objective 4
Describe a gene pool and an allele frequency.
Gene pool: Number of each allele of a gene in a population. Displayed as a percentage.
Allele frequency: How often each allele of a gene occurs in a population.
Explain how gene pool allele frequencies can be altered: mutations, different selection pressures, random genetic drift, founder effect and changes in gene flow.
Natural Selection: the process by which a species becomes better adapted to its environment. Individuals with favourable characteristics have a survival advantage so pass these traits onto future generations.
Random Genetic Drift: the occurrence of characteristics in a population as a result of chance rather than natural selection - occurs only in small populations.
Migration: the movement of a species from one area to another, with the intention of permanent settlement.
Barrier to Gene Flow: geographical barriers - mountain range, ocean, deserts; sociocultural barriers - economic/social status, education.
Genetic Diseases: diseases influence gene frequencies as genes can have a positive or negative effect on diseases.
Mutations
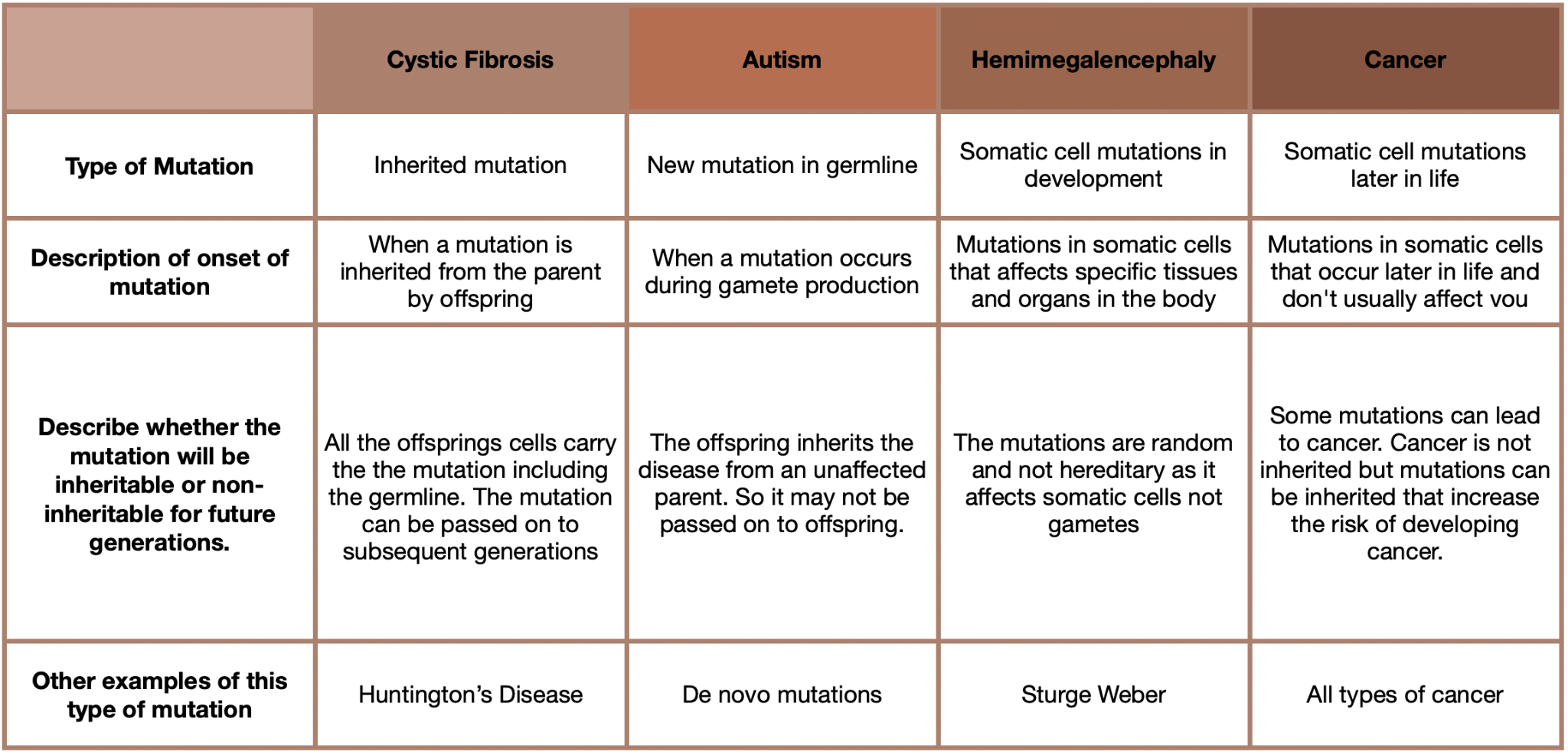
Describe the difference between a gene and chromosomal mutation.
