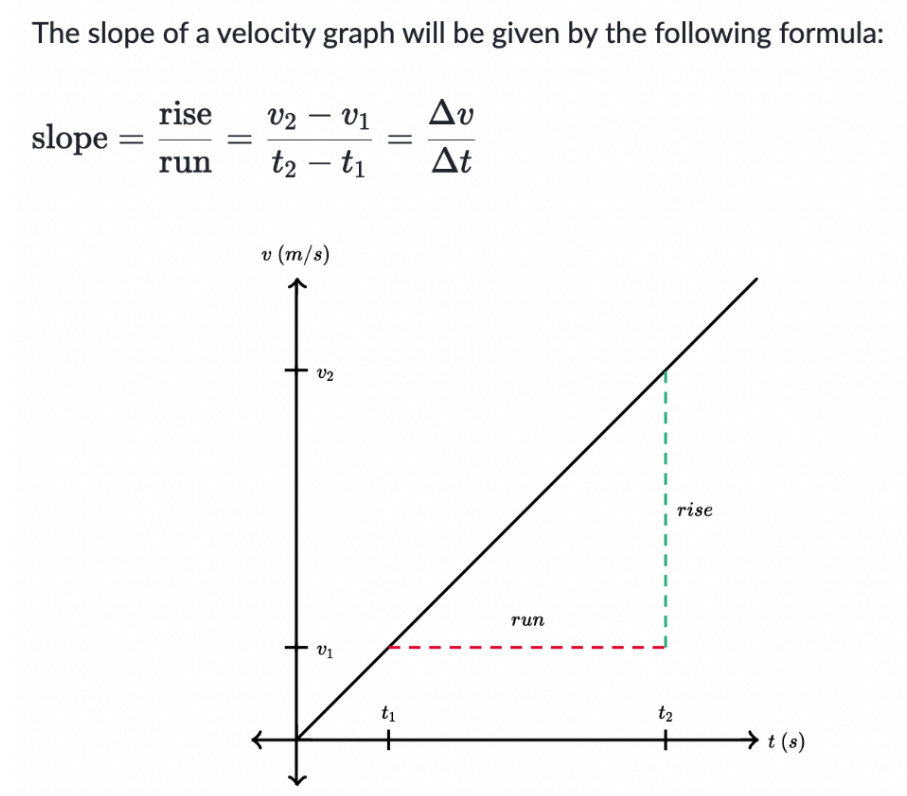
- Velocity vs time graph
- vertical axis represents the velocity of the object
- slope of the velocity graph represents acceleration of the object
formula/example:
- slope is steep = object rapidly changing velocity
- slope is hallow = object not changing velocity as rapidly
- slope is negative/directed downwards = acceleration is negative
- slope is positive/directed upwards = acceleration will be positive
- (area under velocity graph/curve = displacement of the object)
\
- Average acceleration- rate at which velocity changes over a specified interval
- \
- Unit: SI units of m/s^2
- is a vector quantity (can be positive or negative)
- speed of object remains same but changes direction = object accelerating
- velocity and acceleration vectors point in opposite directions = object is slowing down
- Instantaneous acceleration- rate at which velocity changes at a specific instance in time
Motion with Constant Acceleration
kinematic equations:
- earth’s gravity = 9.8 m/s^2
- acceleration is a constant line