Early Europe and Colonial Americas
Early Christian Art, 100-500 CE
Hangs onto the classical canon and much of the art goes to faith. fear of rendering the human body. the commandment “thou shall not make unto thee any graven image, or any likeness of any thing that is heaven above, or that is in the earth beneath, or that is in.” wanted to separate itself from paganism,
Catacomb of Priscilla

gave up land for other christians to be buried
200-400 CE
About 40,000 dead people
Five stories deep
Sarcophagi (usually only the rich had them)
Greek Chapel - Greek lettering found, did not go under to pray, not greek
Orant Fresco - half moon shapes (lunettes), marriage, birth, orant pose (praying, eyes lifted towards heaven, arms up wide), birds, peacocks, doves, quail
Good Shepard Fresco - Jesus, clean shaven, shows the story of jonah (God told him to go somewhere, he hid from God in a boat, was bringing bad luck, somehow got out of the boat and eaten by the whale, inside whale for three days and prayed to God, Jonah was spit out on dry land and went to Ninabah). the fresco has lunettes
Greek cross has even arms and legs, latin cross has a long leg and higher arms.
Sarcophogus of Junius Bassus, Rome with ten relief panels
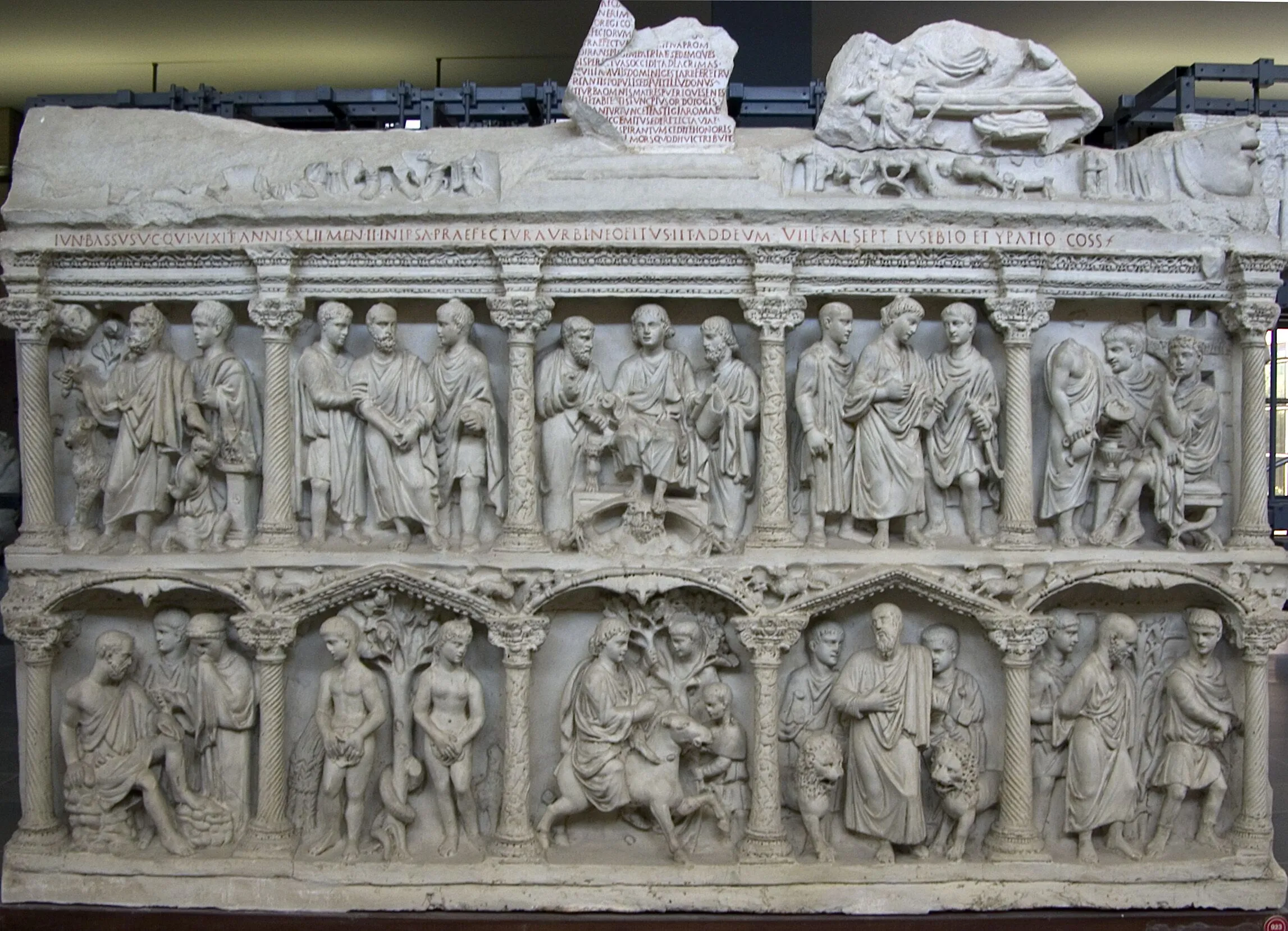

