Friction 🔥
Friction & Its causes
Friction: The force which opposes relative motion b/w 2 surfaces in contact
Applied force = P
Frictional force = f
Relative motion : motion of an object with respect to the other object, aka both objects r moving
Causes :
Interlocking between irregularities: irregular parts of a surface get interlocked
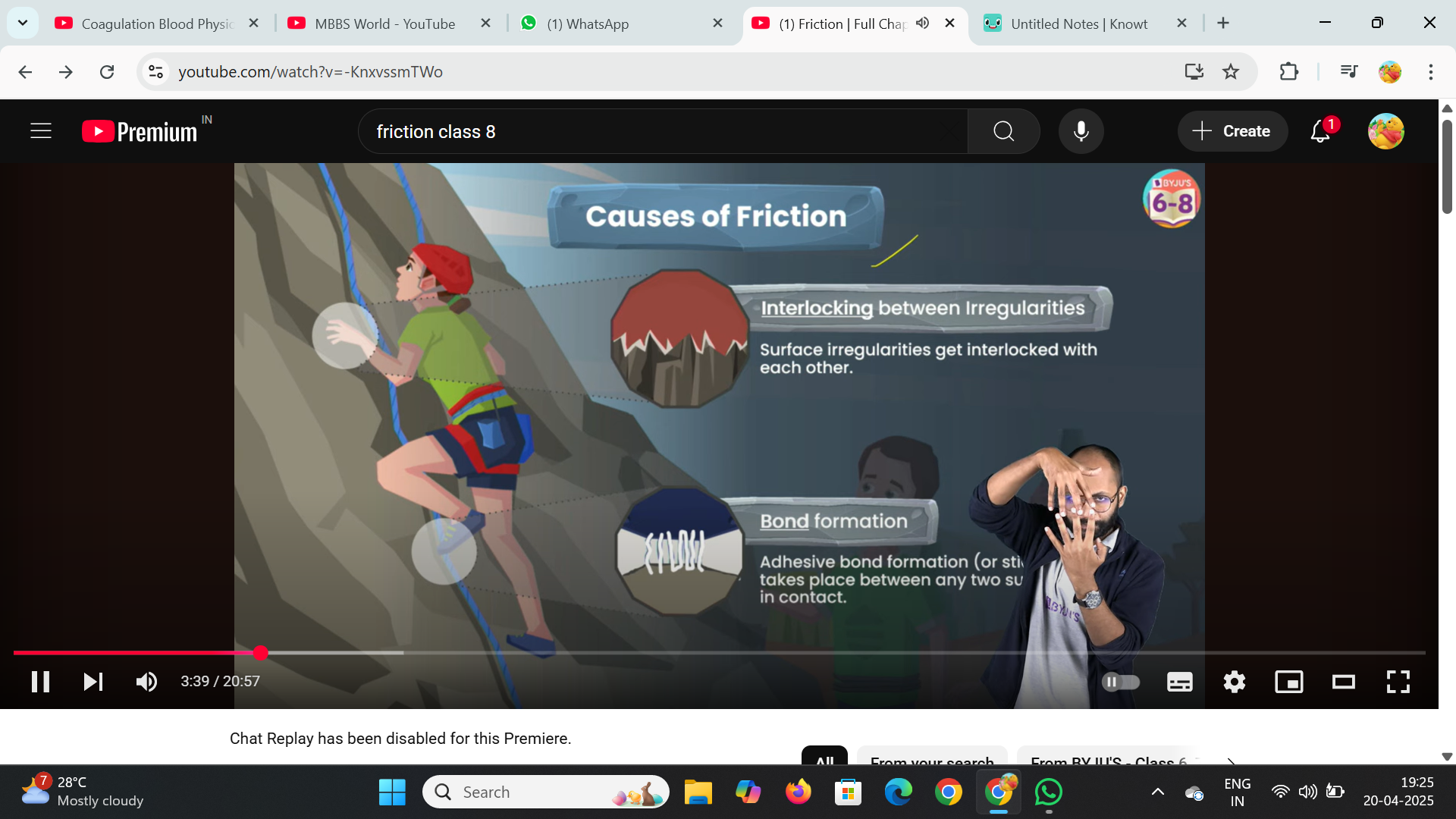
Bond Formation : When 2 surfaces r close to each other, the attractive forces between the molecules of the surfaces cause a bond to form, which increases the resistance to motion.
lekin, these bonds r temporary
Factors affecting Friction
Nature of surface - rough surface = more friction , smooth surface = less friction
Normal Force/ Pressing force - matlab, with how much pressure each surface is pressing the other
If the weight of one thing is more, pressing force will be more
more pressing force = more friction
Less pressing force = less friction
Types of Friction ⚡
Static Friction - When u apply force on a body, but it still doesn’t move, friction is stopping it from moving
Until the body is in rest, static friction is acting upon it
So, the force u apply on the body is being cancelled by the frictional force
Max amount of friction
The force friction is applying is variable, it can change from 0 to max value (limiting friction)
Limiting friction - the maximum value of static friction just befor the object begins to move
The moment body starts to move, friction ka value will decrease
Sliding Friction - Whenever a body is sliding on another surface
When a body is moving in relation to another surface
Value of sliding friction is the same, can’t differ
Also called Kinetic friction & Dynamic friction
Rolling Friction - When an object rolls over a surface
Least amount of friction
Why sliding friction is less than static friction?
Static friction is the maximum frictional force acting on an object and it decreases in sliding friction, so once static friction is overcomed, lesser force is require to move to object
When a body is at rest, it gets good time for bond formation, but when a body is sliding it doesn’t get time to form bonds and stronger bonds = greater friction
Importance of Friction
Being able to walk
Writing
Holding things
Breaks in a car
Lighting match sticks
Increasing ⇡ and Decreasing ⇣ Friction
To increase - Increase the roughness of the surface (grooves)
To decrease - Making surface smoother (grease)
Making stuff roll, by putting wheels, logs
Ball bearings - sliding friction is converted to rolling friction to help
Friction in machinery parts -
Lubrication, putting oil & grease
Ball bearing converts sliding friction to rolling friction
Fluid Friction 🌊
The friction experienced when moving through a fluid = Fluid friction
The friction applied by liquids and gases
Fluid Friction = Drag force
Factors affecting
Relative speed of the body with respect to the medium ,i.e, how fast a body in the fluid is moving
Nature of the medium - Higher viscosity / density = higher friction , Lesser viscosity / density = less friction
Shape of the object - More surface exposed = more friction , Less surface exposed = less friction
Streamlined shape reduces the friction