Biology- oxygen transport
Haemoglobins are a group of chemically similar molecules
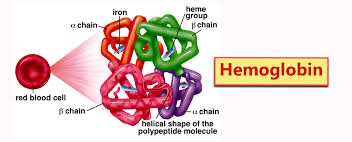
They are made from 4 polypeptide chains, so have a quaternary structure
Found in red blood cells
Structure of haemoglobin:
Oxygen loads to haemoglobin to form oxyhemoglobin
Co-operative nature of oxygen binding
First the oxygen molecule binds
This causes a change in shape of the haemoglobin
Which makes it easier for other oxygen molecules to bind
Affinity of oxygen
How readily haemoglobin loads with oxygen is called its affinity for oxygen.its affinity for oxygen changes as oxygen concentration varies through the body.
At the gas exchange surface:
Partial pressure of oxygen is high
Oxygen diffuses down concentration gradient from alveoli into red blood cells
Hb has a high affinity for oxygen(due to high partial pressure)
So loads with oxygen readily
Co-operative nature occurs ( first oxygen molecule binds to haemoglobin and changes its shape so rest of oxygen binds easier.
Red blood cells travel in blood to tissues
At the tissues:
Partial pressure is lower
Oxygen has a lower affinity
So oxygen unloads
Oxygen diffuses down concentration gradient from RBC to the tissues
Region of body= lungs → oxygen partial pressure high → high affinity for oxygen → oxygen loads to hb
Region of body= respiring issues → oxygen partial pressure high → affinity for oxygen is low → oxygen unloads to hb