Chapter 4: Forces and Energy
Work and Energy
Work
==Work is done whenever a force makes something move.==
==The greater the force and the greater the distance moved, the more work is done.==
It is calculated using the following equation:

Energy
- Forms of energy:
- Kinetic Energy - this is energy due to motion. All moving objects have kinetic energy.
- Potential energy - this is energy which an object has because of its changed position, shape, or state. There are several different types of potential energy. Here are some of the terms used to describe them:
- Gravitational potential energy - a stone held up in the air can do work when dropped because gravity will pull it downwards. The stone has gravitational potential energy.
- Elastic potential energy (strain energy) - a stretched rubber band can do work when released, so can a compressed spring. Both have elastic potential energy.
- Chemical potential energy - it is when a fuel burns, its energy is released by chemical reactions. The energy stored in the fuel is called chemical potential energy, or chemical energy for short. Batteries also store it. So do foods.
- Electrical potential energy - it in circuits, the current is a flow of tiny charged particles called electrons. These come from atoms. Electrons can transfer energy from, for example, a battery to a light bulb. They have electrical potential energy, or electrical energy for short.
- Nuclear potential energy - An atom has a nucleus at its centre. This is made up of particles, held there by strong forces. In some atoms, the particles become rearranged, or the nucleus splits, and energy is released. This is called nuclear potential energy, or nuclear energy for short.
- ==Energy cannot be made or destroyed, but it can change form from one form to another.==
- Work done is equal to energy transformed.
Calculating PE
![]()
Calculating KE
How is the formula derived?

Final formula:

Efficiency and Power
Efficiency
==In simple words efficiency means how good a something (a device) is at transferring energy input to useful energy output.==
Formula:

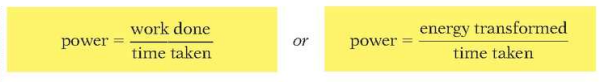
Power
==Power is the rate at which work is done.==
SI unit is watt (W).
Formula:
Energy Resources
Non-Renewable
{{Fossil fuels{{
Coal, oil, and natural gas are called fossil fuels because they formed from the remains of plants and tiny sea creatures which lived millions of years ago. They are a very concentrated source of energy. Oil is especially useful because petrol, diesel, and jet fuel can be extracted from it. It is also the raw material from which most plastics are made.
Natural Gas is the cleanest form of fossil fuel.
Problems
When fossil fuels burn, their waste gases pollute the atmosphere. Probably the most serious concern is the amount of extra carbon dioxide being produced. This may be adding to global warming.
{{Nuclear Fuels:{{
Most commonly uranium.
- Energy is released by fission, a process in which the nuclei of uranium atoms are split.
Problems
High safety standards are needed. The waste from nuclear fuel is very dangerous and stays radioactive for thousands of years. Nuclear power stations are expensive to build, and expensive to decommission (close down and dismantle at the end of their working life).
Renewable
{{Hydroelectric Power{{
Problems
Expensive to build. Few areas of the world are suitable. Flooding land and building a dam causes environmental damage.
Tidal energy
Similar to hydroelectric energy, but a lake fills when the tide comes in and empties when it goes out.
Problems
As for hydroelectric energy.
{{Wind energy{{
{{Generators are driven by wind turbines ('windmills).{{
Problems
Large, remote, windy sites are needed. Winds are variable. The wind turbines are noisy and can spoil the landscape.
{{Wave energy{{
Generators are driven by the up-and-down motion of waves at sea.
Problems
Difficult to build-few devices have been successful.
{{Geothermal energy{{
'Geothermal' means heat from the Earth. Water is pumped down to hot rocks deep underground and rises as steam. In areas of volcanic activity, the steam comes naturally from hot springs.
Problems Deep drilling is difficult and expensive.
{{Solar energy{{
(energy radiated from the Sun)
Solar panels absorb this energy and use it to heat water. Solar cells are made from materials that can deliver an electric current when they absorb the energy in light.
Problems
Variable amounts of sunshine in some countries. Solar cells are expensive, and must be large to deliver useful amounts of power. A cell area of around 10 m² is needed to power an electric kettle.
{{Biofuels{{
These are fuels made from plant or animal matter. They include wood, alcohol from sugar cane, and methane gas from rotting waste.
Problems
Huge areas of land are needed to grow plants.