Stoichiometric Relationships
Stoichiometry - the quantitative relationships between reactants and products in chemical reactions, helps in understanding the composition of substances and predicting the outcomes of reactions.
Balancing Chemical Equations
Balancing equations using coefficients ensures that the law of conservation of mass is obeyed.
Identifying the stoichiometry of a reaction helps in determining the relative amounts of reactants and products.
Combustion Equations: burning organic compounds - CH4 + 2O2 = CO2 + 2H2O
Ionic Equations: aqueous solutions break apart compounds into ions
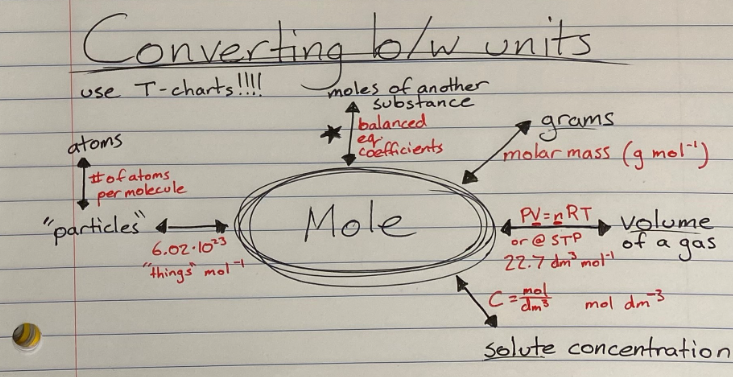
Ideal Gases: Ideal gases are hypothetical gases whose particles have negligible volume and no attractive forces. They follow the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, where P is pressure, V is volume, n is moles of gas, R is the gas constant, and T is temperature.
Mole Concept
Understanding Avogadro's number (6.022 x 10^23) helps in converting between moles and particles.
Calculating molar mass allows us to convert between grams and moles of a substance.
 Empirical Formula:
Empirical Formula:
Stoichiometric Calculations
Applying mole ratios in stoichiometric calculations helps in determining the amounts of reactants consumed and products produced.
Recognizing the limiting reactant is crucial for predicting the maximum amount of product that can be formed.
Percentage Yield
Calculating the percentage yield involves comparing the actual yield of a reaction to the theoretical yield.
Factors such as impurities, side reactions, and incomplete reactions can affect the efficiency of a reaction.
Sub-branches:
Mole Concept:
Avogadro's number represents the number of particles in one mole of a substance.
Molar mass is the mass of one mole of a substance and is expressed in grams per mole.
Balancing Chemical Equations:
Chemical equations are balanced based on whole number ratios of moles.
The law of conservation of mass states that mass is conserved in a chemical reaction.
Stoichiometric Calculations:
Conversion factors are used to convert between different units of measurement.
Identifying the excess reactant helps in determining the limiting reactant and the maximum amount of product that can be obtained.
Percentage Yield:
Calculating the efficiency of a reaction provides insight into the success of the reaction.