A gene mutation affects only a single gene, while a chromosomal mutation affects a number of genes or the whole chromosome. Chromosomal mutations often cause abnormalities so severe that miscarriage often occurs early in the pregnancy.
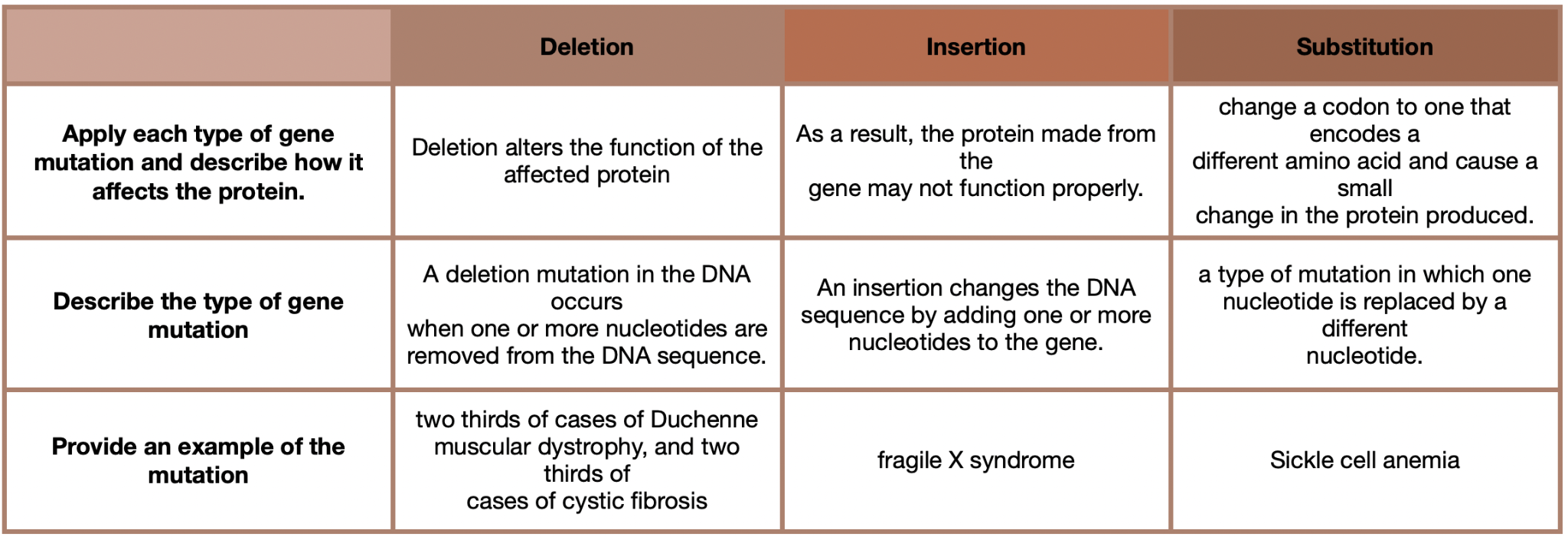
Describe the causes of mutations.
Mutagenic agents (or mutagens): agents known to increase the rate at which mutations occur (also known as induced mutations)
Examples: mustard gas, formaldehyde, sulfur dioxide, some antibiotics, UV light, X-rays, radiation.
