Gauss Law
Notes
8.6 Daily Video 1

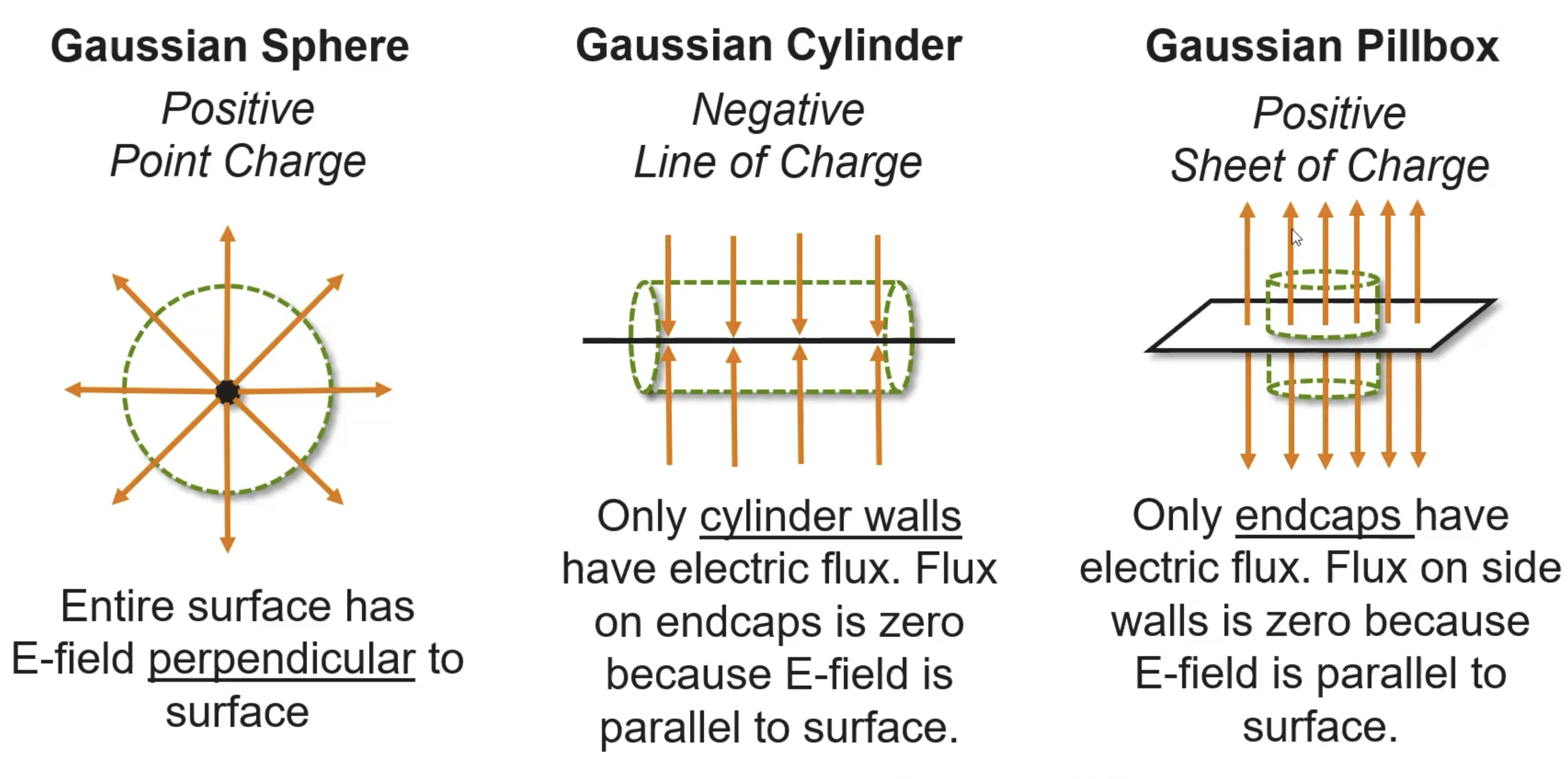
Gaussian Surface
three-dimensional, closed surface
denoted by the circle on the integral symbol
Common symmetries (for charge distribution)
spheres and point charges
cylinders + lines of charge
uniform shapes + flat planes
