1.3 bone & skeleton
Bones
- Bone = connective tissue made of cells suspended in a matrix
- 65% mineral compound (hydroxyapetite)
- 30% organic material (mostly collagen)
- organs made up of bone tissue
- dynamic & respond to changes in their environment.
Layers of bone
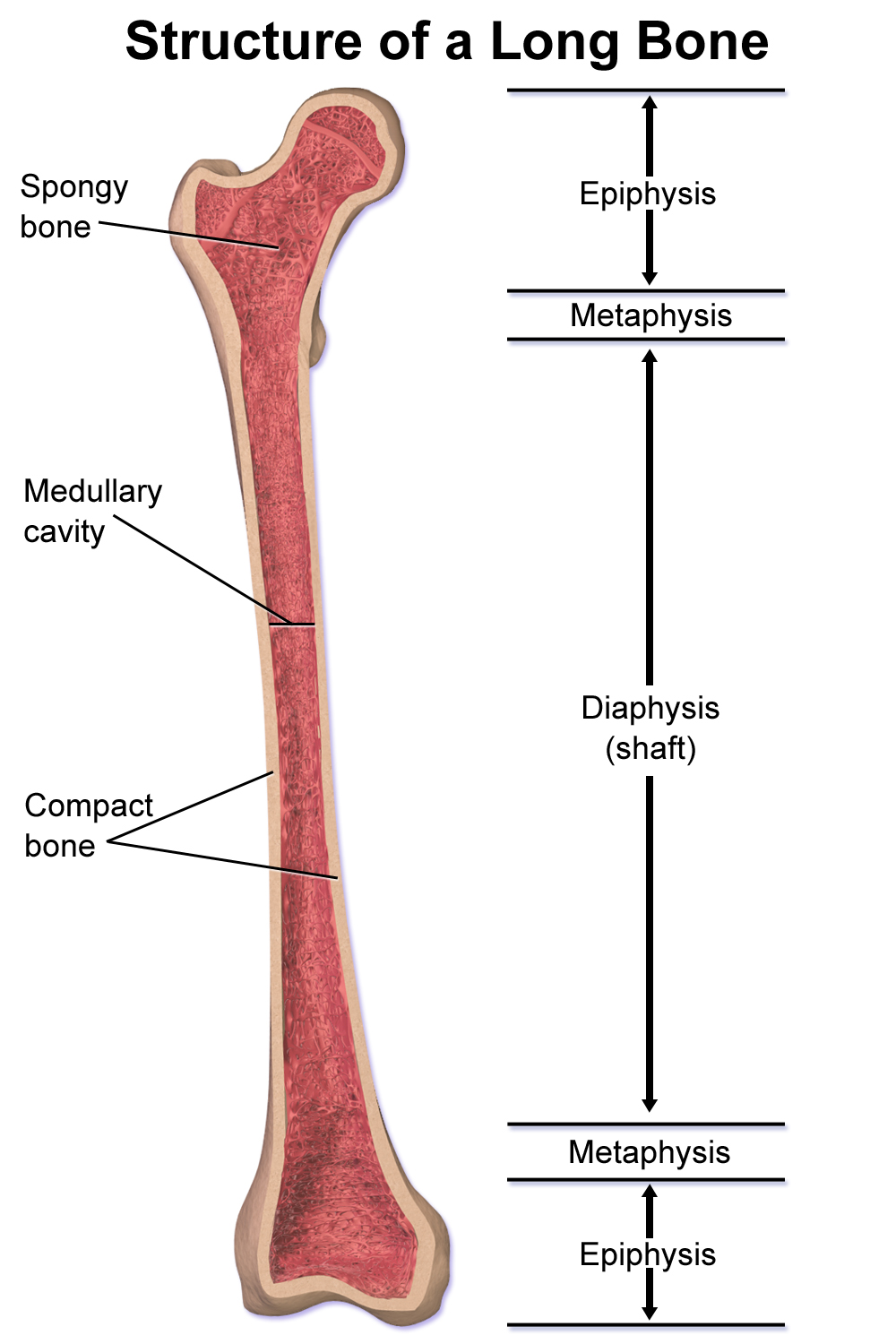
- Outer - periosteum → coats outside of bone, has blood supply which continues into centre
- Mid - cortical (compact) bone
- Inner - trabecular (spongey bone)
- Medullary cavity - contains bone marrow (immunity)
- Epiphyseal plate (growth plate) - filled w/ cartilage, helping juvenile grow via elongation
- Bones join at articular cartilage - smooth gliding & cushioning of joints
Bone marrow
- yellow - adipose tissue
- red - blood cell production (rbc, wbc & platelets)
Other bone structures
- Flat bones
- No medullary cavity
- 2 layers of compact bone surrounding either spongy bone or air/space
- Short bones/irregular bones
- No medullary cavity
- Develop from a single centre of ossification
- Sesamoid bones
- E.g. patella / fabellae (dog)
- Found near joints
- Ease tendon path & prevent excessive tendon wear
- Increases moment arm of muscle
Macroscopic architecture
Osteons
- collection of lamellae
- structure:
- collagen fibres allow each ‘doughnut’ to hold each other
- collagen fibres run in different directions in neighbouring lamellae
- more resistant to twisting forces, but still allows some form of ‘give’
Surface markings
- for leverage & muscle attachment
- Response to strain within bone
- Articulations with other bones
Bone membranes
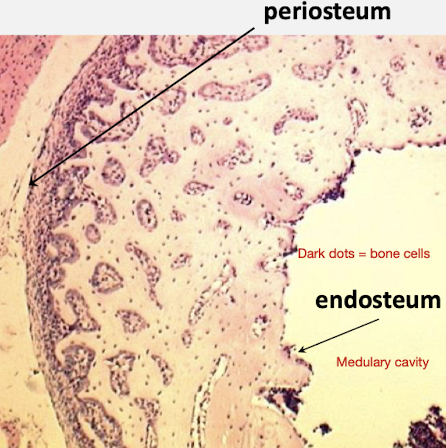
Periosteum - covers outside of bone
- 2 layers
- Protective of underlying tissue
- Greater osteogenesis than osteolysis
- Site of sensory nerves, blood & lymphatic vessels
- highly cellular
Endosteum - lines medullary cavity
- Single layer - thin layer as it only has physiological function (not mechanical)
- Osteolysis great than osteogenesis (can produce new & remove unwanted bone tissue)
Blood & nervous supply of bones
- Well vascularised
- Arteries enter bone via nutrient foramen in diaphysis
- Arteries pass through subchondral bone to supply calcified part of cartilage (CARTILAGE ITSELF IS AVASCULAR, but blood supply is v. close)
- Haversian (ups & down) & volkmann (distal & medial) canals supply cortical bone
- Trabecular bone supplied via bone marrow