Electromagnetism
Electromagnetic waves
We are surrounded by electromagnetic waves.
Electromagnetic wave is produced by the vibration of electric and magnetic fields.
Electromagnetic waves are time varying electric and magnetic fields that are coupled to each other.
Electromagnetic waves are waves that travel through empty space or through insulating materials.
Electromagnetic waves are generated whenever electric charges are accelerated.
The frequency of the waves created equals the frequency of the alternating current.
Electromagnetic waves are emitted by accelerating electric charges.
Electromagnetic waves are traveling as electrical and magnetic transverse waves.
Light Waves
Light is the most evident example of electromagnetic waves.
Light is a form of electromagnetic radiation.
Light waves are produced by the vibration of electric and magnetic fields.
James Clerk Maxwell
1831-1879
Scottish Physicist
Stated that electric current is capable of radiating energy in the form of waves known as electromagnetic waves.
It is due to his interest on the works of Coulomb, Oersted, Ampere and Faraday on the relationship between electricity and magnetism, he was able to make a theory.
He formulated a mathematical theory known as Maxwell’s electromagnetic equations.
Maxwell’s electromagnetic equation states that an oscillating electric current should be capable of radiating energy in the form of waves.
It is known that electromagnetic waves could travel as the speed of light.
Heinrich Hertz
1857-1894
German Physicist
Proved the existence of electromagnetic waves through radio waves.
Heinrich Hertz discovered Hertzian Waves also known as Radio Waves.
Hertz generated electromagnetic waves by using two circuits generated by A and detected by B. Each circuit has shiny metal balls at each end with very small air gap for a spark to occur each time the electromotive force (emf) reached a peak.
It shows that electromagnetic waves from A traveled the space between circuit and the receiving loop.
How Electromagnetic Waves are Created?
Waves are produced by using coil and a capacitor in a parallel circuit.
The light emitted by a light bulb is caused by thermal motion that accelerates the electrons in the hot filament and eventually produce visible light.
Properties of Electromagnetic Waves
Transverse waves are types of waves that do not need a medium to transfer energy.
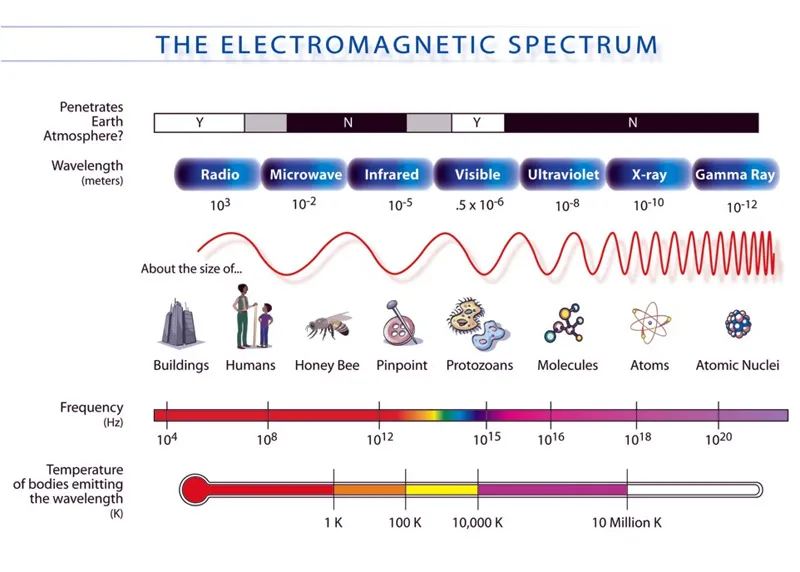
The electromagnetic spectrum which is consists of complete range of electromagnetic waves share common properties, such as:
They exhibit reflection, refraction, diffraction and interference.
They travel at the speed of light. (3.0 × 10^8 m/s)
They obey the wave relation. (v=yf)
Each type of electromagnetic wave occupies a particular range of wavelengths we called as a band.
Each type of EM waves come from different sources and has different uses and effects.
Radio Waves
Radio waves have the longest wavelengths and the lowest frequencies in the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radio waves are produced by making electricity oscillate in an aerial or antenna.
Lightning and stars also give off radio waves.
Uses:
They are used to transmit sound and picture information over long distances.
Radio waves are used in radio devices that we listen to, such as AM and FM stations, which have very long wavelengths.
Due to long wavelengths, it is best suited for long distance broadcasts.
Radio waves extend over a very wide range of wavelengths and the frequencies of the different wave bands are the following:
Very high frequency (VHF) radio waves – this is usually used in communication in civilian aircraft.
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) radio waves – which has greater frequency compared to VHF. These are commonly used in radio communications and TV transmission.
Danger:
Large doses are believed to cause cancers, leukemia, and other diseases.
Microwave
They are described as radio waves of very short wavelength.
Compared to radio waves, microwaves have shorter wavelengths and higher frequencies.
Most of the newest technology relies on the utilization of microwaves.
Due to reflected property of the microwave, they are best used in radar (radio detecting and ranging) .
This involves the transmission of waves at microwave frequencies and then detecting its echo after reflection from a distant objects.
Uses:
They are commonly used in satellite communication, early warning radar, missile guidance systems, weather monitoring, mobile phone networks and even for cooking.
Microwave are used in satellite communication as they can penetrate the ionosphere (a layer in earth’s atmosphere which has a high concentration of charged particles.)
Microwave are used in mobile phone networks. They operates within the lower end of the microwave range.
