1.1.1 The Market
Mass Marketing
Mass Marketing is the attempt to create products or services that have universal appeal
a mass market product is sold to all consumers in the same way
aimed at the whole market
eg Coke - one advert for everyone - appeals to all ages
Ultimate prize of mass marketing is the creation of generic brands, when customers use the brand name as a product category such as Ketchup, Fitbit, iPad
Pros:
large scale of productions means lower average unit costs.
Easy as everyone is equally targeted so you can reach a lot of people with one ad.
Large volume of sales means high revenue.
Cons:
Lots of competition
Homogenous products (simple and not standing out) need to be differentiated through marketing which can be exspensive
High volume production is not flexible to demand changes.
Niche Market
A niche market is a subset of the main market and cater to a particular segment of consumers within the market with specific wants and needs. eg Rolex
Key characteristics
It is a small segment of a larger market - eg Ferraris of car market
You need to identify the needs of the consumers that make up the niche
Then you need to design a specialised product or service that meets the distinctive needs of these consumers - eg gluten free chocolate
Usually low volume (amount of units) to high price
Niche market operators often distribute their products through specialist retailers, or directly to the consumer via the internet.
The niche must be large enough to support a profitable business…
But it also needs to be small enough not to attract the attention of the big players in the larger market so that they do not steal your idea.
Pros:
Niche market can be profitable markets to be in as they are often premium and prices can be high as consumers in that niche are willing to pay for the right product, also they may not have other options.
It is easier to target customers directly and accurately. - eg High end magazines for very rich.
Small Scale production can be flexible and follow trends.
There is usually less competition than in the mass markets.
Cons:
Can be risky as demand may not be constant.
The market for some items may be very limited so usually sell low volumes
You tend to have higher unit costs as there are no economies of scale. This could mean that not enough products are sold for the business to be profitable!
Good profits can often bring more competitors to enter the market
Businesses in niche markets often have a small range of products which makes them more risky.
For the exam:
Edexcel says… The difference between mass and niche markets should be considered and students should be able to give examples. Also, be able to explain what being in a different type of market could mean in terms of market size and market share.
Market Size
Market share can be measured by:
Volume of sales
Value of sales - the amount spent by customers
Market Share
Market share is the percentage of a market that is taken by a business, product or brand.
Calculated with this formula:
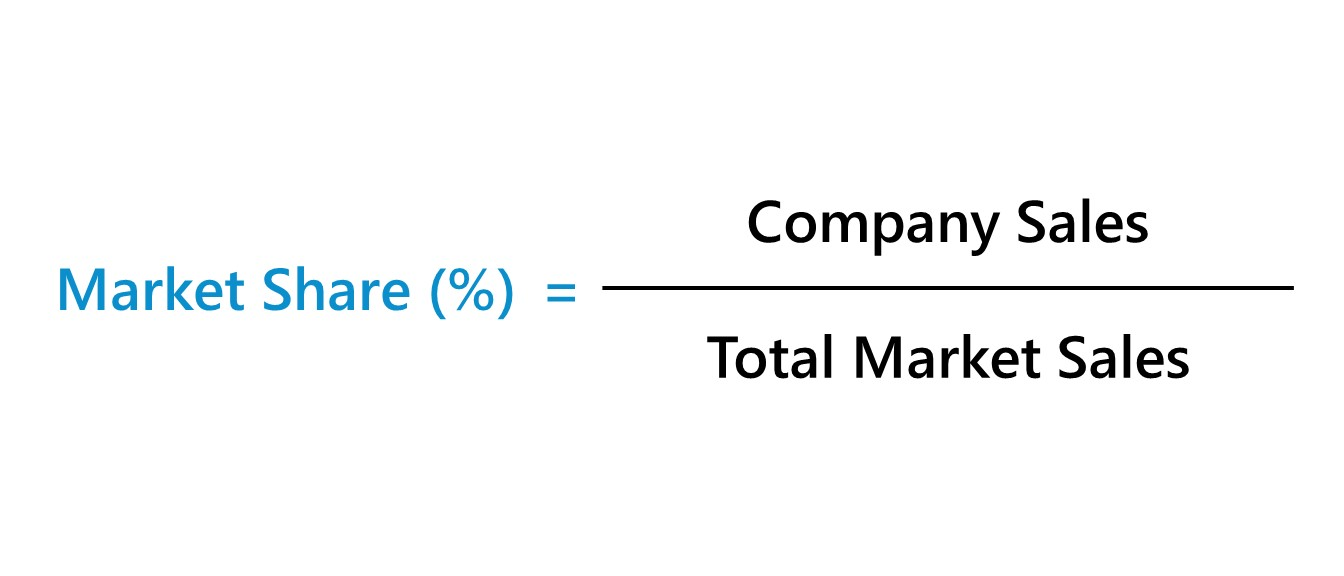
Market share is very important to marketing departments as they can see how popular their products is compared to others.
TO boost market share they will try using the 4P’s:
Product
Price
Place
Promotion
Dynamic Market
A market that is subject to rapid or continuous changes - eg shoes
Online Retailing
Dynamic market because it is constantly changing, devoping and expanding - offering customers new ways to shop.
Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
Shop is always open | 71% of customers still prefer to browse online then purchase in a shop |
Orders can be taken automatically without the need for staff | Issues with returning items can put customers off (especially with clothes) |
Low overheads, no need for a physical shop | Older customers may not understand |
Stock can be easily updated to keep up with dynamic market changes such as tastes | Very competitive and hard to drive people to your site |
Flexible | Problems with fraud |
Opportunities for fast growth | Competitors can be aware of your business model and pricing |
Easy to set up |
Innovation And Market Growth
Markets are constantly innovating. This changes customers expectations and gets them to try new things.
It can increase the market share for the person who introduces the innovation. It can also attract new customers to the market place making the entire market grow.
This also means that customers are constantly changing tastes and preferences.
Adapting to change
as tastes in fashion change so rapidly products are made to satisfy these new needs.
Businesses need to be one step ahead of the competition.
From Edexcel…
The advantages and disadvantages of online retailing to both consumers and businesses should be explored. Markets that are subject to change - because of changes in consumer tastes should be compared to to static product markets.
Students should explore how companies have responded to the growth and significance of online retailers such as Amazon and ASOS.
Risks vs Uncertainty
Risk is something that can be planned for. Probabilities of outcomes are known or understood.
Uncertainty is caused by unexpected often external factors outside of a businesses control.
When evaluating:
when discussing whether or not a company is niche or mass market look at who their competitors are
Do they have a clear USP?
Have they spotted a market that no one else has yet
Have their consumers got clear wants or needs that are different from mainstream consumers
Can they chare premium prices to cover higher overhead costs?
Look for evidence in the case study that talks about what the consumers value most about the product.
Key Definitions
Mass Market
Market for product or services that are sold or advertised to everyone at the same time in the same way.
Niche Market
Subset of main market that caters to specify consumer wants and needs
Dynamic Market
A market that is constantly changing to suit customers wants and needs
Direct Competition
When businesses produce similar goods or services to the same group of consumers.
Indirect Competition
When businesses make and sell products that are not the same but compete for the same consumers. - eg Netflix vs Cinema
Market Size
measured by volume of sales or value of sales
Market Share
Percentage of sales in a market by a business or product
Economies of Scale
when price per unit decreases and level of production increases