Jesus has a clean shaven beard
Classical Calm
Columns and Capitals
Jesus is being prompt up on god of the sky
Adam and Eve, Daniel and the lions, Abraham and Isaac sacrifice, divided into registers on the christian side by the old testament and the new testament
Plan of Old St. Peters
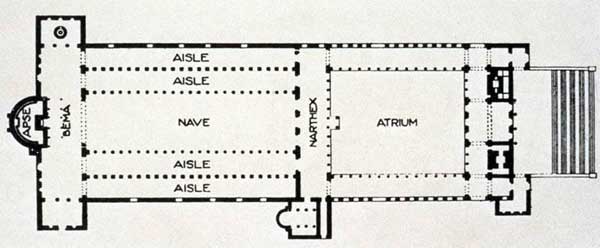
crucified on cross
died upside down because he did not view himself as worthy to die the way Jesus died
Julius the 2nd tore down the first church, Levatican was built in its place
Constantine was the patron of the church
Basilicas were usually built on the outskirts to avoid conflict
Face east for the rising sun of your faith
Santa Sabina, Rome
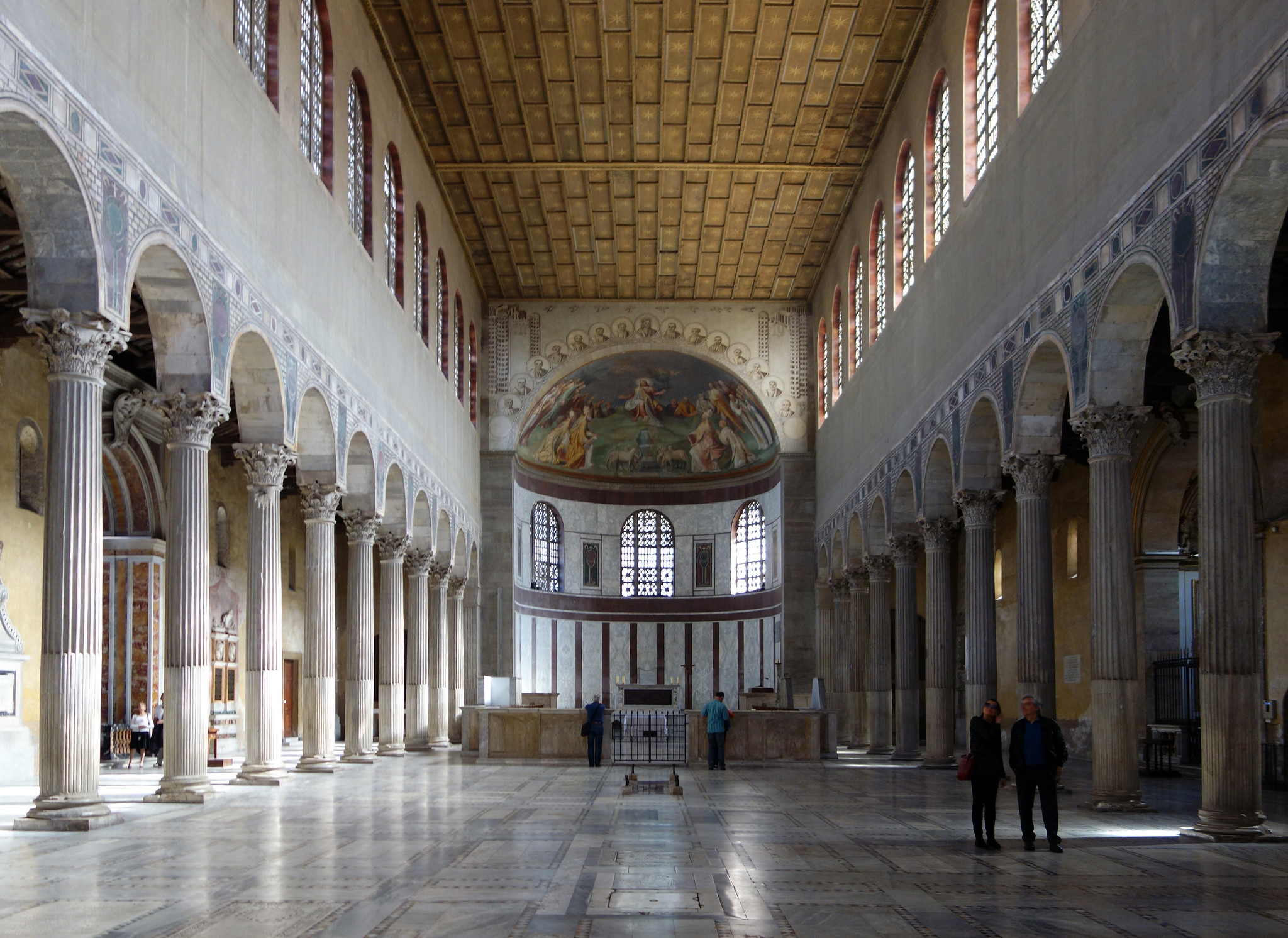

