1. Intro to Imaging & Digital Image Processing
Defining Imaging
- Modality: The difference between different bioimaging methods and machines (ex: CT and MRI are different )
- Four necessary components of a modality: source (illumination), camera (detector), digitizer (frame grabber), imaging processing unit
- Imaging processing unit (hardware and/or software)
- acquisition (takes in the data and understands it)
- preprocessing (combines information from multiple points)
- segmentation (identifying components, facial recognition)
- & more
- An image is a 2D representation of a physical quantity as rendered by an imaging modality
- X-ray attenuation (projection x-ray yor CT)
- Proton density (MRI)
- Acoustic reflectivity (ultrasound)
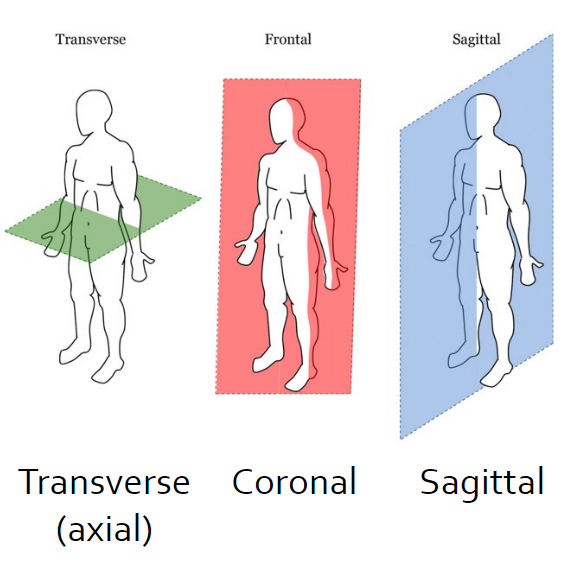
- An image represents a “finite-thickness” plane within a volume of interest
- Types of imaging
- Anatomical: Imaging that represents structure/composition of objects (e.g. CT imaging)
- Functional: Imaging that represents function/physiology of an organ (e.g. PET scans)
- Projection: Imaging that shoes a single planar representation (e.g. x-ray)
- Tomographic: Imaging that shows cross-sectional representation (e.g. CT imagings)
- Imaging mechanisms
- Transmission: The imaging mechanism by which information comes from what travels through the body (e.g. x-ray)
- Reflection: Transmission: The imaging mechanism by which information that comes from what reflects back from the body (e.g. ultrasound)
Modality Comparison
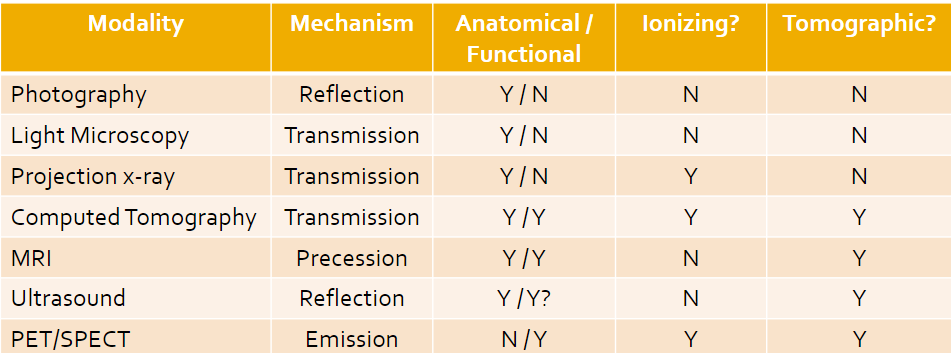
Ionizing is when the energy we work with is higher than others, and electrons in the atoms can bump up to unsafe levels; this is something we want to avoid (can lead to cancer)
Digital Imaging
- Digital images are digital files saved on a computer
- 2D arrays of “picture elements” called pixels
- Voxels are for 3D elements
- Image size = width x height
- Real-world image size (or FOV) is (Ncolumn x pixel width) x (Nrow x pixel height)
- Resolution: Number of pixels per square inch
- Image Pixels
- Addressed with x,y coordinates
- Top left corner is (1, 1)
- (coumn, row)
- Storage type
- Pixel values depend on the storage type
- Grayscale images are NOT called black and white
- 8-Bit: Greyscale images with values from 0 to 2^8 minus 1
- 16-Bit: Greyscale images with values from 0 to 2^16 minus 1
- Color images: each pixel can have 4 values
- 1 value per pixel – e.g. indexed image
- 3 values per pixel e.g. 3x1 bytes – RGB, 3x2 bytes – RGB, …
- 4 values per pixel RGB e.g. 4x1 byte – RGB_Alpha, …
Image Processing
- Enhancement/restoration of image info for human reading
- Segmentation
- Characterization
- Representation of images for machine analysis
- Visualization
- Processing of image data for storage
- Processing of image data for transmission
- Matlab
- Load the image and info
- imread()
- iminfo()
- Display image
- imtool()
- imshow()
- imagesec()
- image()
- imshowpair()
- Perform needed operation
- Display and evaluate results
- Save resulting image
- imwrite()