Gaussian surfaces are typically constructed such that the electric field generated by the enclosed surface is either perpendicular or parallel to different regions of the Gaussian surface → simplified surface integral
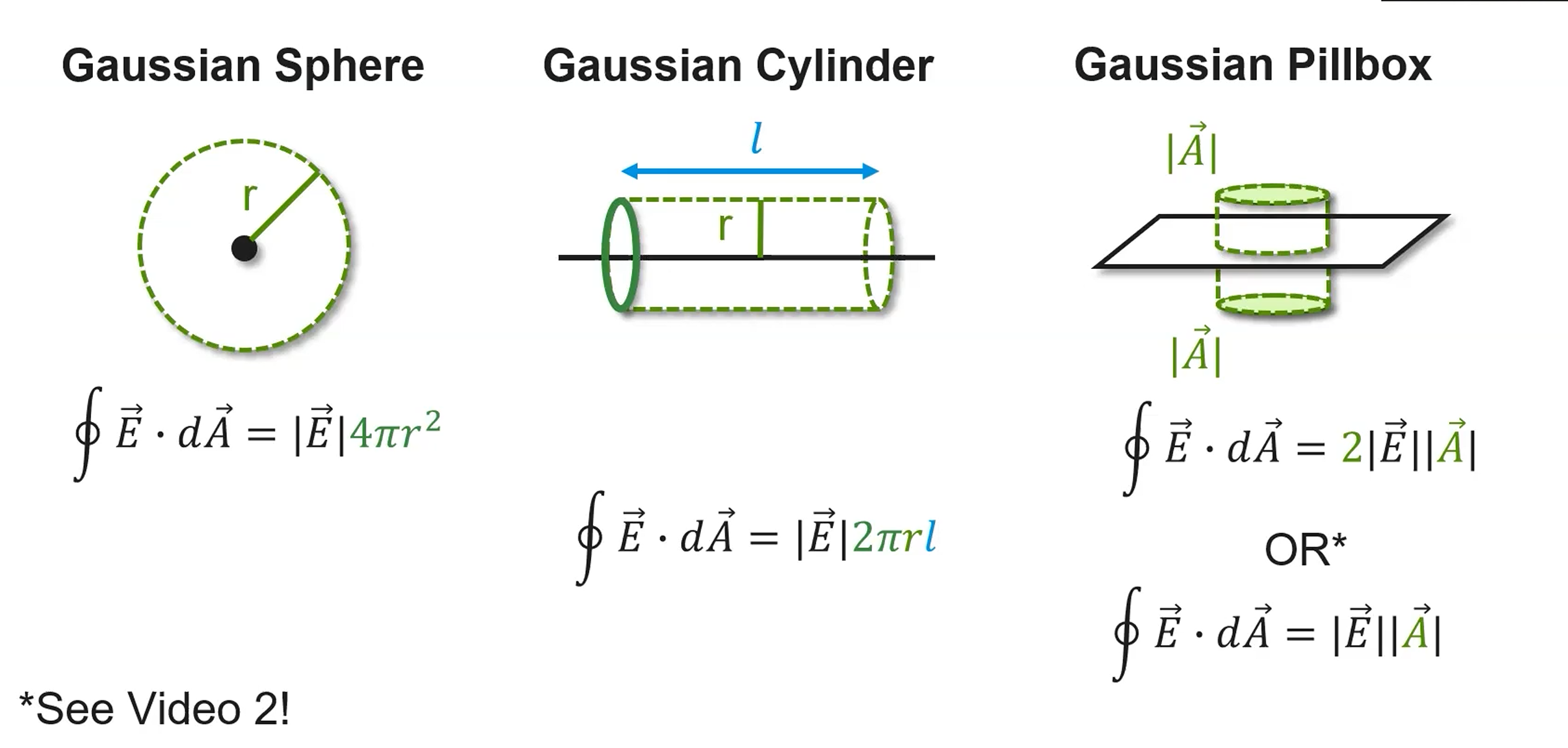
Remember surface area of a sphere
8.6 Daily Video 2 (Planar Symmetric example)