Coffered wooden ceilings
Spolia - take things from other places and repurpose it. Took columns from temple of JUno in Rome
Clerestory made of gipsome
Women would be in side aisle, men would be in front
Precessional space
Lots of glass and mosaics
Missing a transept
The Parting of Lot and Abraham

wall mosaic
located in the mauve of Santa Maria
Lot is Abraham’s nephew
Lot chooses to go to Sodom and Abraham goes to Canaan
Head Cluster - cluster of heads, a way of showing depth
Glance and Gesture - where a figure is looking and/or pointing to
Woman sacrificing at Alter

400 CE
Ivory
Early christian
Priestess who is performing the rights of Bacchus
Diptych - art work consisting of two pieces or panels that create a single piece of art together
Triptych - art work consisting of two pieces or panels that create a single piece of art together
Polyptych - art work consisting of many pieces or panels that create a single piece of art together
St. Michael the Archangel
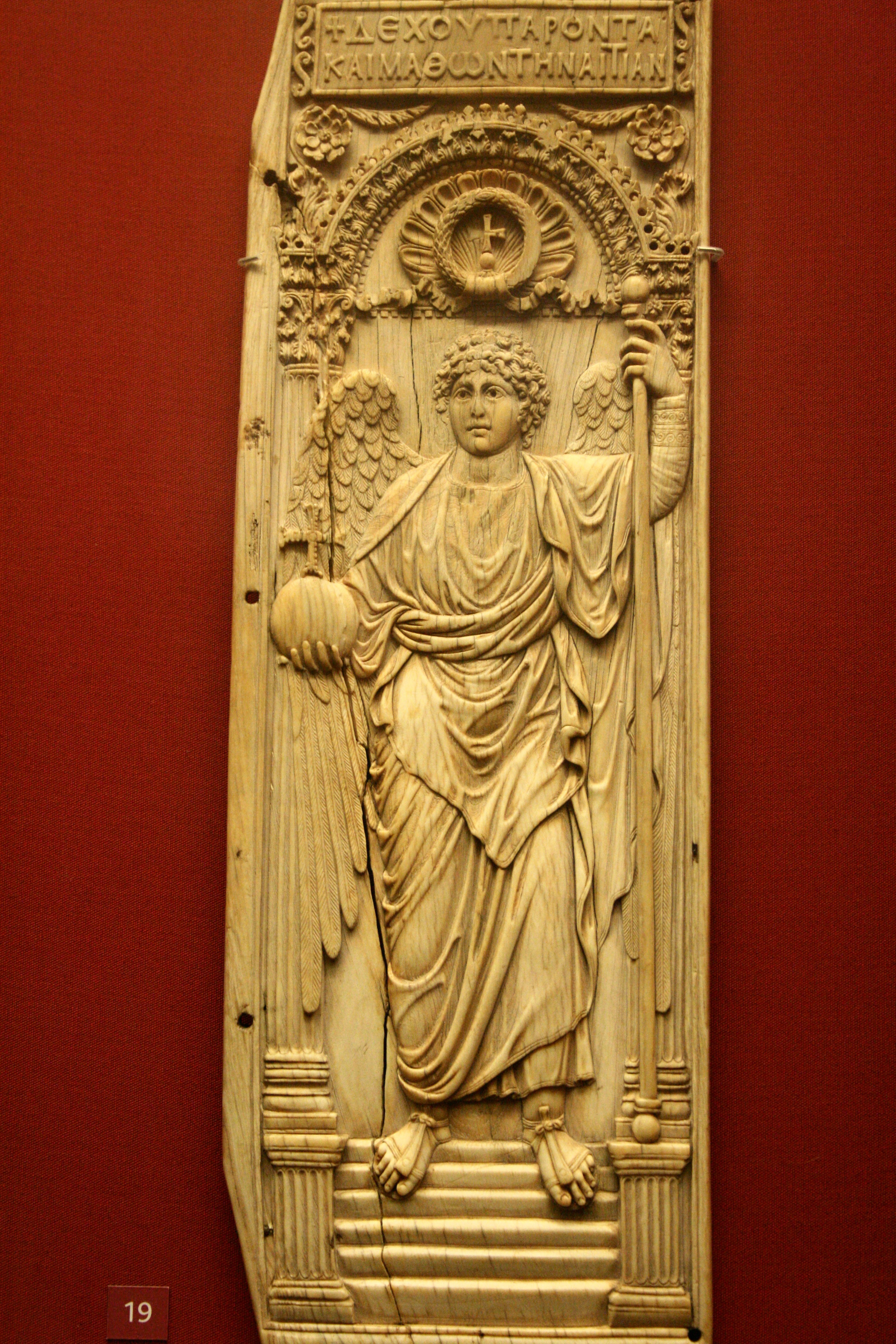

Large Byzantine panel
Ivory
6th century
Floating; goes against classical tradition of grounded figures
Loss of contrappasto, his foot is taking up three steps
Holds an orb with cross on top
Wet drapery and some classical calm
Lack of concern for natural representation
In an architcutral frame but his body doesn’t fit through it
One panel of a diptych
Illumination from the Vatican Vergil, “Old Farmer of Corycus”

Illuminated manuscripts would be on scrolls or codex (ancient manuscript, book form)
Pages made of vellum or parchment
Sacred texts were copied by literate scholars
Despite second commandment, illumination was needed to instruct the illiterate
From Vergil, Aenied
Content is Pagan
Style is pompeiian
Rebekah and Eliezer at the Well

