FW 404: Managing Reptile and Amphibian Habitat, 10/30
Managing Reptile and Amphibian Habitat
What are Herpetopauna?
Amphibians = frog, toad, salamander
permeable, moist skin
susceptible to contaminants
2 phase life cycle (larvae and adults)
one or both is linked to aquatic systems
Reptiles = lizard, snake, turtle
dry, scaly skin
warm temperatures for egg incubation
both groups are exothermic, relying on environment to regulate body temperature
Southeast is Hotspot for Herps
½ of North American herp species
20% are endemic
45% of southeastern vertebrates
Mountains and salamander speciation
Coastal Plain vs. Mountains
Disturbance more frequent in coastal plain
fire, wind, etc
Water table higher in coastal plain
Coastal plain herps evolved with frequent disturbance
Threats
Habitat loss/fragmentation (urbanization)
Roads
Air and water pollution
Disease (e.g. chytrid fungus, ranavirus)
Pet trade
Land management
NOT CLEARCUTTING according to Moorman
Effects of Timber Harvest
decrease canopy, increase light, increase soil temp, increase evaporation
increase and decrese CWM, decrease leaf litter, increase or decrease understory
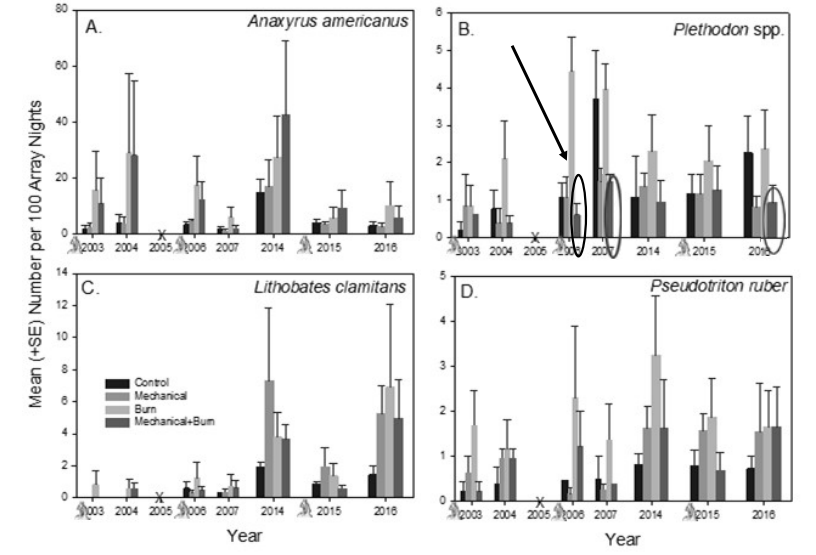
Plethodontids
Stream salamanders
aquatic and semi aquatic
respire through skin (lungless)
sensitive to terrestrial and aquatic change
dominate clearcutting effects research vs reptiles like snakes and lizards
2 lined salamander, 3 lined salamander are streamside
red-backed salamander, white-spotted slimy salamander are woodland
Woodland salamanaders
fully terrestrial
respire through skin (lungless)
require most micro-environments
Lungless Salamanders
High richness in Southern Appalachians
decrease after harvest
clearcut, shelterwood, and group selection
recovery time varied from 20-100 years
woodland salmanaders like northern red decline after clearcut
losers not winners
Amphibians in Coastal Plain
Some frogs and toads increase after harvests
heat tolerant and store water in bladder
southern toad and narrowmouth toad
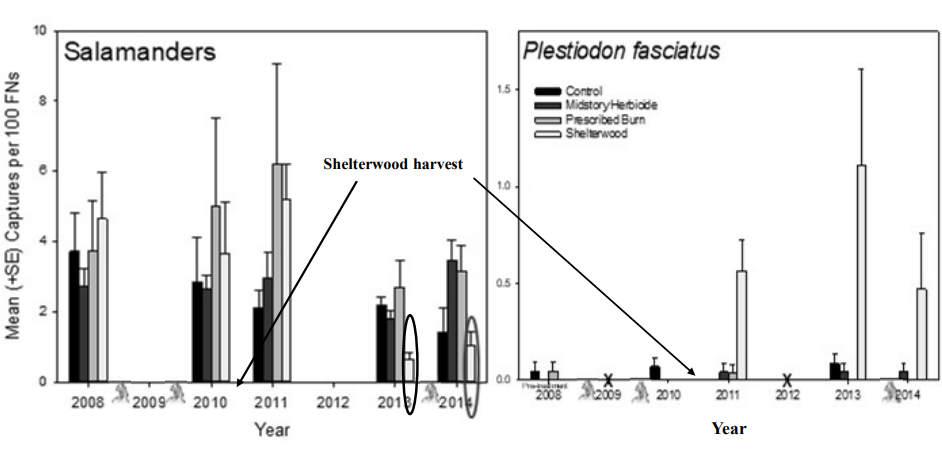
Salamanders decrease after harvest
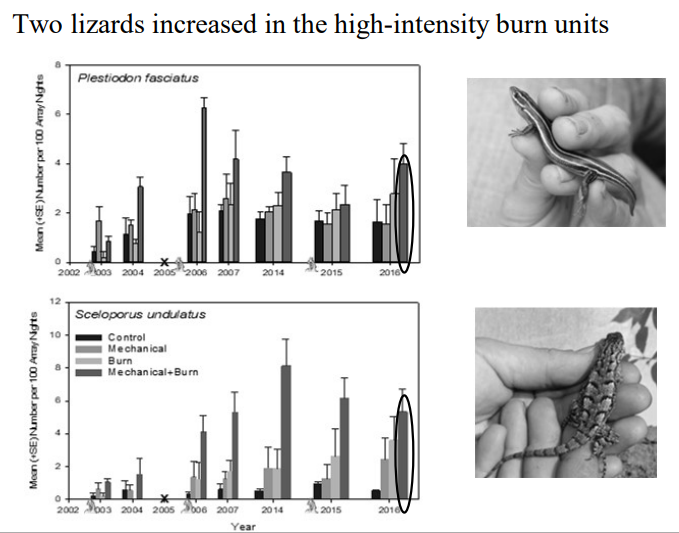
Reptiles and Timber Harvest
Generally increase
mimics severe fires
hotter, drier afterwards
thermo-regulation
Forest species decline