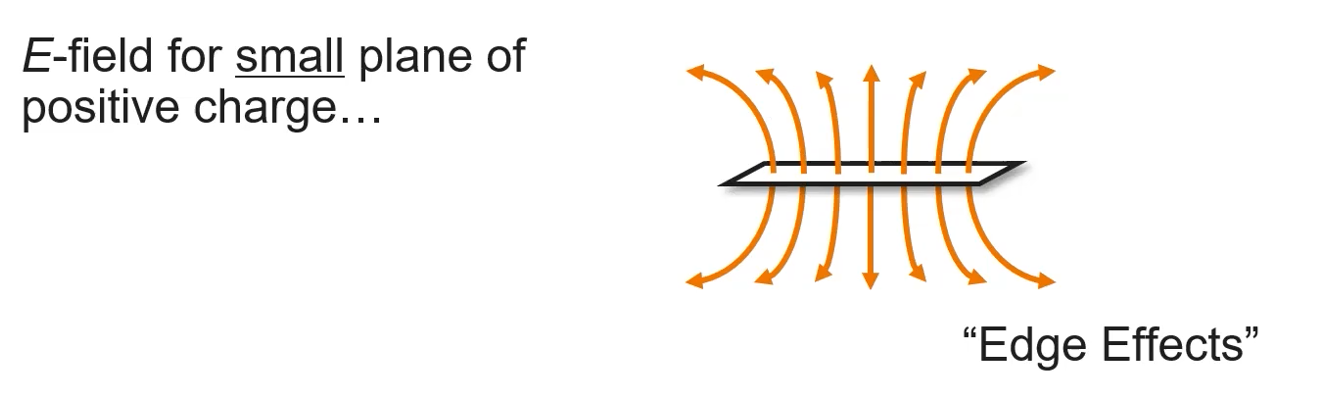
Edge effects → think of people raising their arms up in a room
Edge effects will NOT appear on AP test (zooming into a small portion or assuming the plane is infinite)
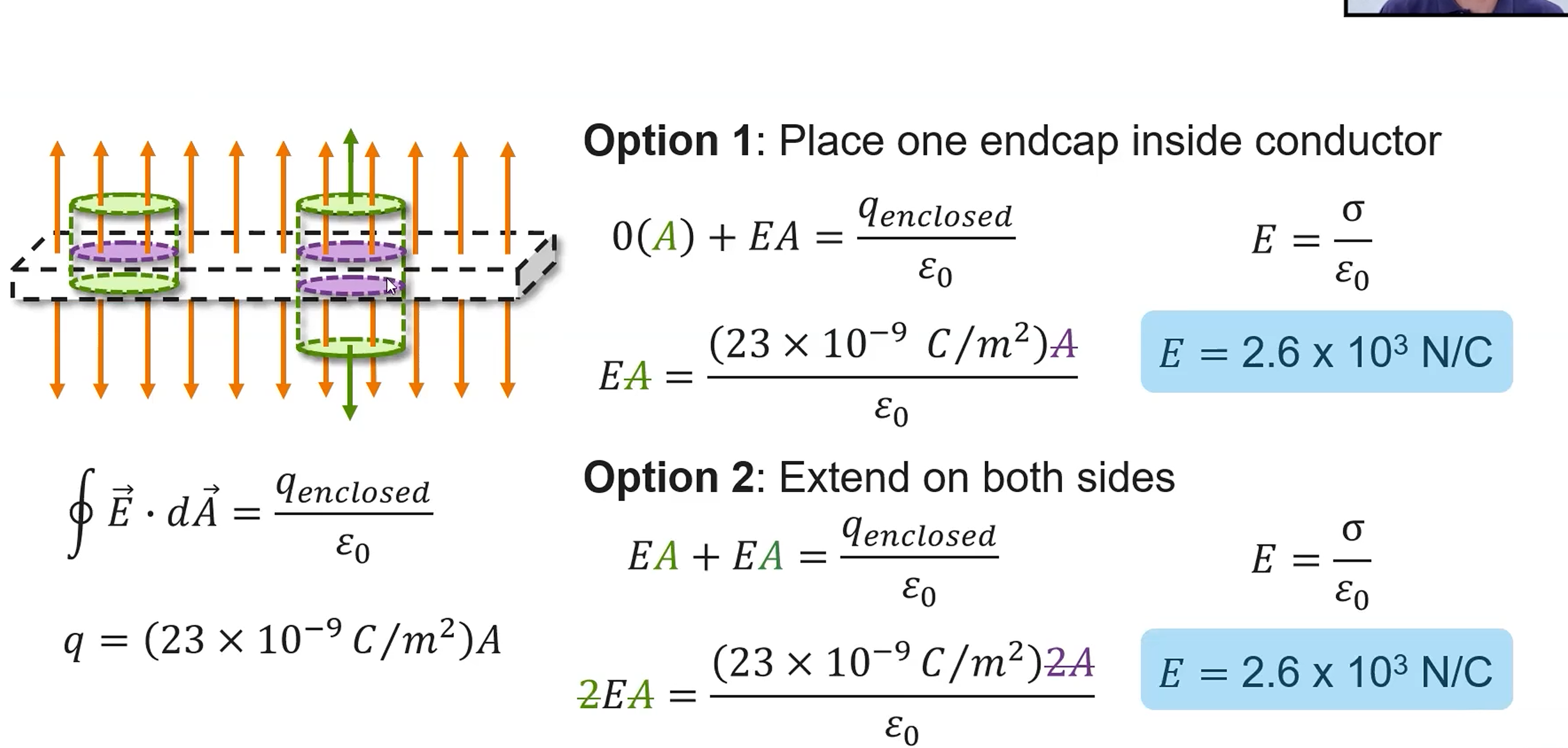
Problems to know how to do
infinite line of charge
infinite surface