Microwaves can also be used in cooking. In microwave oven, the magnetron of oven generates microwaves that penetrate food being heated and agitate the water molecules within. The movement of the molecules produces heat, hence cooking the food.
Microwaves are also used by police to track motorists who are driving faster than the speed limit.
Danger:
Prolonged exposure to microwaves is known to cause "cataracts“ in your eyes and recent research indicates that microwaves from mobile phones can affect parts of your brain
Infrared
These are waves that lie in the region beyond the red end of the visible spectrum.
The word “infrared” suggests that this spectrum of wave is “below” to red, which in this case means that the energy and frequency of this wave is lower than red light.
As to describe the wavelength of these infrared, they are too long to be visible to the naked eye.
Infrared radiation is given off by hot or warm objects.
Uses:
Infrared is used to take pictures from satellite with special films to assess the vegetation of the earth’s surface.
They can also be used to take images used by biologists to track wildlife.
Scientists also utilized infrared detectors which help in monitoring volcanoes and hotspots.
They can be used to measure the temperature which give rise to infrared thermometers and scanners which can gets an instant reading of temperature and to show temperature variation of the body for medical diagnosis.
They are utilized in the aspects of electronic communications. For example, in remote controllers that can send instructions and/or communicate with the television through an infrared beam.
They are also used in circuit switching. For example, a faucet that turns water on whenever it detects a person’s hand; when the hand is not there anymore, the circuit will turn the water off.
Visible Light
This is the only part of the electromagnetic spectrum that is visible to human.
Also known as light wave makes up only a small portion of the entire electromagnetic spectrum.
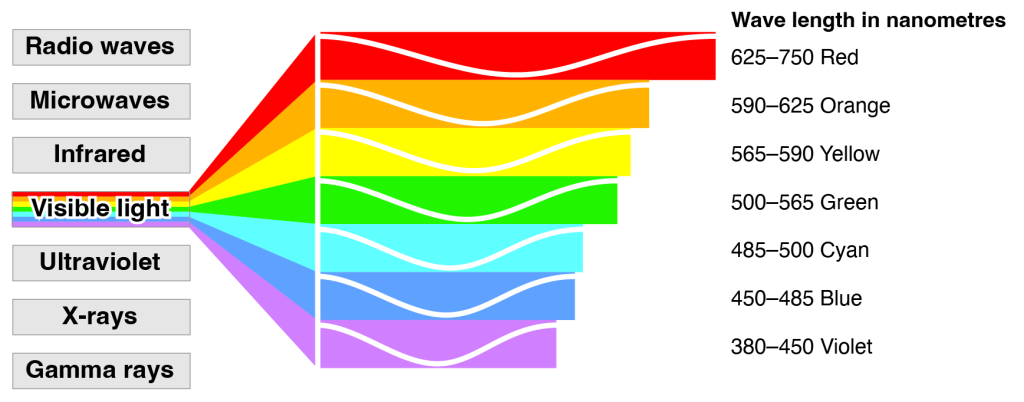
This light wave appears as white light, and when this white light passes through a prism, it is separated into its constituent colors: ROYGBIV.
Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet
700, 600, 580, 550, 475, 450, 400
Violet has the shortest wavelength and Red has the longest wavelength.
Ultraviolet Waves
These waves are invisible radiation that lie beyond the violet end of the visible spectrum.
The name ultraviolet suggests that its frequency and energy is greater compared to violet light.
Ultraviolet radiation is produced by high-temperature surface such as the sun.
They can also be produced by electric arcs and specialized lights, such as mercury-vapor lamps, tanning lamps, and black lights.
Ultraviolet radiation from the sun is classified according to their frequency: UVA, UVB, and UVC.
Uses:
Production of Vitamin D by the inner layers of the skin.
Sterilizing water in drinking fountains.
To prevent counterfeiters. (Through ultraviolet lamps, they can identify fake bank notes and check sensitive documents such as credit cards, passbook, passport, or anything that has UV watermarks.)
For detectives / crime scenes. (Ultraviolet radiation (UVA) makes certain pigments fluorescence or emit light from within. Detectives and forensics use a UV light source called “black light” on crime scene. Through this black light, it helps reveal blood and other biological fluids and footprints.)
For entertainment. (Black lights can also be used in entertainment. Some paints that contain fluorescent chemicals or objects sprayed by fluorescent powder may glow in a dark room illuminated only by black light.)
Danger:
Can damage the retina in your eyes and cause sunburn and even skin cancer.
X-ray
They are described to have short wavelengths and high frequencies and have a very high penetrating power.
X-ray are produced and emitted by fast-moving electrons that strike a heavy atom.
Uses:
Medical Applications. (X-ray with long wavelengths are used extensively in medical applications as these waves can penetrate through the human body. The high energy of X-ray allows them to go through skin and muscle and helps doctors to look inside the body.
Security. (Another application is in the security aspects. With the use of x-ray machine, it helps scan baggage found at airport terminals.)
Industry. (Meanwhile, X-ray with short wavelengths are used in industry. These waves can penetrate through metals and can help inspecting welds and manufactured parts.)
Danger:
Can cause cell damage and cancers
Gamma Waves
Gamma rays are high-energy waves generated by radioactive atoms and in nuclear explosions.
They are more penetrating and have shorter wavelengths compared to X-rays.
Uses:
Sterilizing medical equipment and some applications in astronomy.
Treat Cancers. (Multiple concentrated beams of gamma rays are directed on the growth in order to kill cancer cells.)
Radiotherapy
Danger:
Can cause cancer and mutation