1.3 Aromatic Hydrocarbons (Benzene Rings)
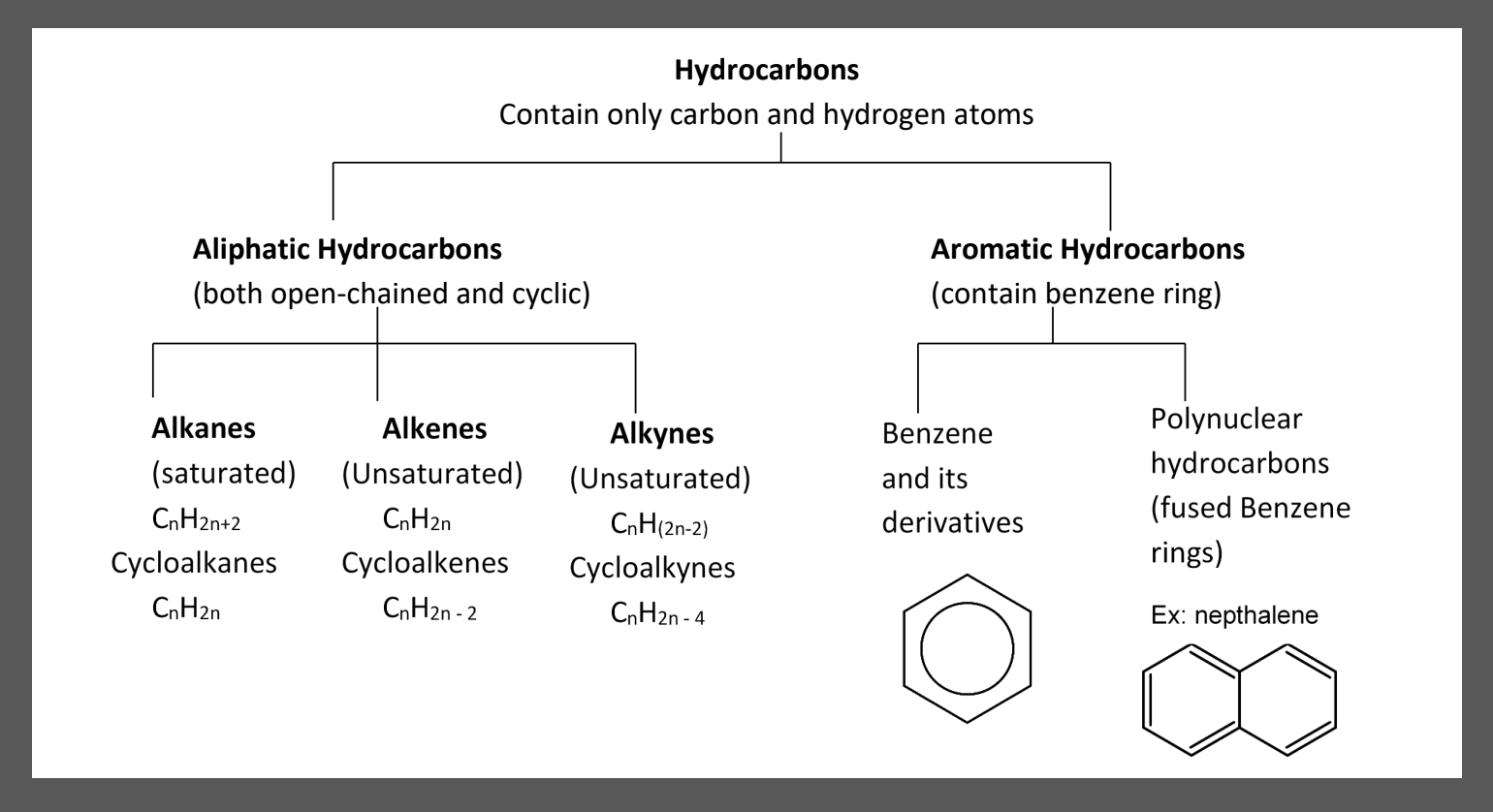
- Benzene: alternating double bonds in a cyclohexane. Drawn as a circle inside a hexane.
