CHAPTER 4
MEDICARE
Medicare is Australia’s universal health insurance scheme that provides
access to health care that is subsidised by the government.
NOT FREE it is subsidised
Schedule fee: the amount medicare covers towards certain treatments and consultations
patient co-payment: payment made by the patient for the service, that is in addition to the cost covered by Medicare
Bulk billing: when a doctor only charges the schedule fee for an appointment
COVERED
consultation fees for doctors and specialists
tests and examinations needed to treat illnesses, including x-rays and pathology tests, and eye tests performed by optometrists.
Most surgical and other therapeutic procedures performed by general practitioners
some surgical procedures performed by approved dentists.
Some dental services for children aged 2 – 17 (Child Benefits Dental Scheme)
In hospital expenses
NOT COVERED
Treatment in a private hospital
general dental examinations and treatment
home nursing care or treatment
ambulance services
cosmetic or unnecessary procedures
Most allied health services such as physio, chiro
Medications
Health aids such as glasses, hearing aids
FUNDING
Medicare levy
2% tax placed on all taxable income
Medicare levy surcharge
People without private health insurance earning more than ($ 90,000 a year for individuals and $ 180,000 for families in 2017–18) have to pay an extra tax.
aims to encourage individuals to take out private hospital cover and, where possible, to use the private system to reduce the demand on the Medicare-funded public system.
general taxation
ADVANTAGES + DISADVANTAGES
Advantages Disadvantages | |
|
|
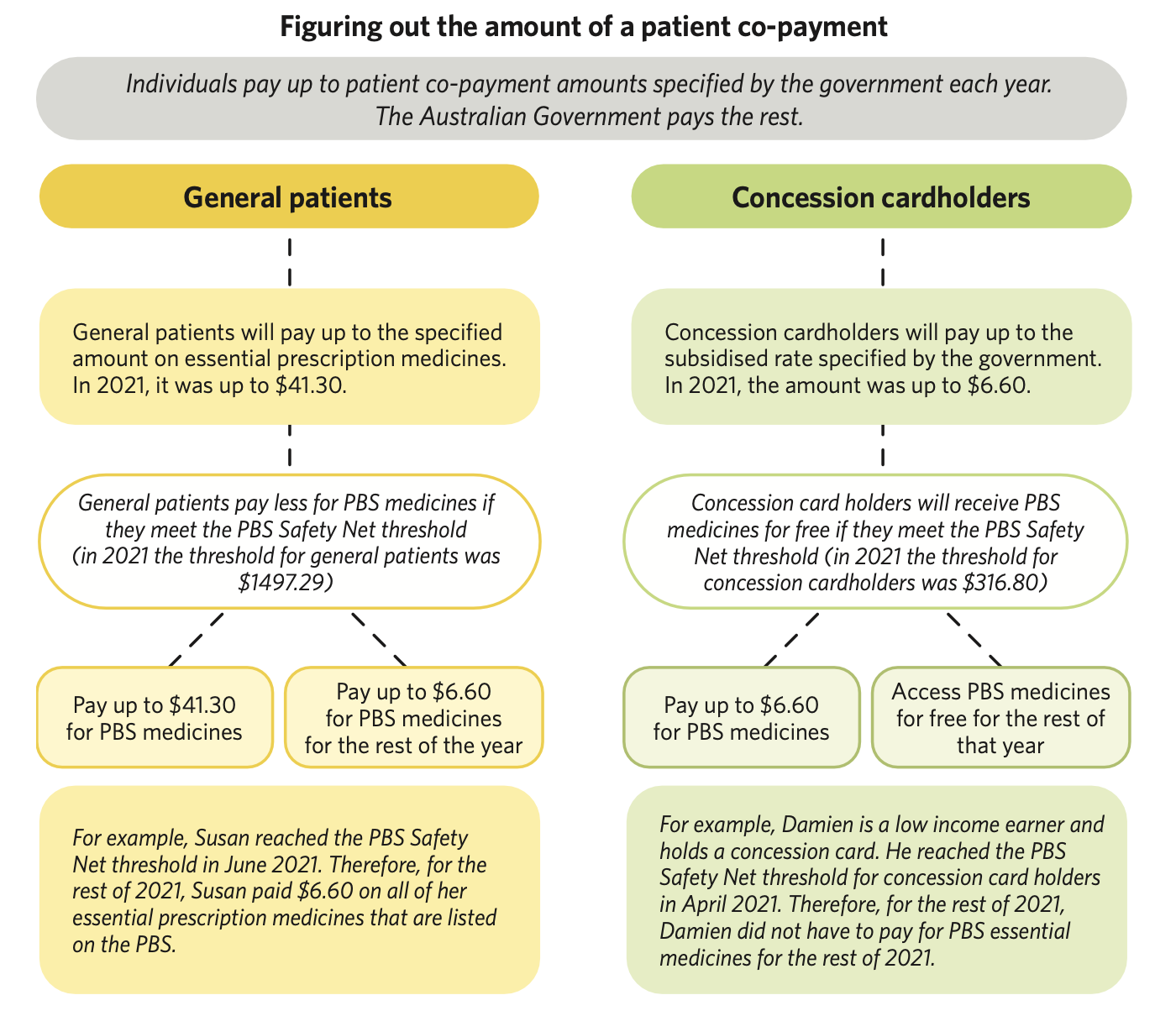
PBS
Provides essential medications at subsidised costs
The federal government funds the PBS and decides which medications will be included under the scheme.
There are a number of drugs not on the PBS- patient then needs to pay full amount.
NDIS
national disability insurance scheme
national insurance scheme that provides services and support for people with permanent, significant disabilities, and their families and carers.
ELIGABILITY
Age and residency requirements:
be aged under 65 years
Australian citizen/permanent resident or on a protected special category visa
Disability requirements:
you have an impairment or condition that is likely to be permanent
your impairment substantially reduces your ability to participate effectively in activities, or perform tasks or actions unless you have:
assistance from other people or you have assistive technology
equipment (other than common items such as glasses)
