B5: plant nutrition
Photosynthesis
the process by which plants synthesize carbohydrates from raw materials using energy from light
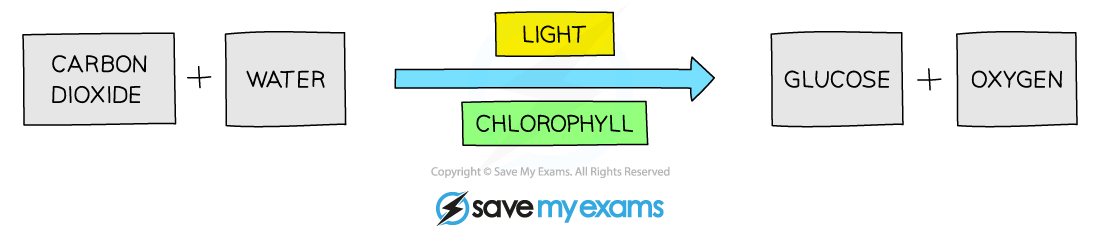 6CO2+6H2O → C6H1206 + 6O2
6CO2+6H2O → C6H1206 + 6O2
chlorophyll: green pigment found in chloroplasts within plant cells
Absorbs light energy → transfers light energy into chemical energy
uses of carbohydrates
converted to starch molecules as an effective energy store
cellulose to build cell walls →
used in respiration→ provides energy
sucrose for transport
nectar to attract insects
converted to lipids for energy source in seeds
converted into amino acids when combined with other minerals
minerals in plants

leaves
structure of a leaf
wax cuticle: protective layer on top of the leaf → prevents evaporation
upper epidermis: thin and transparent → allows light to enter palisade mesophyll
spongy mesophyll: contains air spaces → increases surface area for diffusion
lower epidermis: guard cells and stomata
stomata: where gas exchange takes place → opens during the day, closes at night
mostly found under the leaf
vascular bundle: contains xylem and phloem → transports substances
xylem: transports water
phloem: transports sucrose and amino acid