Spontaneous mutations: occur due to random error in a biological process (such as mitosis or meiosis)
Heritability of the mutation:
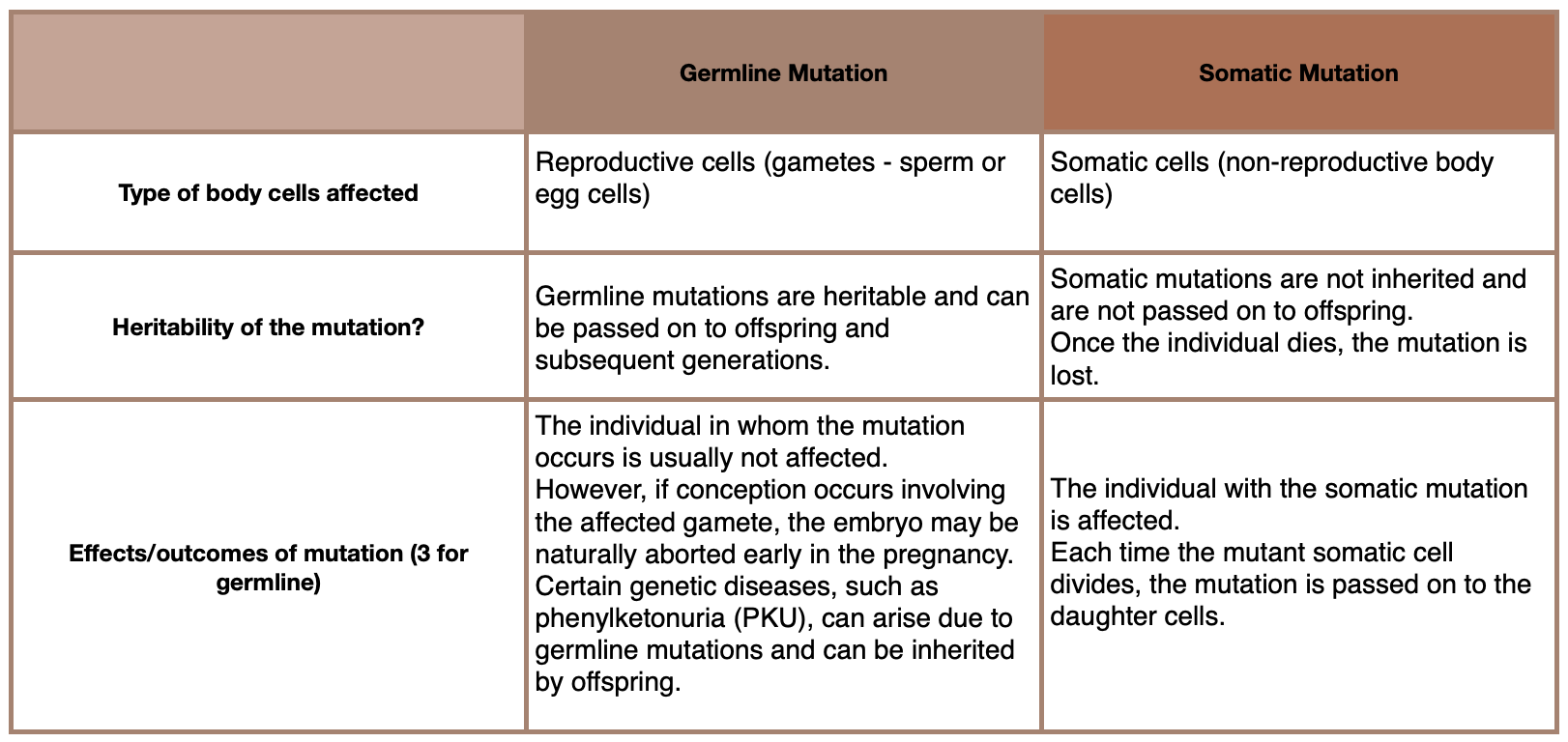
By the type of cells where they occur (body cells or reproductive cells)
Effect of the mutation:
Missense: cause a change in the amino acid & the protein produced.
Nonsense: change based on sequence to STOP code
Neutral: change in amino acid, but same type and doesn’t change the protein structure enough to change its function.
Silent: no change in amino acid so same protein.
Extent of the mutation: The amount of DNA affected (single base to whole chromosome).
Change in the DNA
Point mutations: single nucleotide changed (thus only one base). Insertion, substitution & deletion.
