Unit 11.6 Pseudocode - Files
Aims
Know why files are used in programming code and the different modes that are used to interact with text files.
Be able to write pseudocode that writes data to a text file and reads data from a text file.
Files
Whilst program is running, data is held inside variable/constant/array etc. all held data is lost when the program ends.
To permanently keep data it needs to be held in an external file. e.g. text file
Text files need to specify mode:
READ - data to be read from the file.
WRITE - data to be written to the file, new file is created & any new existing data in the file is lost.
APPEND - data to be added to file after any existing data currently in file.
Writing To A Text File
Syntax

E.g. allow user to input their name & then add this to a text file called names.txt
DECLARE name : STRING
INPUT name
OPENFILE “names.txt” FOR APPEND
WRITEFILE “names.txt” , name
CLOSEFILE “names.txt”
Reading To A Text File
Syntax:
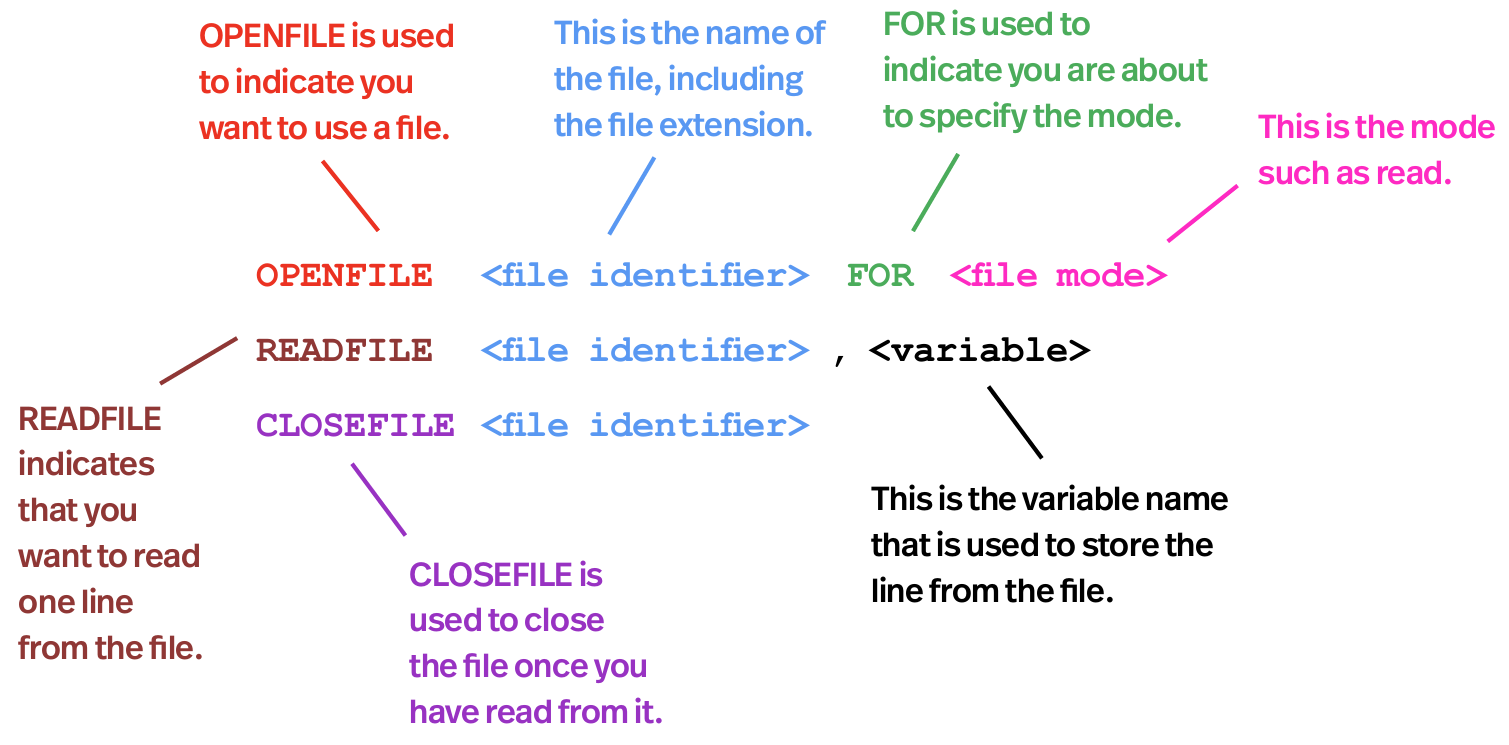
Variable should be STRING, when READFILE command is executed, next line of text in file is read and assigned to the variable.