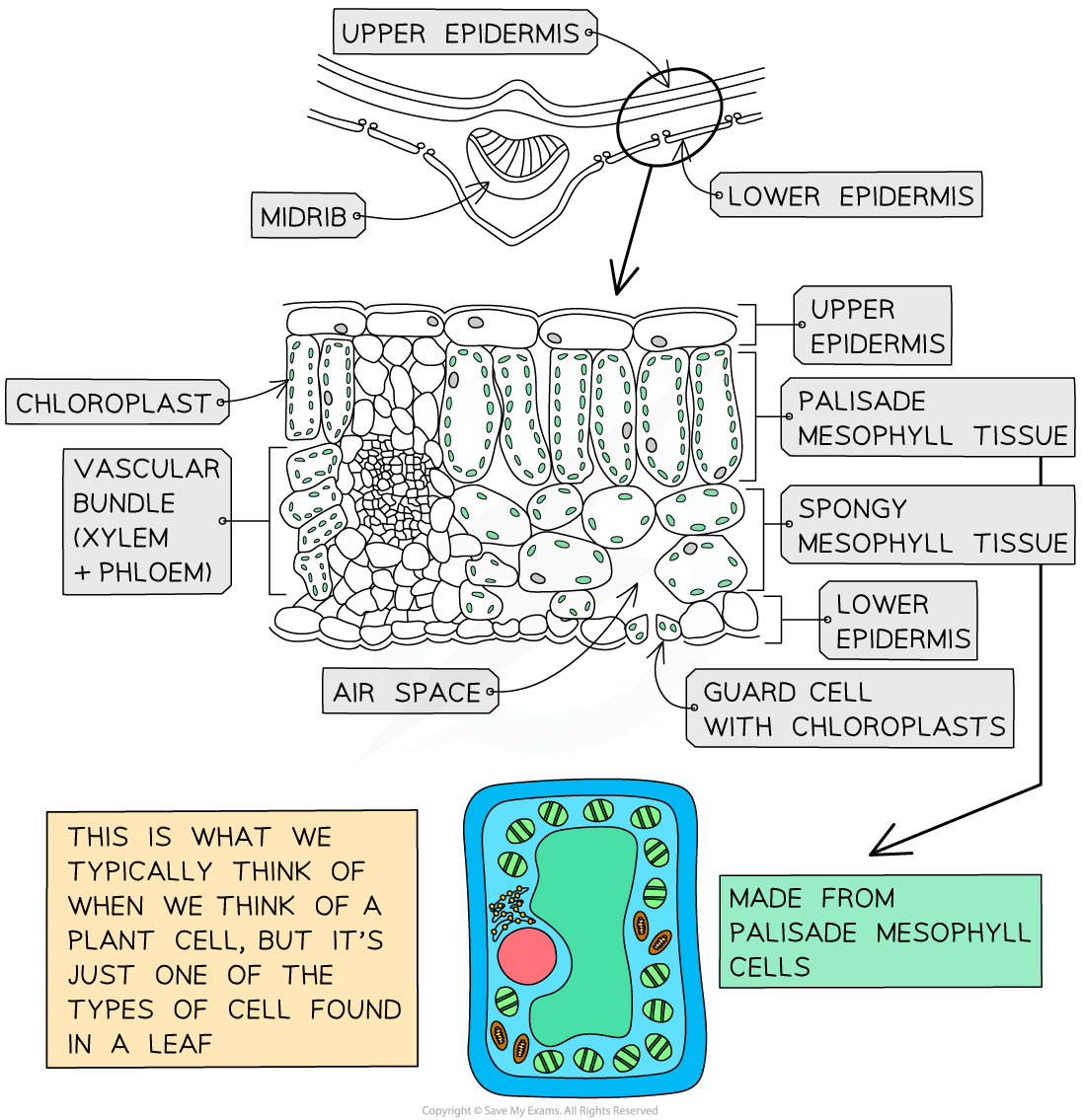
Adaptations of leaf structure:
large leaf surface area: increases rate of diffusion of CO2 and absorption of light
thin: allows CO2 to diffuse to palisade mesophyll cells quickly
chlorophyll: absorbs light energy for photosynthesis
network of veins: allows transport of nutrients
thin cuticle made of wax: protects the leaf without blocking sunlight
palisade cell at the top: maximizes absorption of light
vascular bundles: thick cell walls of tissue → help support the stem and leaf
Factors affecting photosynthesis
Temperature: increases → rate of photosynthesis increases as photosynthesis is controlled by enzymes
temperature increases too much → enzymes could denature → photosynthesis rate goes down
light intensity: more light → faster rate of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide: more co2 → faster rate of photosynthesis
investigate the effect of light on the net gas exchange in an aquatic plant using a pH indicator such as hydrogencarbonate indicator
Hydrogencarbonate indicator shows the carbon dioxide concentration in solution
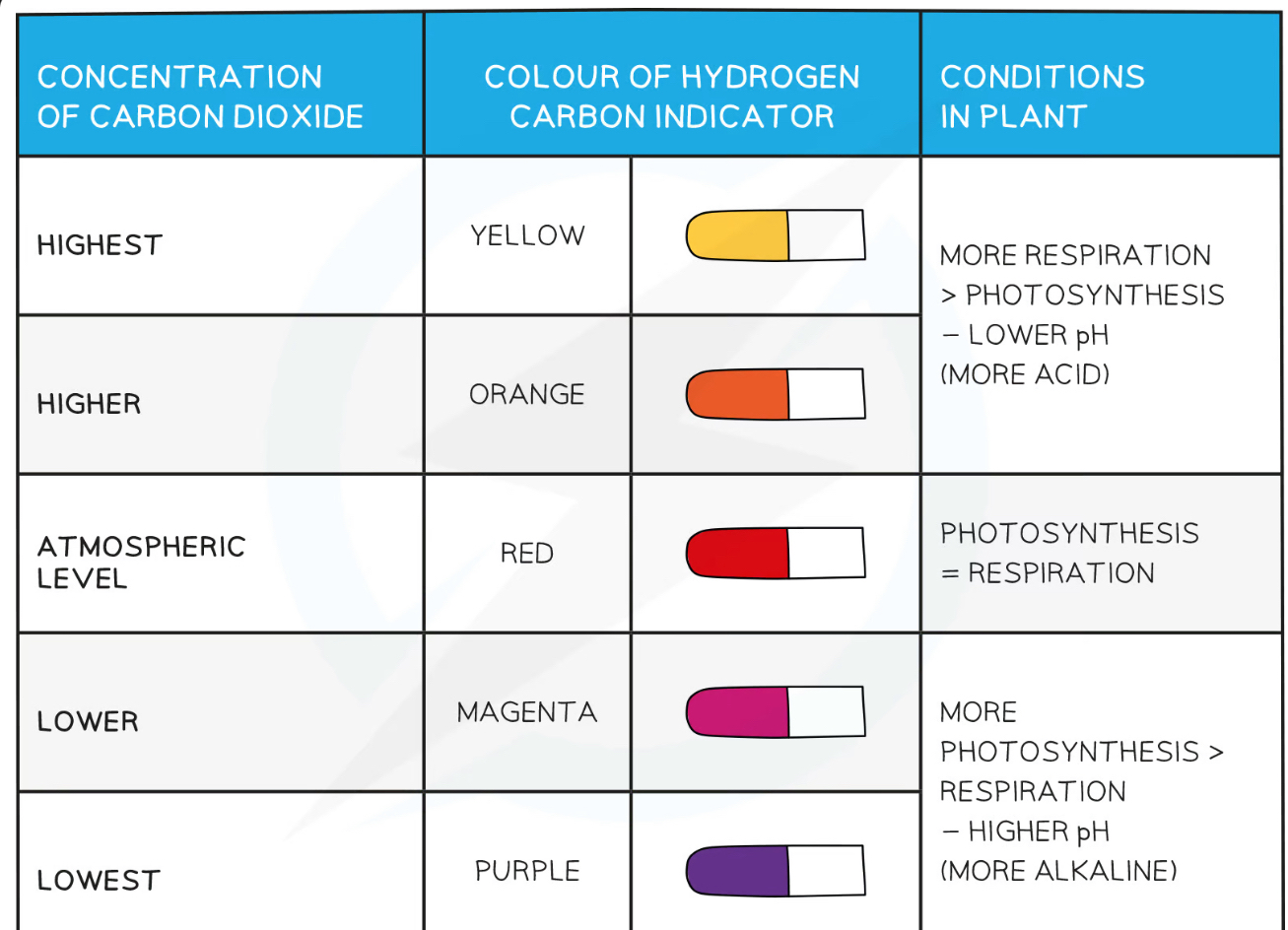
Several leaves from the same plant are placed in stoppered boiling tubes containing some hydrogencarbonate indicator