WEEK 5
LOOK AT 2ND POWERPOINT
Learning Objectives
Understand equities, main types of shares.
Describe the characteristics of equity-based investments.
Calculate investment ratios measuring performance and appreciate limitations.
Understand employee share schemes and incentives.
Explain AIM shares and unlisted securities characteristics.
Understand the main features of derivatives.
Distinguish between primary and secondary markets.
Equities
Definition of Equities: Represents ownership in a company through shares.
Types of Shares:
Ordinary Shares: Common stock, typically offering voting rights and dividends.
Preference Shares: Fixed dividends but usually no voting rights.
Deferred Ordinary Shares: Dividends paid after other shares.
Partly Paid Shares: Shareholders pay part of the share price upon purchase.
Convertible Preference Shares: Can be converted into ordinary shares under certain conditions.
Listings and Quoted Shares: Shares that are registered and traded on a stock exchange.
Share Dealing & Taxation
Equities include portfolio and pooled investments.
Buying & Selling Shares:
Execution Only: Broker executes trades without providing advice.
Advisory: Broker provides advice and executes trades.
Discretionary Service: Broker makes investment decisions on behalf of the client.
Costs Associated with Investing:
Purchase Cost: Price paid for shares.
Broker’s Commission: Fee for executing trades.
Stamp Duty/SDRT (Stamp Duty Reserve Tax): Tax on share transactions.
PTM Levy: Charged on transactions exceeding £10,000.
Shares & Taxation
Taxation of Dividends: Tax on earnings from shares distributed to shareholders.
Capital Gains Tax (CGT): Tax on profit made from selling shares.
Stamp Duty/SDRT: Additional tax on share transactions.
Tax Wrappers & Incentives:
Equity ISA: Tax-free savings account for equities.
Enterprise Investment Scheme (EIS): Tax relief for investors in small companies.
Employee Share Scheme: Incentives for employees to own company shares.
Share Prices
Factors Affecting Share Prices:
Past Performance: Historical company performance impacts perception.
Value of Share: Current price versus intrinsic value.
Dividends/Re-investment: Dividend announcements influence prices.
Supply & Demand: The balance between buy and sell orders affects price.
Investor Information: News and analysis impact investor decisions.
Company Management: Leadership and their decisions can sway investor confidence.
Interest Rates: Higher rates may lower share prices due to higher borrowing costs.
Investor Sentiment & Market Psychology: Market moods can drive prices up or down.
Share Valuation
Fundamental Analysis: Evaluates a company's financial health through statements and ratios.
Technical Analysis: Studies chart patterns and market trends.
Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH): Suggests that stock prices reflect all available information, making it impossible to consistently outperform the market.
Mergers & Acquisitions (M&A): Transactions that can impact share values and market perceptions.
Measuring Company Performance
Financial Statements Include:
Chairman’s Statement: Insight into company outlook.
Income Statement: Summary of revenues and expenses.
Balance Sheet: Snapshot of assets, liabilities, and equity.
Cash Flow Statement: Reports cash inflows and outflows.
Assess Activities:
Operating Activity: Core business operations.
Investing Activity: Buying/selling of long-term assets.
Financing Activity: Borrowing and equity financing.
Notes to Accounts: Additional details on specific items in financial statements.
Ratios & Analysis
Common Ratios:
Earnings per Share (EPS): Indicator of profitability.
Price/Earnings (P/E): Valuation measure comparing share price to EPS.
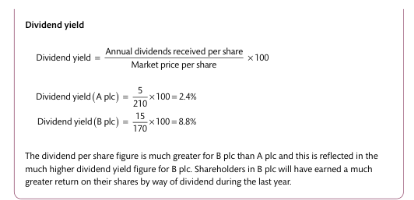
Dividend Yield: Ratio of annual dividends to share price.
Loan Capital Gearing: Measure of financial leverage.
Net Asset Value (NAV): Value per share of an asset-based business.
Stock Market Indices
Importance of Stock Market Indices: Benchmark for market performance.
UK Indices include:
FTSE 100 (Footsie): Top 100 companies in the UK.
FTSE All Share: Represents the entire UK stock market.
FTSE 250: The 250 largest companies after the FTSE 100.
FTSE Small Cap: Companies with smaller market capitalization.
FT Ordinary: Represents ordinary shares in public limited companies.
International Indices
International Indices Include:
DJIA (Dow Jones Industrial Average): Tracks 30 large companies in the US.
S&P (Standard & Poor's): Includes 500 large US companies.
S&P 500: Similar to S&P, focusing on top 500 companies.
Nikkei 225: Leading index in Japan.
FTSE World: Measures global stock performance.
FTSE Eurotop 100: Represents major European companies.
Hang Seng: Index of the Hong Kong stock market.
Derivatives & Warrants
Definition of Derivatives: Financial instruments whose value is derived from an underlying asset.
Types of Derivatives:
Futures: Agreements to buy/sell an asset at a future date.
Options:
Calls: Give the right to buy an asset.
Puts: Give the right to sell an asset.
Warrants: Long-term options issued by a company.
Contracts for Difference (CFD): A trading agreement reflecting price movements.