LABOUR ECONOMICS
Marginal Effective Tax Rate (METR):The METR measures how much additional income is taxed away through higher taxes and reduced benefits. A high METR discourages extra work.
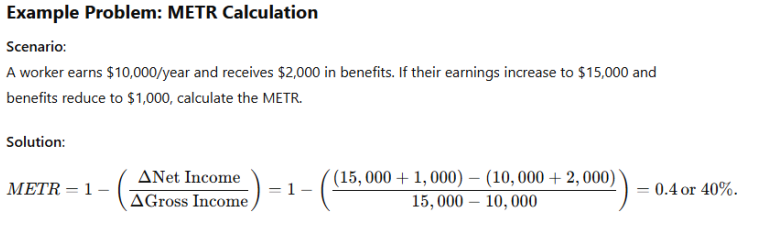


The graph shows how increasing the Marginal Effective Tax Rate (METR) reduces labor participation rates:
Higher METRs discourage workers from increasing their labor supply due to diminished net income gains.
WAGE DETERMINATION
Example Question:
Q2. Suppose the wage equation for a given job is $W = 15 + 0.5E$, where $E$ represents years of education. Calculate the wage for a worker with 10 years of education.
To determine the wage, we simply substitute the value of $E$ into the wage equation:
$W = 15 + 0.5(10) = 15 + 5 = 20$.
Thus, the wage for a worker with 10 years of education is $20.
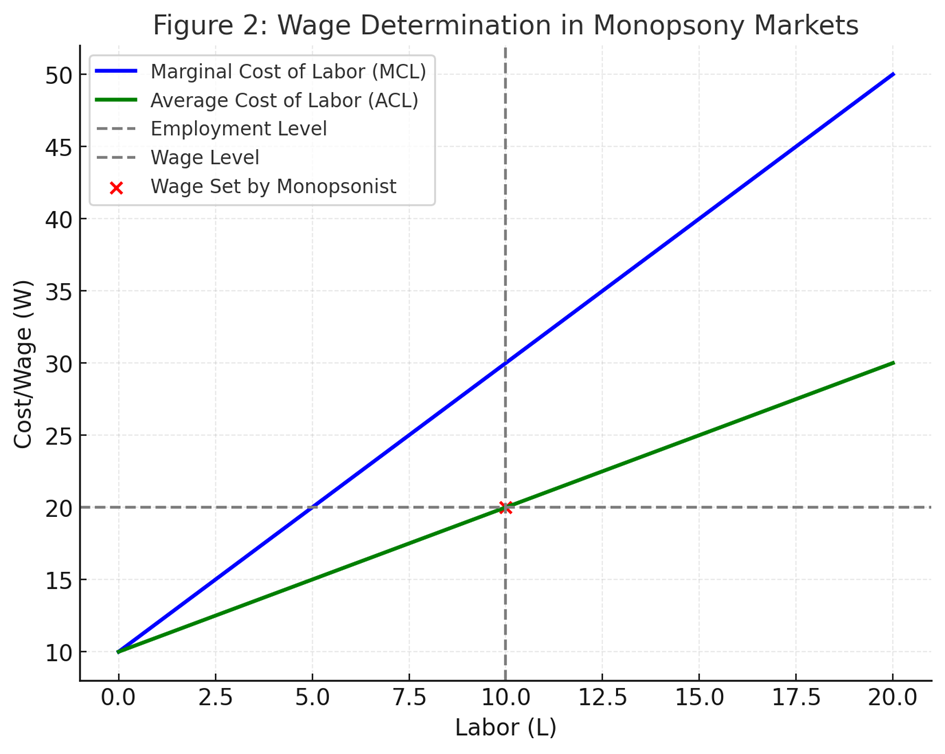
This graph illustrates how a single employer (monopsonist) determines wages in the labor market. The marginal cost of labor (MCL) and average cost of labor (ACL) curves explain how the monopsonist sets wages at levels lower than the market equilibrium.
Labor-Leisure Tradeoff:
Workers allocate their time between labor and leisure, seeking to maximize their utility.
A higher wage increases the opportunity cost of leisure, pushing workers to reconsider their time allocation.
Mathematical Representation: The worker's budget constraint C=w⋅L+V
Where: C: Consumption, w: Wage rate, L: Hours worked, V: Non-wage income.
The utility function: U=f(C,Ls) Where: Ls: Leisure time, C: Consumption.
Substitution and Income Effects:
Substitution Effect: Higher wages make working more attractive than leisure.
IncomeEffect: Higherincomemayleadindividualstoworkless, as theyvalueleisuremore
Calculation of Labor Participation Rates
•Formula:
•Labor Force Participation Rate (%) = (Labor Force / Working Age Population) × 100
•If the labor force is 50 million and the working-age population is 80 million:
•Participation Rate = (50 / 80) × 100 = 62.5%

Structural Unemployment: Impacts and Solutions (çok önemli)
Impacts:Structural unemployment arises due to a mismatch between the skills of the workforce and the requirements of available jobs. Its main impacts include:
Increased Duration of Unemployment: Workers may experience prolonged periods of joblessness as they struggle to find positions that match their skills.
Economic Inequality: Certain groups may become marginalized, leading to steep divisions in income and employment opportunities.
Reduced Productivity: The economy may suffer from lower productivity as businesses cannot find qualified workers to fill essential roles.
Solutions:To mitigate the effects of structural unemployment, several strategies can be applied:
Retraining Programs: Implementing government and private sector initiatives to retrain workers in skills that are in demand can help align the workforce with job market needs.
Career Services: Providing enhanced career counseling and job placement services assists individuals in identifying which areas offer employment opportunities, fostering smoother transitions into new roles.
Mobility Support: Encouraging geographic mobility by offering relocation assistance can help workers move to areas with higher job availability and demand.
Cyclical unemployment happens when the economy goes up and down. During bad times, people buy less, so companies make less and may need to lay off workers. When the economy gets better and people buy more, this type of unemployment tends to go down.