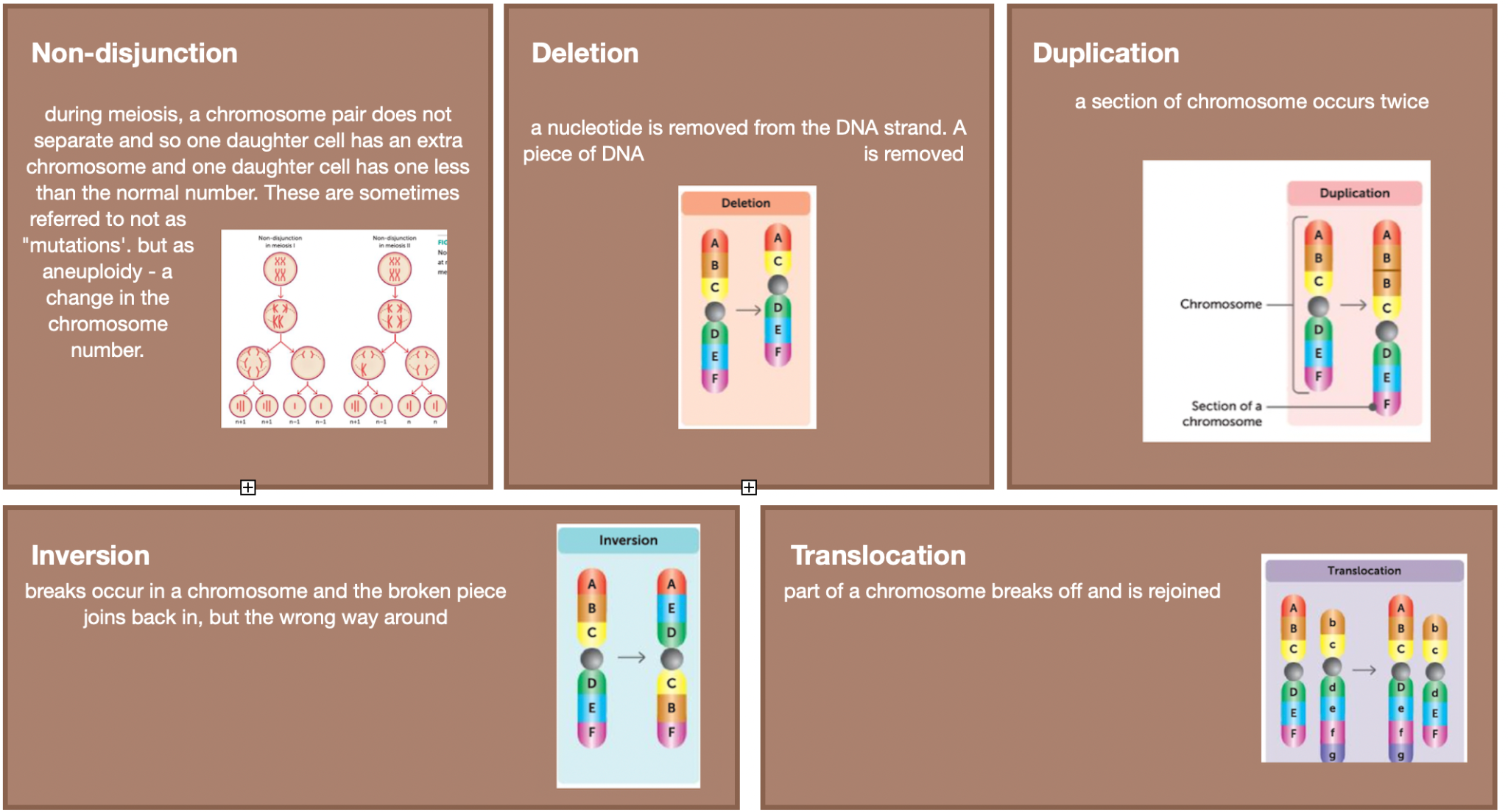
Other mutations affect a larger section of DNA. Duplication, deletion, inversion, translocation, non-disjunction.
Describe the difference between somatic and germline mutations.
Describe the effects of mutations.
Migrations
Describe how migration changes the frequency of alleles in gene pools.
Migration:
Immigration brings new genes to the gene pool.
This may bring alleles that are not already in the population and the frequencies for the alleles of that gene will be altered.
Barriers to gene flow:
Populations are kept apart from breeding (and therefore gene flow does not occur)
Geographical barriers: oceans, mountains, deserts, ice. Each side of these barriers faces different selective pressures so results in different allele frequencies.
Sociocultural: Language, religion, economic status prevents gene flow.
Natural Selection
Understand that humans can show multiple variations and how the changing environment can influence the survival of organism with genetic variation.