E.g. Read first line from text file called test.txt
DECLARE lineOfText : STRING
OPENFILE “test.txt” FOR READ
READFILE “test.txt”, lineOfText
CLOSEFILE “test.txt”
Function EOF can be used to test whether there are any more lines to be read from a given file. Function returns true if there are no more lines to read/empty file & false otherwise
E.g. DECLARE lineOfText : STRING
OPENFILE “test.txt” FOR READ
WHILE NOT EOF (“test.txt”)
// READFILE “test.txt”, lineOfText
// OUTPUT lineOfText
CLOSEFILE “test.txt”
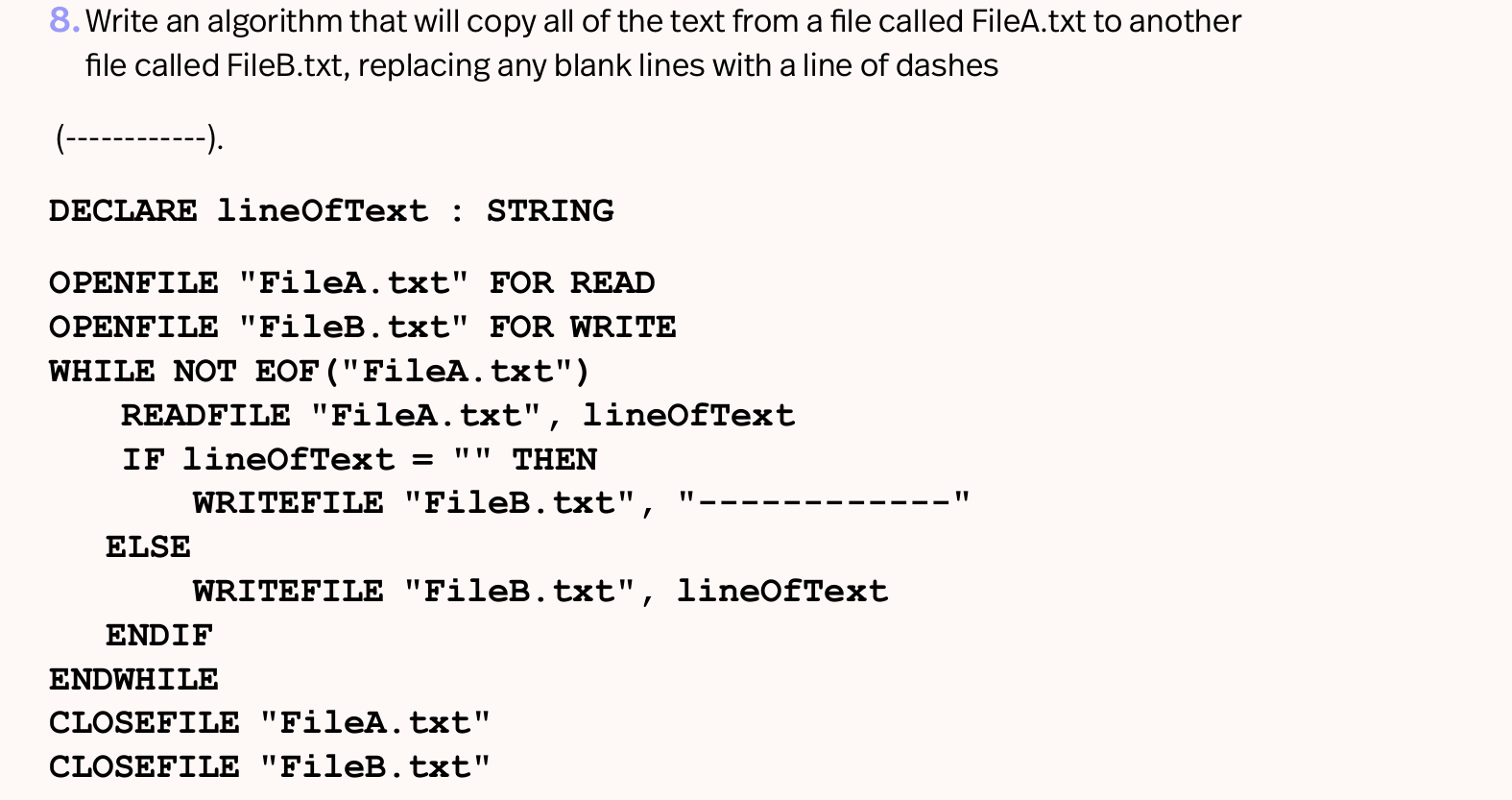
Example of A Level question - how to copy from one file to another