Wk 2.1 Professional Communications in Pharmacy Practice Part 1
Lecture Objectives
Define professional communications and establish its significance within pharmacy practice.
Identify critical elements of interpersonal communication essential for patient care.
Discuss strategies to safeguard patient privacy during communications.
Recognize barriers to effective communication and strategies to minimize these impediments.
Understand factors impacting communication with culturally diverse patients and those with unique communication needs.
Define what constitutes appropriate language in interactions with patients and healthcare professionals.
Importance of Communication
Clear, respectful, and effective exchange of information between pharmacists, patients, healthcare professionals
AHPRA Registration Standard: Adherence to standards set by the Australian Health Practitioner Regulation Agency.
National Competency Standards: for pharmacists in Australia.
Charter of Healthcare Rights: Highlighting rights including safety, respect, communication, participation, privacy, and feedback.
Access to resources like the Communicating for Safety portal to improve communication in healthcare settings.
Common Communication Issues
Barriers that include:
Rude and discourteous attitudes.
Providing incorrect or conflicting information.
Incomplete or incomprehensible communication (e.g., use of jargon).
Neglecting the specific needs of individuals (e.g., requiring interpreters or disability considerations).
Failures in interprofessional team communication.
Communication and Patient Safety
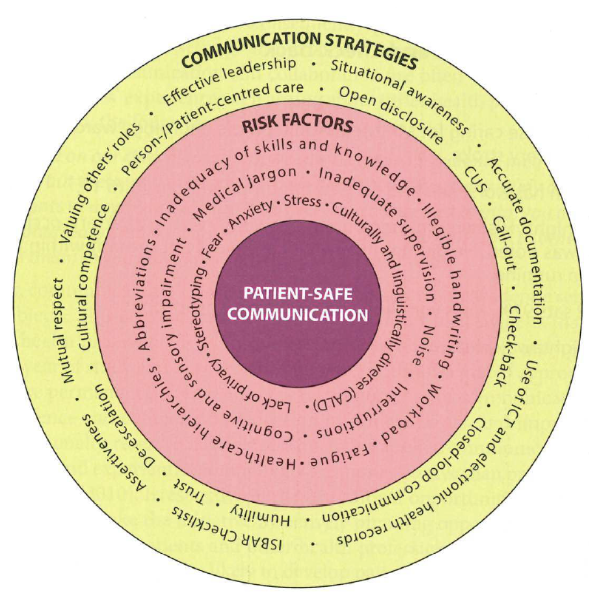
Key Attributes of Patient-Safe Communication
Mutual Understanding:
Based on perceptions and interpretations of the message by sender and receiver.
What they believe the massage says
The individual sending the message
Risks of misunderstandings if assumptions about patient understanding are made.
Overcoming barriers
Avid the use of equivocal term
Avoid to use jargon
Avoid abstract, non-specific language e.g. does it hurt a lot?
Taking a nonjudgemental stance
Patient Centeredness:
Shift from viewing patients as passive recipients health care.
Emphasis on informing patients, involving them in decisions, and respecting their cultural values.
Patient-centred care
Strategies for Patient-Centered Communication:
Acknowledge patients.
Provide clear information
Provide explanation
Express empathy.
Use prompting
Active listening
Seek clarification
Active Listening, Prompting and Probing
Importance of demonstrating listening through eye contact, head nodding, and supportive verbal affirmations.
Use prompting questions to delve deeper into patient narratives without redirecting discussions.
Type of probing question
Clarification
Justification
Relevance
Exemplification
Extension
Restatement
Echo
Consensus
Non-verbal Communication
Elements include:
Physical distancing: Respect personal space
Body Movements: Open and relaxed posture to convey availability and approachability.
Eye Contact: Direct eye contact during most parts of communication enhances connection.
Facial Expressions: Should align with spoken words to convey sincerity and understanding
Culture Competency in Communication
Ethnic and religious diversity may bring special cases in the spectrum of human differences
e.g. less common ground for languages, beliefs and practices relating to kinship, family, marriage, chlid-rearing, touch, gender, clothing, death, disease, etc
Risk Factors for Patient-Safe Communication
In Pharmacy Environment
External noise
dispensary counter
lack of privacy
frequent interruptions
involvement of third parties
For Pharmacists
Lack of time
Lack of knowledge
Lack of confidence
Poor communication skills
Fear of moving out of scope of practice
Lack of awareness of patients needs
Emotional barriers
Attitude
For Patients
Lack of time
Emotional barriers
Poor perception of illness
Perception of medication
Strategies to Overcome Barriers - The 4 A's
Attitude: Cultivate a positive approach.
Atmosphere: Create a conducive environment for communication.
Approach: Utilize appropriate interpersonal strategies during interactions.
Availability: Ensure time is allocated for effective dialogue.
Conclusion
Reinforcement of the significance of professional communication in pharmacy practice to enhance patient safety and care outcomes.