Explain how survival can be enhanced if particular phenotypes are selectively advantageous. Give examples of genetic diseases found in specific populations (eg Tay-Sachs)
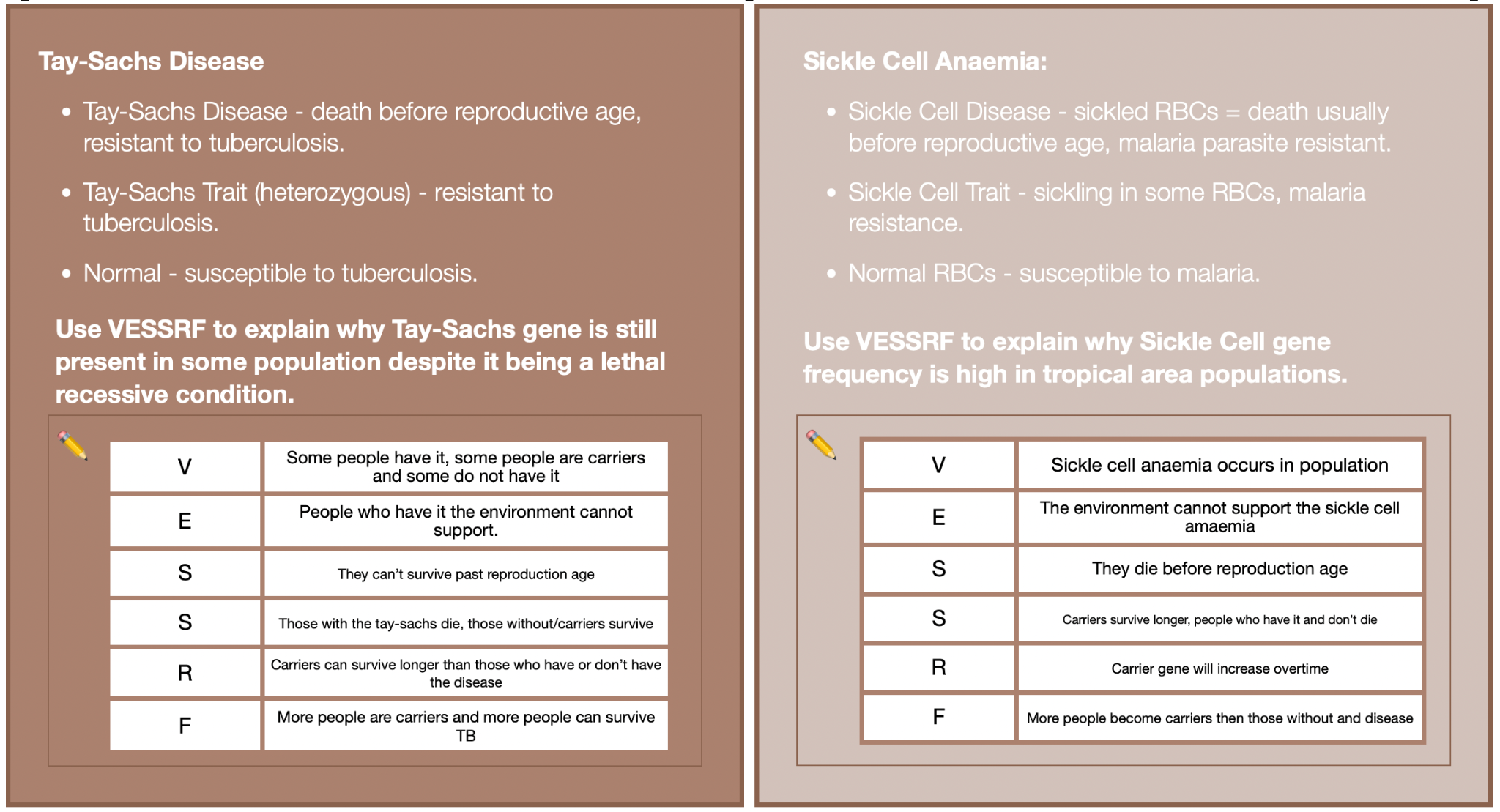
Explain the theory of Evolution using Natural Selection as the key process – Variation, excess population, struggle for existence, selection/survival of the fittest, reproduction, frequency (VESSRF).

Genetic Drift & Founder Effect
Describe genetic drift and the founder effect, and how this changes the allele frequency.
Random Genetic Drift:
When there is small population, there may be statistical anomalies, which can lead to random changes in allele frequencies.