you can't participate effectively even with assistance or aides and equipment an
your impairment affects your capacity for social and economic part
you are likely to require support under the NDIS for your lifetime
FOCUS
Develop individualised plans based on goals and aspirations
Identifies the functional support needed for daily living and participation
Support required to pursue goals
Access mainstream services and supports
Access community services and supports
Maintain informal support arrangements
Receive reasonable and necessary funded supports
PRIVATE HEALTH INSURANCE
a type of insurance under which members pay a premium (or fee) in return for payment towards health-related costs not covered by Medicare.
It is additional insurance purchased on top of Medicare.
forms an important part of Australia’s health system.
INCENTIVES
Private health insurance rebate
based on income
some people with private health insurance are eligible for a rebate (or refund) from the federal government ranging from 9 to 27 per cent
Lifetime Health Cover
those who take out insurance after the age of 31 pay an extra 2 per cent on their premium for every year they are over the age of 30
The Medicare levy surcharge
high income earners who do not have private health insurance pay a higher premium.
This is income tested so those with higher incomes pay a higher surcharge (the surcharge can be 1, 1.25 or 1.5 per cent)
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES
Advantages Disadvantages | |
|
|
SAFE
SUSTAINABILITY
Relates to:
its capacity to provide a workforce and infrastructure such as facilities and equipment
to be innovative and responsive to emerging needs through interventions such as research and monitoring
ACCESS
Providing all people with timely access to quality health services based on their
needs, not ability to pay, regardless of where they live in the country.
FUNDING
relates to the financial resources that are provided to keep the health system adequately staffed and resourced so a high level of care is available for those who need it.
Through the Medicare levy
General taxation
Individual payments
Medicare payments
PBS payments (government and patient)
Private health insurance (premiums and payments)
Insurance (TAC and business insurance)
Government grants
EQUITY
All Australians should be able to access healthcare when required.
Equal access, however, does not necessarily mean the system is equitable.
As Australians have different healthcare needs, the health system must take these
differences into account if it is to be equitable and fair for all people.
Medicare safety net
PBS safety net
Public dental health service
NDIS