Naming Aromatic Compounds
Use the benzene ring as the parent chain
“benzene” becomes the root
other rules remain the same
- Use this method when the substituent is simple
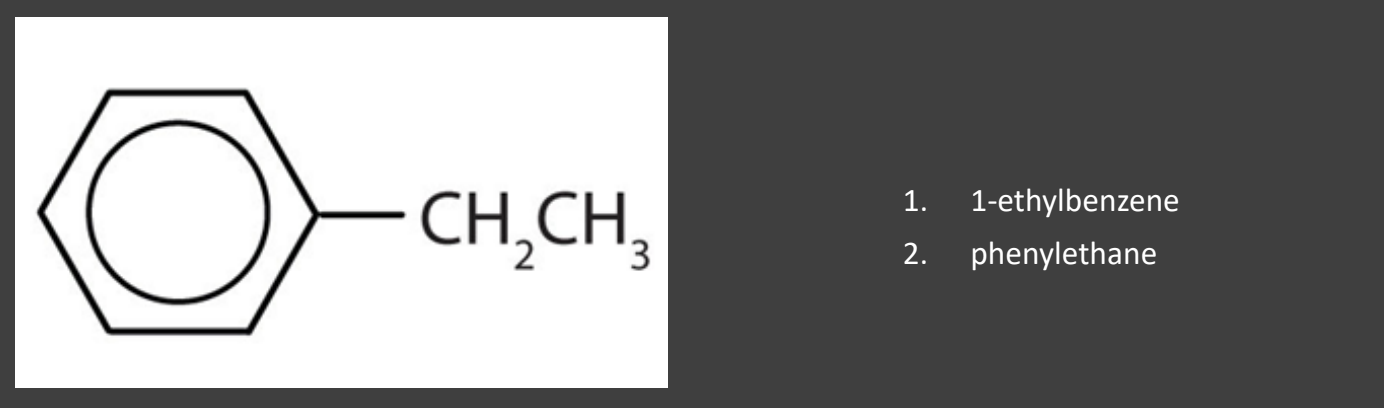
Name the benzene ring as the substituent with the name “phenyl”
- Use this method when the substituent is complex
