SLR 18
Input | Output | Storage |
Keyboard | Monitor | Hard Disk Drive |
Mouse | Speaker/ Headphones | Optical Disk |
Microphone | Camera Screen | SSD |
Touchscreen | Printer | CD/ DVD |
Camera |
| Magnetic Tape |
Scanner |
| Virtual Memory |
Graphics Tablet |
| USB Memory Stick |
Sensor – infrared and motion |
|
|
Input/ Output Devices (I/O Devices):
Barcode Reader
Used for identification
Shops
Tickets/ boarding passes
Passenger luggage
Medical samples and products
Recipes
Libraries
Parcels
Hyperlinks
Map information
Accessing websites and apps
Make payments
QR (Quick Response) Codes(2D) and Linear Barcodes(1D)
QR Codes store more information than a Linear Barcode
Types of barcode reader:
Pen-type readers – require a light source and photo diode located next to each other at the tip
Measures light intensity of the light reflected – generates a waveform – light is reflected better on white than black
Dragged across at an even speed
Used when a barcode is handheld – e.g. books
Can take longer, especially for a long barcode and if the speed is not right
Barcode must be clear – not covered in dust or the reader can be damaged
Laser reader – uses a laser beam
Laser is reflected off a moving mirror – barcode can be read in multiple positions
Shops, self-checkouts
Doesn't need a specific speed
Can be used on a non-linear surface
More robust – nor damaged by dust or water
Need a lot of equipment – not as portable – scanner can’t move – more difficult to fix
More expensive
CCD – charged coupled device
A row of many light sensors
Measures light intensity
Voltage pattern is recorded
Limited by cable
Handheld – not affected by shaking hands – easier to hold
Must be held somewhat horizontally
Can be used on rounded surfaces
Camera based – imaging scanner which uses camera and image processing
Can be used on any surface, including screens
Software does most of the work
Easily accessible
Can run out of charge
Not used for linear barcodes
DSLR Camera
Uses CCD or CMOS (complementary metal oxide semi-conductors) - millions of tiny light sensors in a grid
Shutter opens, light enters and projects the image onto photosites at the back of the lens
Photosites measure the brightness of each pixel – the light becomes electricity and stores the charge as binary
Photosites are placed under a Bayer filter to separate wavelengths
RFID
Radio Frequency Identification
Needs a tag and a reader
Uses radio signals so no need for line of sight
Tag contains a chip and antenna – chip is in the middle
Antenna sends/ receives signals and chip processes
Each tag has a unique identifier and a non-volatile memory cell storing additional data
Reader transmits an encoded radio signal
Tag will respond to the signal with the identifier
Types of RFID tag:
Passive
Does not have power
Reader gives power via radio energy
Tag must be very close to the reader
Active
Has a small battery so has power
Tag transmits identifier at regular intervals
Vastly increases the distance the tag can be read from
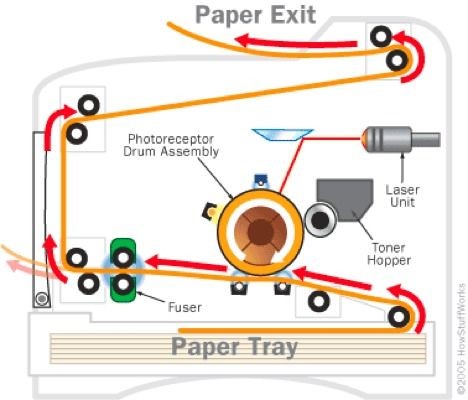
Laser Printer
Bitmap image of the page is created
A negative charge is applied to the print drum
A laser with a mirror is used on areas of the drum to lose that charge, creating a reverse image of the drum
Drum continues to rotate, and is exposed to a positively charged toner, which is attracted to the negatively charged areas on the drum
A sheet of paper is passed under the drum and the toner is transferred onto the paper
The toner passes through a fusing process to ensure the toner sticks to the paper
For colour, the process is repeated 3 times – cyan toner, magenta toner, and yellow toner
CCD is more expensive and produces higher quality images
CMOS uses less energy, so helps save power on mobile devices
Secondary Storage Devices:
Hard Disk Drive
uses a metal disk (platter) which is coated in a think film of magnetic material
film is made up of concentric tracks, which are each split up into sectors
the platter spins at high speed and a read/ write head is moved over the platter, which can detect and change the magnetic charges in that sector
Solid State Disk
has no moving part
made up of NAND flash memory and a controller
NAND flash memory is non-volatile and is based on floating gate transistors
storage is split into blocks, and each block is split into pages
pages cannot be overwritten - must be erased first - whole block must be erased
controller is used to manage this
have lower latency and faster access speeds than HDDs due to having no moving parts
have a lower number of read/ write cycles before the flash memory degrades
NAND Flash Memory:
when the control gate is turned on, electrons flow from the source to the drain and some electrons are attracted to the floating gate
when the control gate is turned off, the electron flow stops, and the electrons are trapped in the floating gate
the presence or not of electrons correlates to a 1 or 0
Optical Disk
includes CD (Compact Disk) and DVD (Digital Versatile Disk )
data is read using a laser beam (optical = light)
data is stored on a spiral track and this track uses pits and lands
the laser is shone at the track
the laser’s light reflects back to the sensor while the disk spins at a constant linear velocity
where a pit or land continues, a certain amount if light is reflected back to the sensor and this represents a 0
if the state changes, the light is scattered and this represents a 1
Comparing Capacity and Speed
HDD | SSD | Optical | |
Capacity |
|
|
|
Access |
|
|
|
Cost |
|
|
|
Robustness |
|
|
|
Application |
|
|
|