9/15/25 Fon Lecture (fields)
You can characterize an elementary particle
mass, charge, spin, etc.
interactions on different fields
Our universe is based off of two charges (positive and negative)
electrons represent an excitation in the electrical field
e = 1.63 × 10-19 C
1 C = 6.6 × 1018 e-
Coulomb’s law
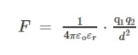
charges should have absolute value around them
ε₀ (epsilon naught) is the permittivity of free space
8.8 × 10-12
measure of how easily an electric field can be established in a vacuum
εr
permittivity of substance
μ0
permeability of free space = 4 pi * 10-7
What is a conductor/insulator
free electron gas is a conductor, free electrons can carry current
when you apply electrical field → free electron tends to move in a direction
insulator
no free electrons, tightly bound to atom
no current
semiconductor
in between conductors and insulators
EACH charged particle creates an electrical field
the source of an electrical field is a charged particle
The source of a magnetic field
is a moving charged particle (no movement, no magnetic field)
How to charge objects
induction
polarization
dipoles are formed (temporary charges)
friction
think rubbing a marker onto your head (electrons jump from head to marker, static)