Classic elements
Ties to paganism
Nude pagan woman
The town is small, but Rebekah is large
Linear drapery - Lines that show form, but doesn’t really show body
Head clusters within the camels
Continuos narrative
Rebekah is giving Eliezer water at the well
Abraham sends Eliezer to find a wife for his wife and Eliezer prays for Abraham to find a servant, poof, Rebekah arrives
Jacob Wrestling the Angel

Byzantine Era
Illuminated manuscript on purple vellum
From the early 6th century
Roman arches under the bridge where the water goes through
Shows Jacob leading his family across the bridge
At night, Jacob wrestles with an angel, “wrestling with faith.”
Shows the power of forgiveness'
U shape continuous narrative and includes a head cluster
Byzantine and First Golden Age
Ancient Byzantium, Eastern Roman Empire (The Middle Ages). Associated with Eastern orthodox churches, believes they are the “origin.” This is the mosaic era, had the central plan church, will flourish in Constantinople until 1453 (The Ottoman Turks come in). Focuses heavily on religion and removing themselves from Classical Rome. The First Golden Age (500-650 CE). Reign of Justinian the Great; major patron of the arts. Conquers Raveena, but rules over Constantinople.
Hagia Sophia/Santia Sophia
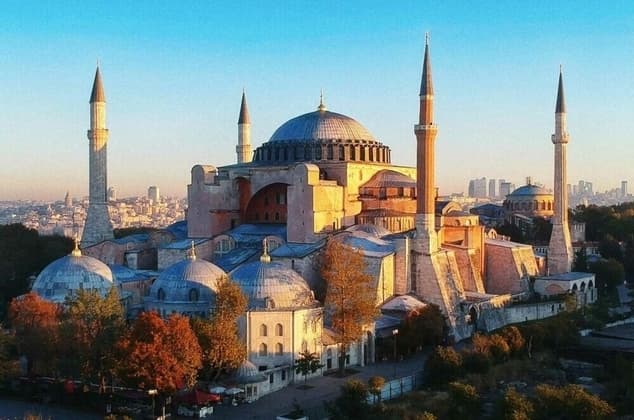

Islamic (Hagia) and Santia (Christian)
Former church turned mosque
532 and 537 CE
Centrally planned to be accommodating
Central dome placed on pendentives for structural support and light
270 ft tall, 240ft wide
Now in Istanbul as a museum
San Vitale Church