down wood/litter specialists
e.g. ring-necked snake
Site Preparation
Differ whether mechanical or chemical
Mechanical
direct mortality?
decrease in cwm, litter, root channels
fossorial species decline?
Pesticides and Herps
Permeable skin makes some susceptible
Insecticide use = fewer Cali frogs
Roundup and frogs
herbicide and not insecticide
active ingredient or surfactant
with herbicides, follow label, esp in aquatic systems
Riparian buffers
decrease sedimentation for stream salamanders
limit increases in soil and water temps
refuge from adjacent harvests
buffer widths range up to 300 m
Isolated Wetlands
unique sites with high richness
anurans
ambystoma
predator free ephemeral pools
for semi aquatics, buffers up to 300 m
Downed Woody Material
Redistribute harvest debris into piles
Retain large dbh snags
Snags become downed logs
Fire interacts with CWM dynamics
Fire and Herps
Lack of fire causes some herp declines
woody encroachment of wetlands
promotes herbaceous cover
Removes litter, changes thermal condition
depends on historical exposure
fire prevalent on southwest aspects
Depends on Fire Characters
Few effects of fire on population documented
studies short-term
low intensity fire
Longer term
repeated fire
high severity
canopy mortality
need more research in these areas

Petranka et al. (1993)
75-80% salamanders “die” after clearcut
10,000 salamander/ha (4,000 acre)
NC USFWS clearcut 1709 ha/year
eliminated 13.7 million salamanders/year
about 0.34% of salamanders on national forest
Chronic reduction by 267 million
How do you respond to this research?
How would it influence your management?
Cookbook Recommendations
consider historical disturbance
consider management goals and target species
maintain snags and downed wood
use fire when appropriate
consider the scale of effects
Retain canopy during regen. harvests
group selection
two-aged stands
use small clearcuts, depending on objective
leave riparian buffers
protect isolated wetlands
TOPHAT
Which is true about reptile and amphibian response to disturbance?
A
salamanders tend to increase following shelterwood harvest
B
toads tend to decline following shelterwood harvest
C
lizards tend to increase following shelterwood harvest
D
all answers are correct
E
no answers are correct