Biology Study Notes: Chapters 1, 2, 5
Characteristics of Living Organisms
Made of Cells
Example: Humans are made of trillions of cells forming various tissues and organs.
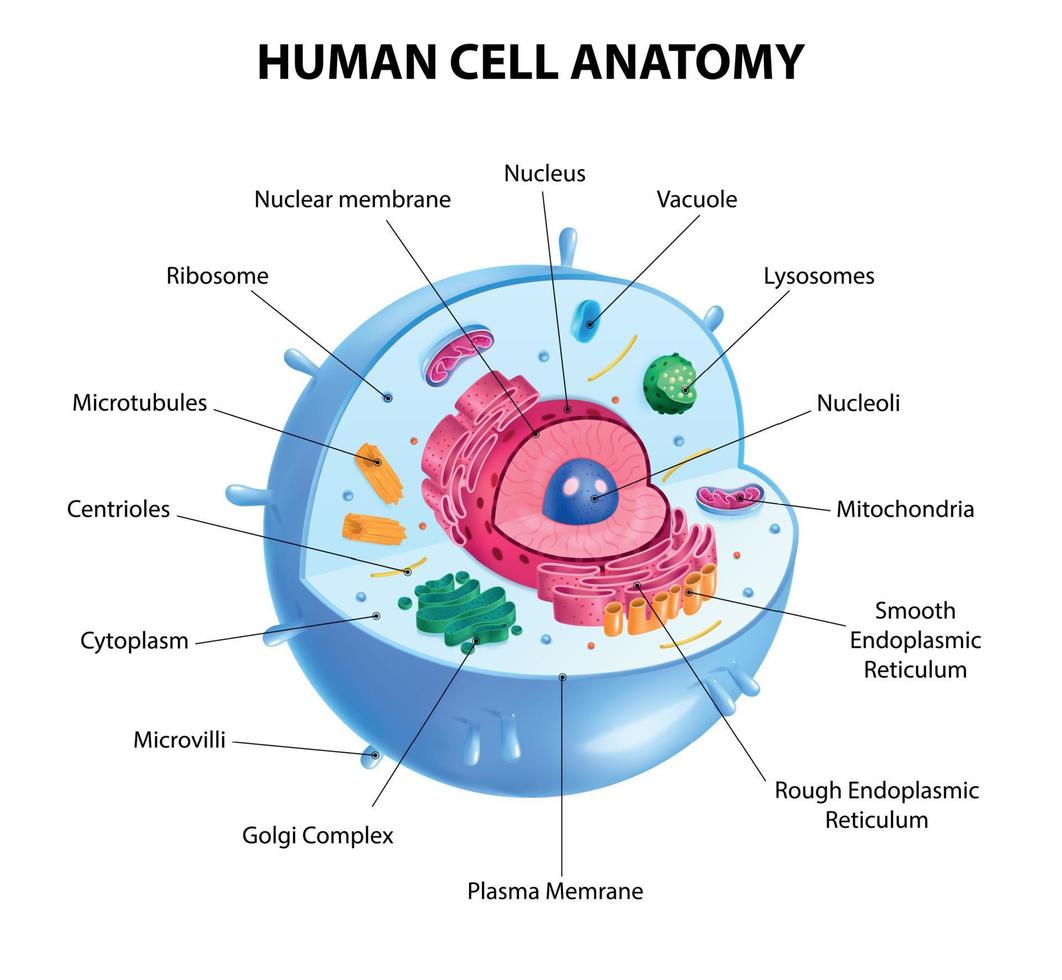

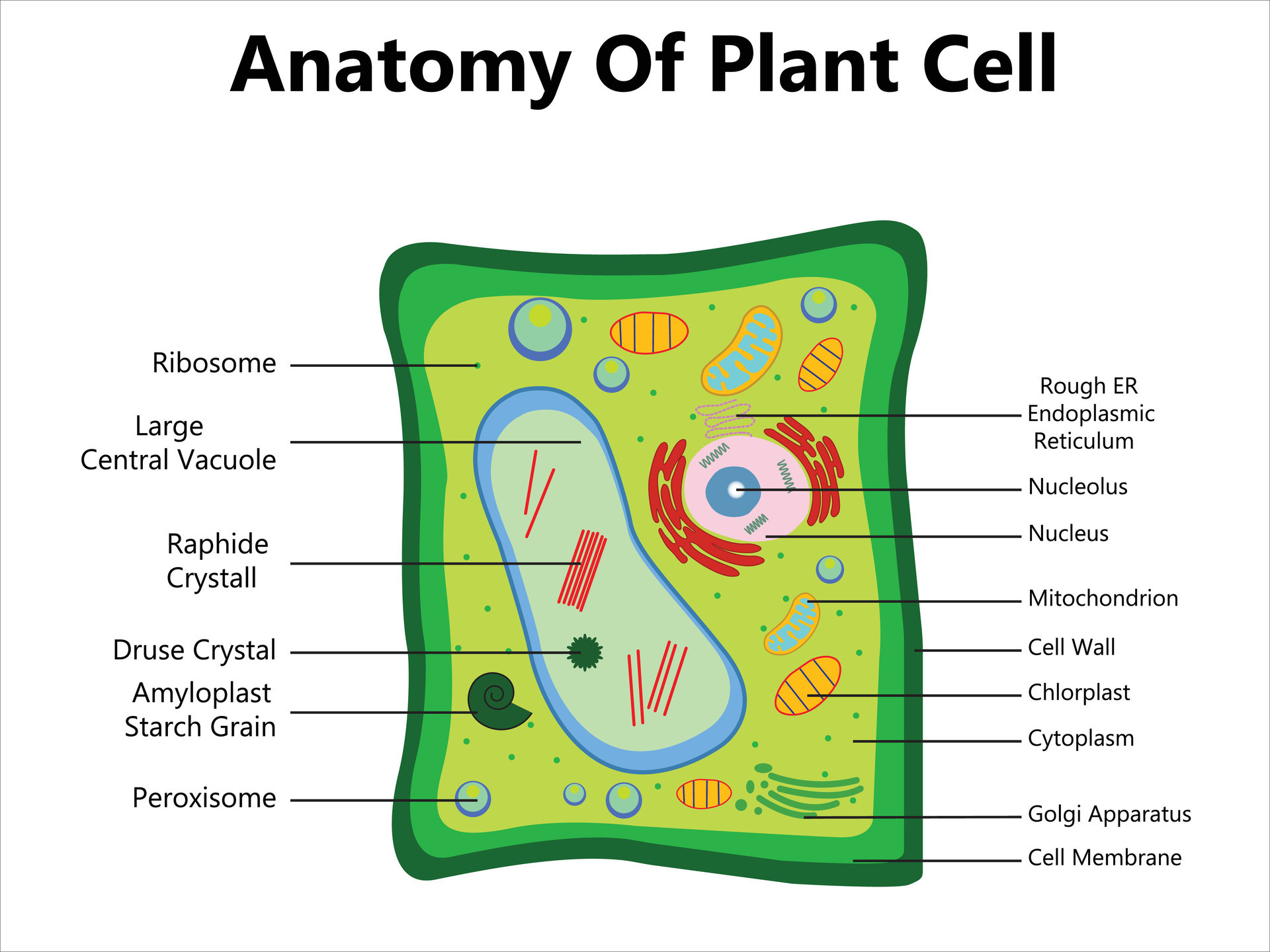
Use Energy (Metabolism)
Example:
Plants: Convert sunlight into energy through photosynthesis.
Animals: Consume food for energy.
Maintain Homeostasis
Example: Humans regulate body temperature around 37°C (98.6°F) despite external temperature changes.