Octagon, with large windows and columns
Mosaics and colorful marble
526-547 CE
Apse like shapes
Brick, marble, and stone
Under Ostrogoths rule
Can’t see anything from the apses and nave
Emperor Justinian and his Attendants, San Vitale mosaic
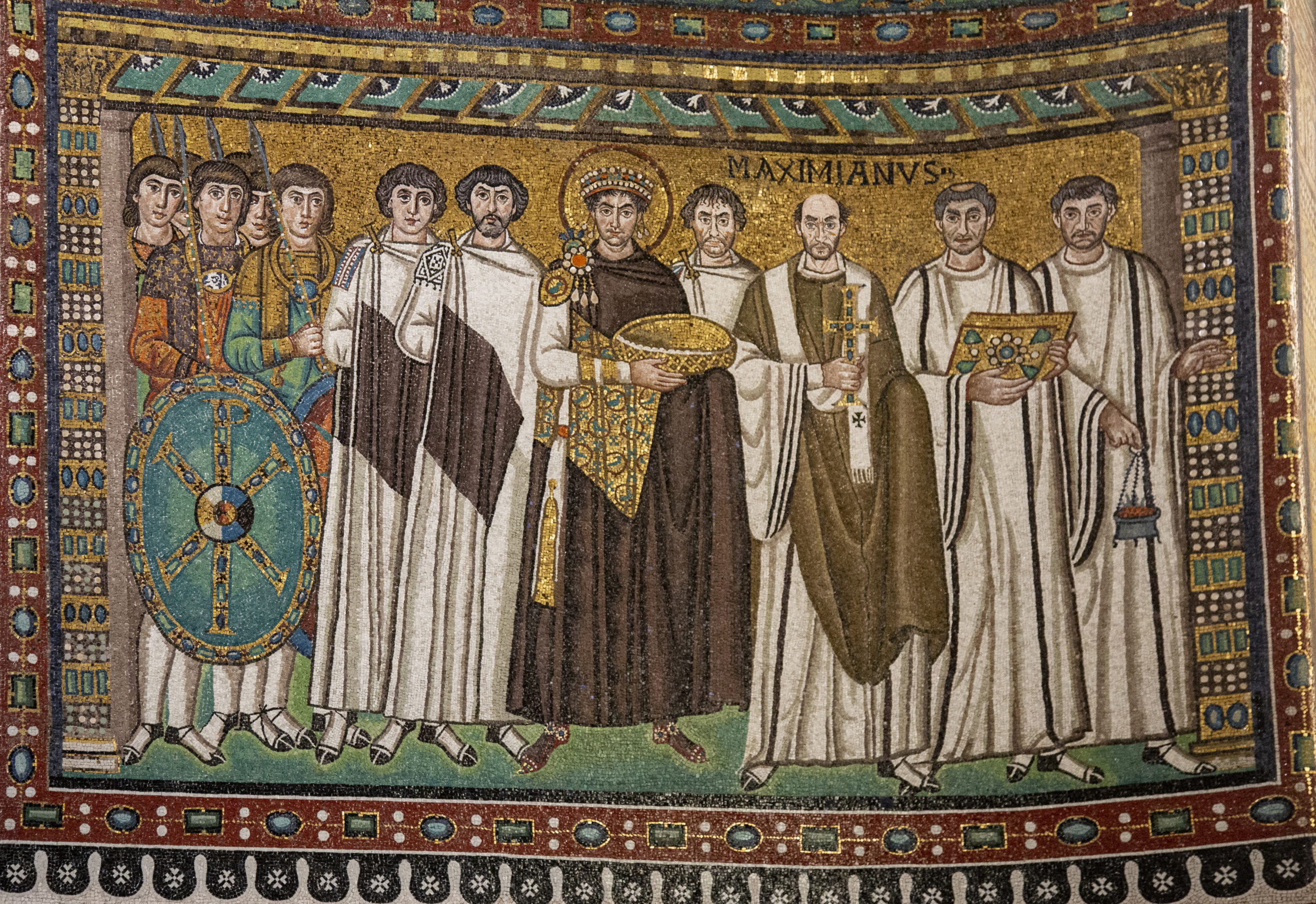

Halo around his head
Bread and wine
A lil jesus imagery lwky
Linear drapery
Head cluster with twelve people
Ballet feet
Empress Theodora and her Attendants