There is no selective pressure that leads to this, it is a purely chance occurrence.
Requires a small population.
Random event - catastrophic
Establishment of a new area (founder effect)
Founder Effect
A type of Random Genetic Drift
Change in allele frequency is due to migration
A small group moves to a new area to establish a community that is isolated from the parent population
Because migrant group is small its allele frequency is not representative of the original population
It can end up with features that are not typical of original population
Explain that genetic drift is a process that occurs due to chance.
It is due to chance
Compare the allele frequencies of the original population and the new founding population.
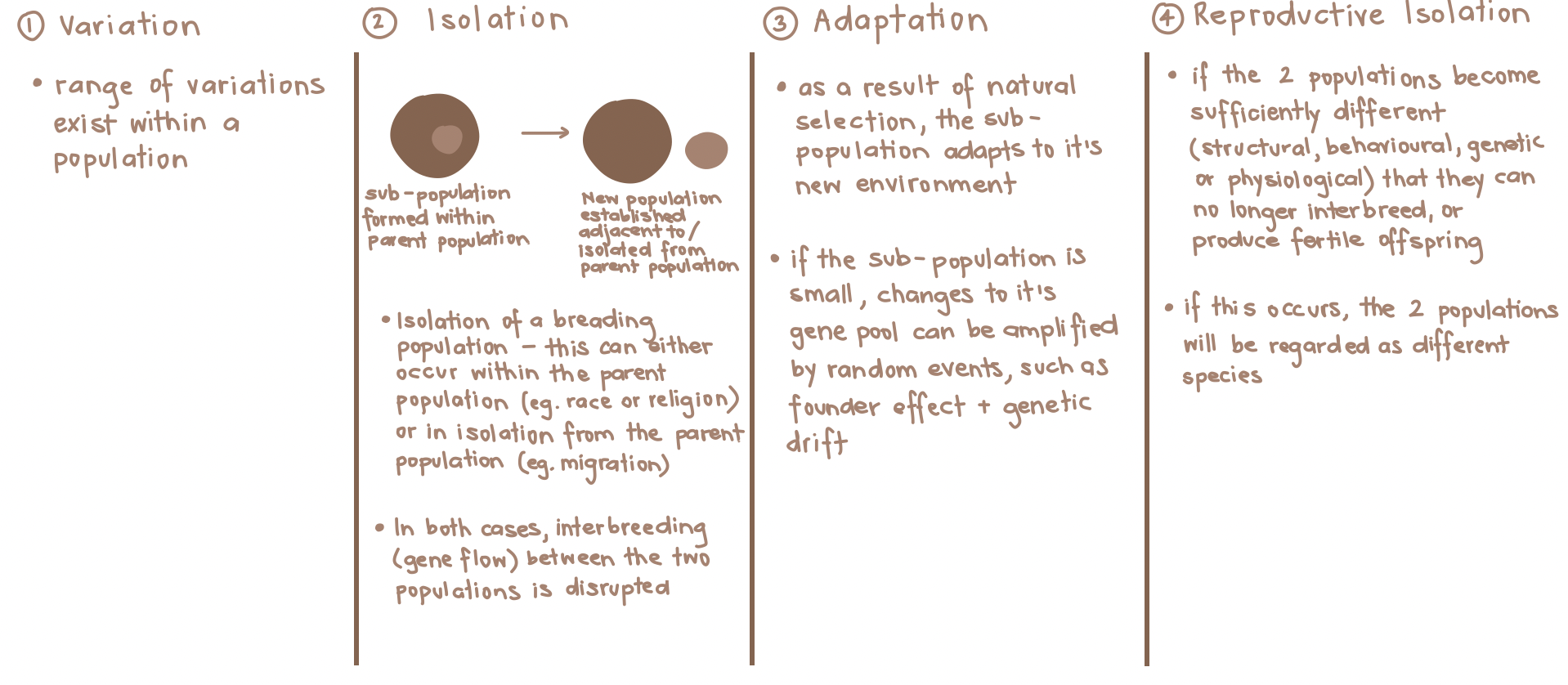
Define speciation (including how the gene pool is affected) and explain how isolation plays a factor in its occurrence.
Speciation:
Changes in allele frequency may eventually lead to a new species forming.
Requires the populations to be separated (reduce gene flow)
Results in the inability of two populations to breed and produce fertile offspring.