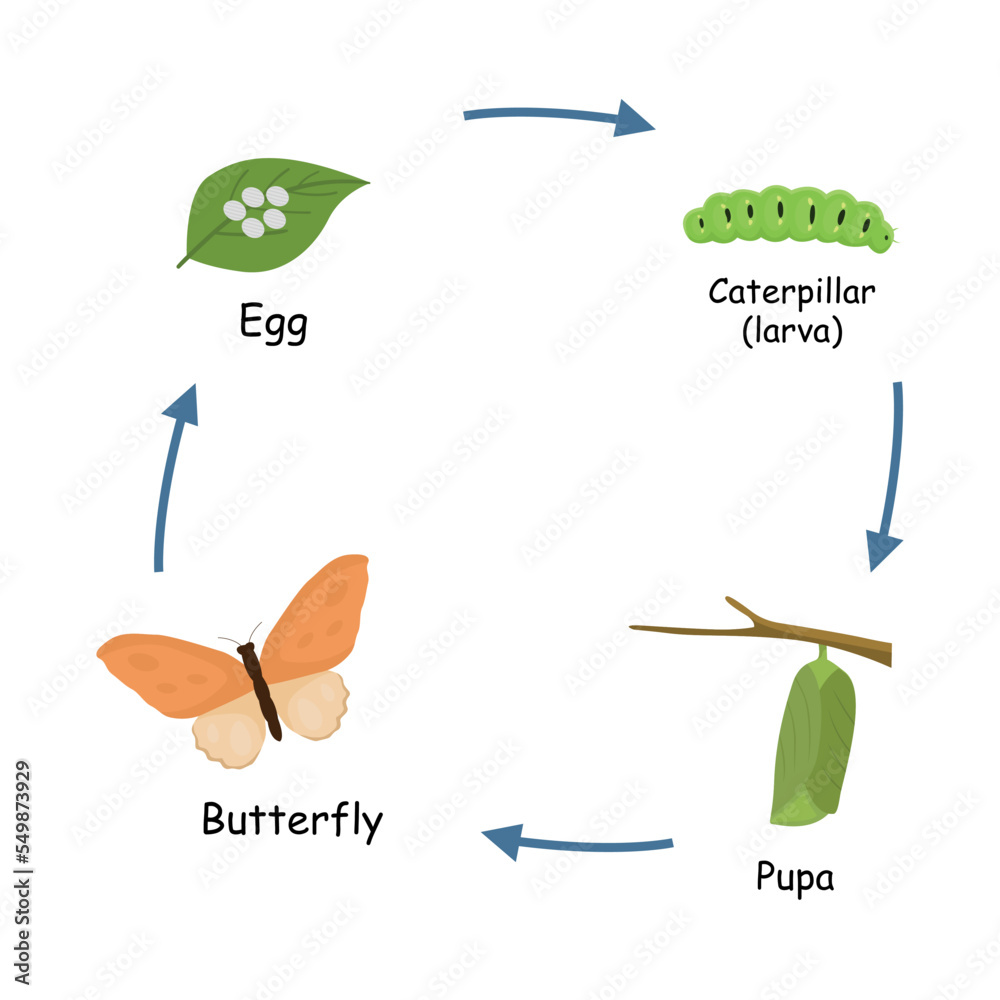
Grow and Develop
Example: A caterpillar grows and undergoes metamorphosis to become a butterfly.
Reproduce
Example: Bacteria can reproduce through binary fission, creating identical offspring.
Respond to Stimuli
Example: A plant bends toward sunlight (phototropism) or flowers bloom in response to temperature changes.
Evolve Over Generations
Example: The development of antibiotic resistance in bacteria demonstrates evolution in response to environmental pressures.
Biology Themes
Evolution
All living organisms, including humans and apes, share a common ancestor based on evolutionary theory.
Structure and Function are Related
Example: Bird wings are designed in a specific shape to allow for efficient flight.
Information Flow
Example: DNA is transcribed into RNA and then translated into proteins, which perform functions within cells.
Systems Interactions
Example: The human digestive system interacts with the circulatory system to provide nutrients to cells.
Scientific Method with Examples:
Observation:
Noticing that plants in one area grow taller than those in another area.
Hypothesis:
Plants receive more sunlight in that area, leading to their increased height.
Prediction:
If I move plants to that area, they will grow taller.
Experiment:
Transplanting identical plants to different areas with varied sunlight exposure.
Results:
Measuring the growth of plants in both locations over a month.
Conclusion:
Analyzing whether the plants in more sunlight indeed grew taller, refining the hypothesis as needed.
Good Experiments:
Should include controls like having some plants in the original positions and replicates across multiple plants to ensure reliability.