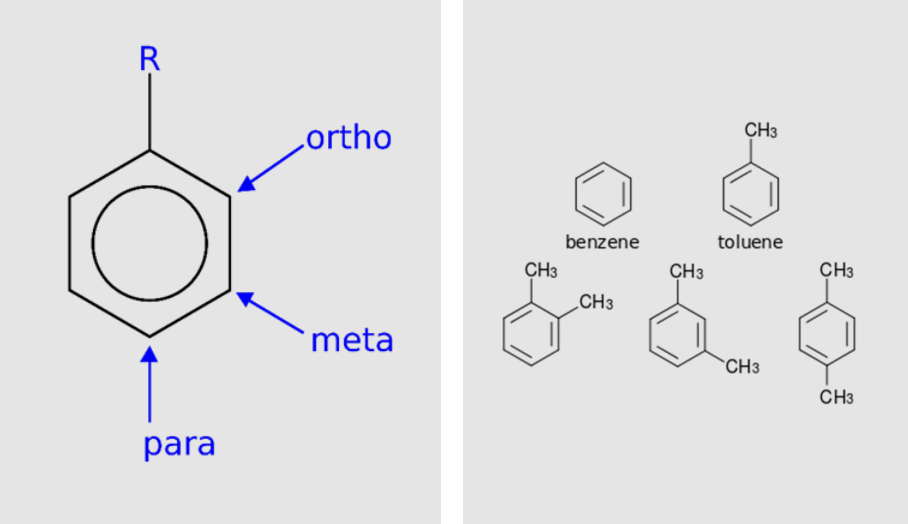
Special Cases
Orthodimethylbenzene
Metadimethylbenzene
Paradimethylbenzene
Properties of Aromatic Hydrocarbons
- Liquids of crystalline solids at room temperature
- Non-polar
- Insoluble in water
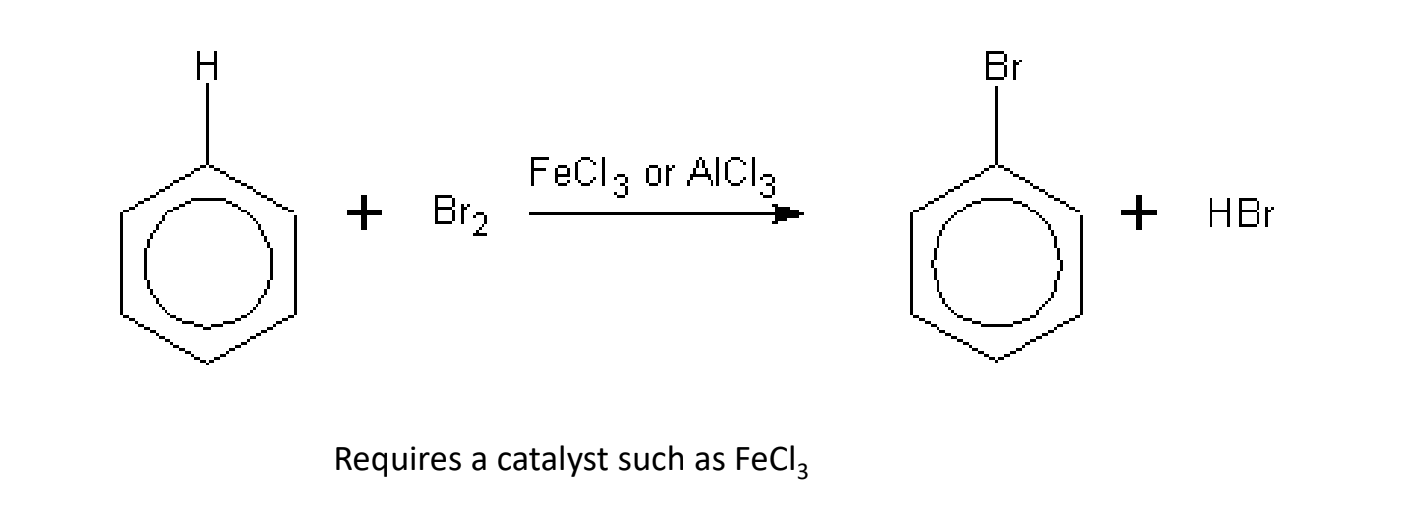
Reactions of Aromatic Hydrocarbons
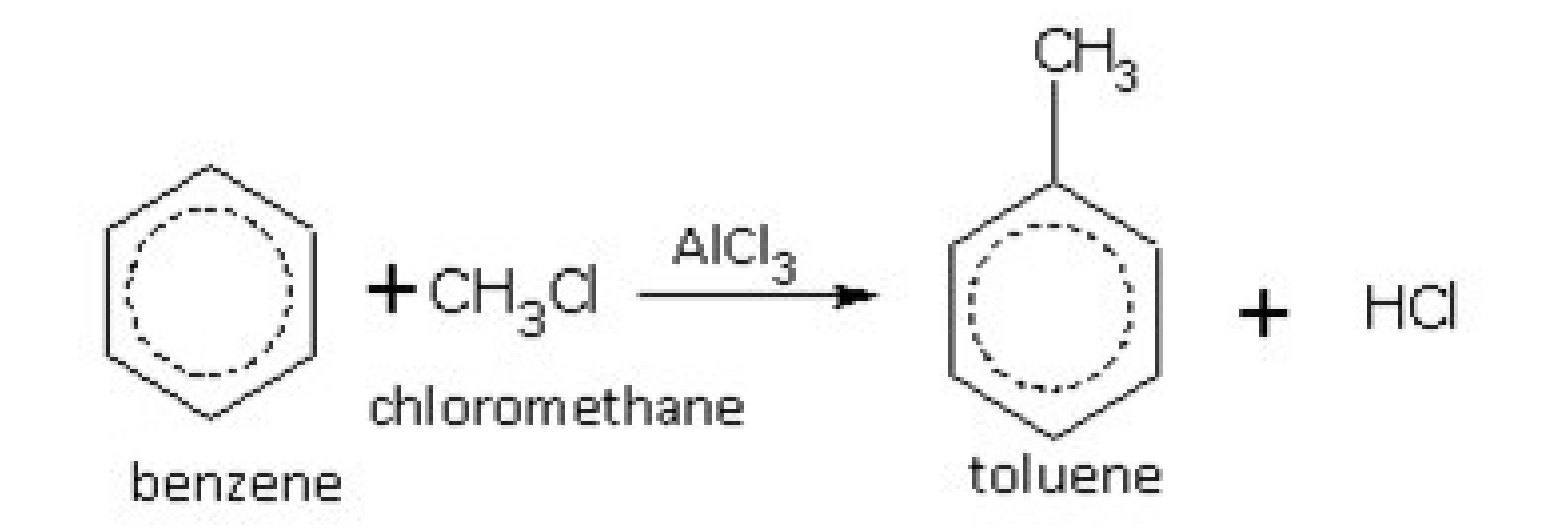
