TOPIC 1.2 - SYSTEMS AND MODELS
MODELS
models (def). a simplified version of a real life situation that can be used to understand how something works and predict how it will respond to change
STRENGTHS
allow people to make predictions
can simplify complex/inaccessible situations
inputs and factors can be manipulated
can be shared with others
accessible
WEAKNESSES
approximation and simplification can be overdone - meaning information can be misleading or missing
leave some room for differing interpretations
rely on the knowledge and information of those making them
also often rely on technology - what happens when that technology fails?
TOK : As models are simplified constructions of reality, how do we know which factors of the world to include and which to ignore?
SYSTEMS
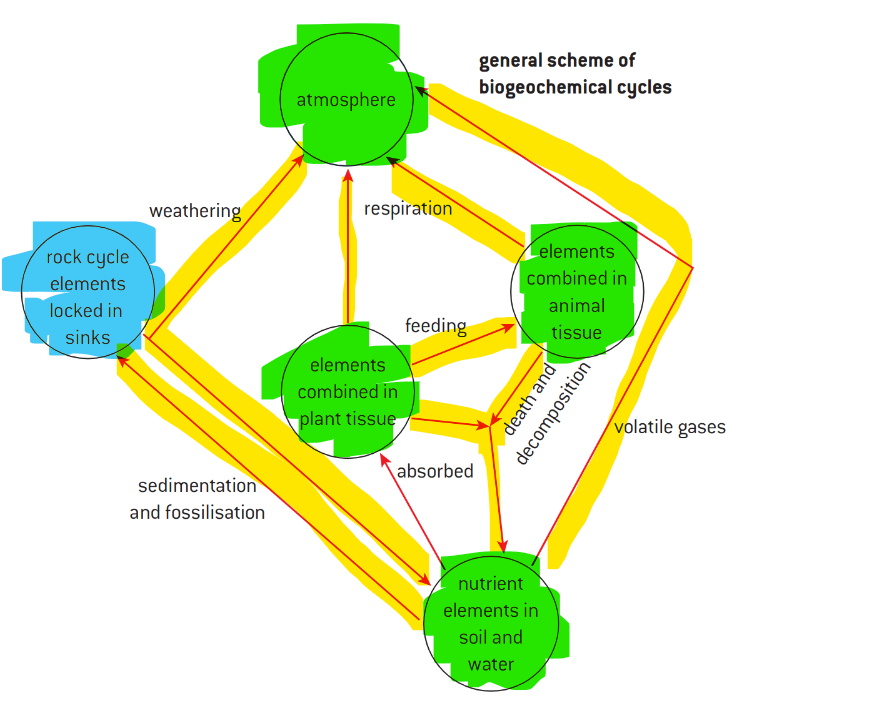
systems (def). a model designed to simplify an intertwined set of interactions or moving parts, comprised of storages, flows, inputs and outputs
open systems (def). an open system is one that transfers both energy and matter over its boundaries and with its surroundings
closed systems (def). a closed system is one that only transfers energy across its boundaries, but not matter - e.g. the nitrogen cycle, hydrological cycle and carbon cycle, but only on a global scale
isolated systems (def). an isolated system is hypothetical concept of a system that does not transfer either matter or energy with its surroundings
you can only really think of the entire universe as an isolated system - but even that is hard to prove
TRANSFERS AND TRANSFORMATIONS
transfers (def). when energy or matter only changes location (storage)
e.g. water moving from river to ocean, movement of heat energy from one organism to another, sugar moving from one organism to another when its eaten
transformations (def). when energy or matter changes location and state or chemical nature
matter to matter - e.g. glucose to starch, water to ice
energy to energy - e.g. light energy to heat energy
matter to energy - e.g. combustion of fuels
energy to matter - e.g. photosynthesis
FLOWS AND STORAGES
flows (def). how matter and energy travels between different stores or in and out of the system
e.g. photosynthesis, respiration, absorption and combustion
represented through arrows within system diagrams
storages (def). places within systems that matter or energy is stored
e.g. the atmosphere, water, within plants or animals and within soil
can be short term or long term - e.g. stored within a plant vs. stored within fossil fuels
represented by boxes within system diagrams
 short term storages long term storages flows
short term storages long term storages flows