Correlational Studies
Correlation means association; it measures the extent to which two variables are related. One of the variables can be regarded as the predictor variable with the other one as the outcome variable
Correlational studies typically involve obtaining two different measures from a group of participants and then assessing the degree of association between the measures
In some sense, the predictor variable can occur before the outcome variable. It is called the predictor variable because it forms the basis for predicting the value of the outcome variable
Relationships between variables can be displayed on a graph or as a numerical score called a correlation coefficient
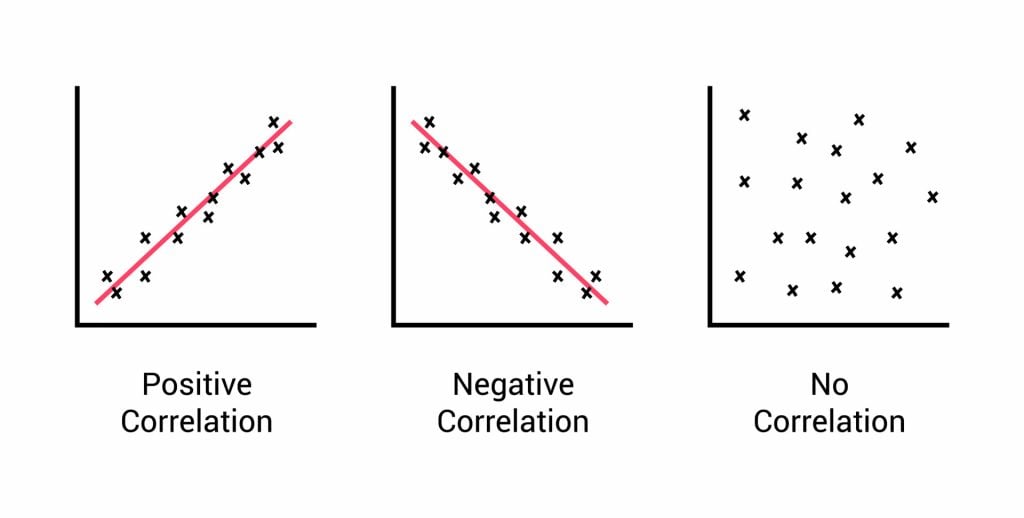
If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with an increase in the other, then this is known as a positive correlation
If an increase in one variable tends to be associated with a decrease in the other, then this is known as a negative correlation
A zero correlation occurs when there is no relationship between variables
After looking at the scattergraph, if we want to be sure that a significant relationship does exist between the two variables, a statistical test of correlation can be conducted, such as Spearman’s rho
The test will give us a score, called a correlation coefficient. This is a value between 0 and 1, and the closer to 1 the score is, the stronger the relationship between the variables. This value can be both positive e.g. 0.63, or negative -0.63
A correlation between variables, however, does not automatically mean that the change in one variable is the cause of the change in the values of the other variable. A correlation only shows if there is a relationship between variables
Correlation does not always prove causation, as a third variable may be involved