- Aromatic hydrocarbons unlike alkanes are unsaturated, but they undergo ^^substitution reactions like alkanes.^^
- This is because the bonds are not alternating single-double bonds like in the structural diagram, but ^^equal bonds in resonance.^^
Halogenation
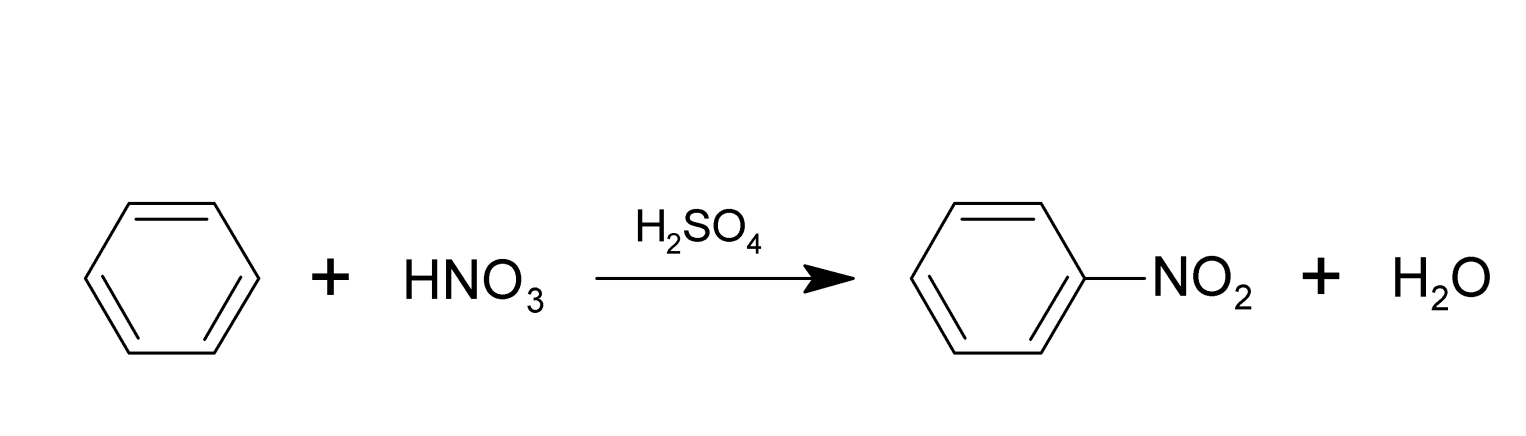
Nitration
Alkylation