high class prostitute
Had a reputation in Constantinople, but pretty unknown for prostitute rep in Raveena
Holding wine cup
Mosaic of the St. Apollinaire
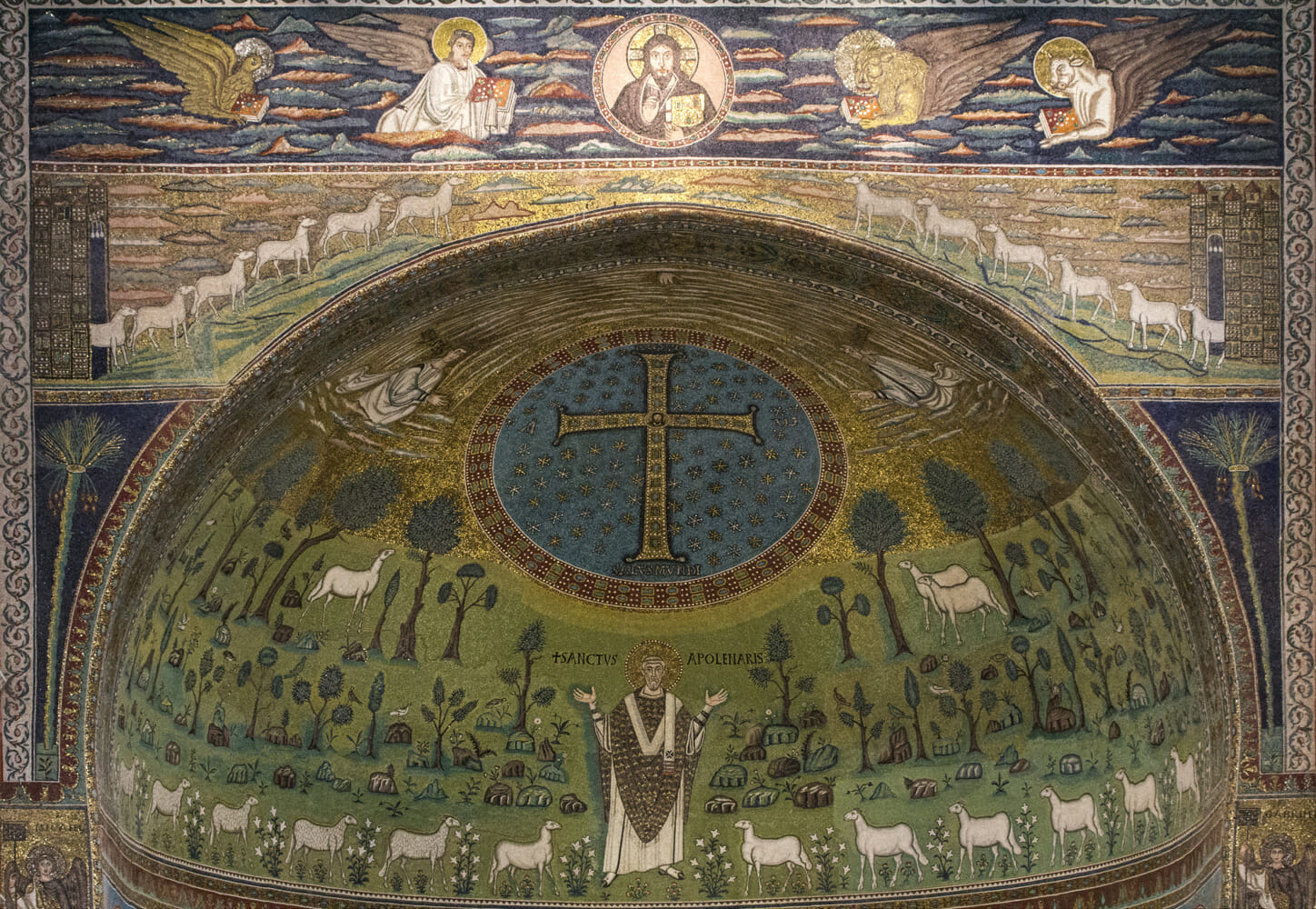

500 AD
In Apse, semi-circle dome
Lintel above it
large blue medallion represents Christ transfiguration
first bishop of Raveena
flat and paper doll like images
unrealistic landscaping
Moses and Elijah in the clouds, hand of God poking down.
Matthew, Mark, Luke, and John. ALOE. Four evangelists/gospel writers
Matthew = Angel
Mark = Lion
Luke = Ox
John - Eagle
Virgin (Theotokos) and Child Between St Theodore and St George
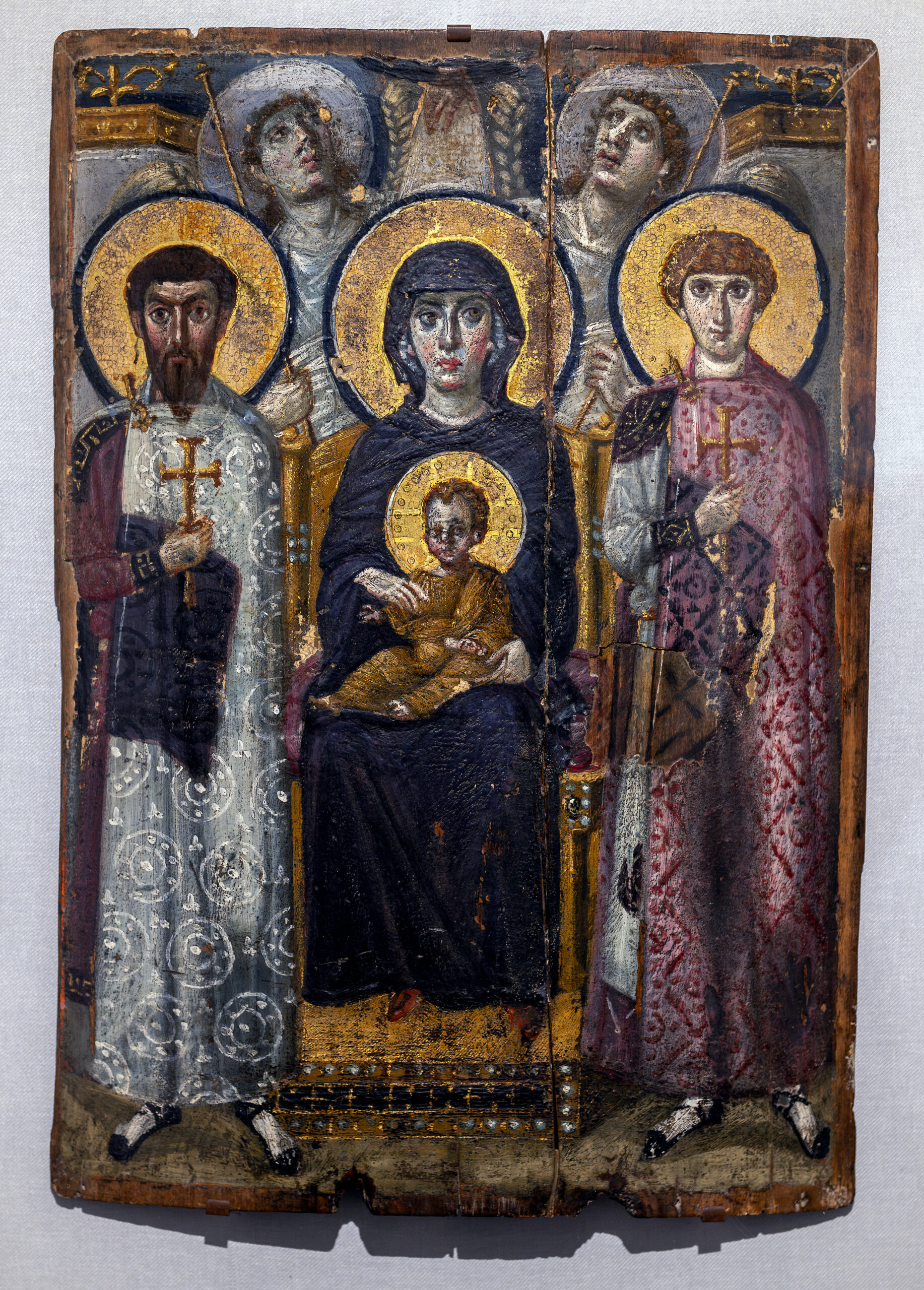

6th and 7th century
encaustic on wood
even on both sides
purple and gold = symbol of royalty
hands of God at top
Icon - small portable painting
Iconaclas - image destroyers
Iconaphiles - image lovers
Second Golden Age
Inconoclasts vs. Iconophiles, the iconophiles win. Religious victory. Turks come in
St Marks, Venice

Had most mosaics works until the 20th century, St. Louis Basilica
Cruciform plan
Patron Saint
Bell tower is by itself, not apart/in the church
Destroyed by fire
The Crucifixion, Church of the Dormition
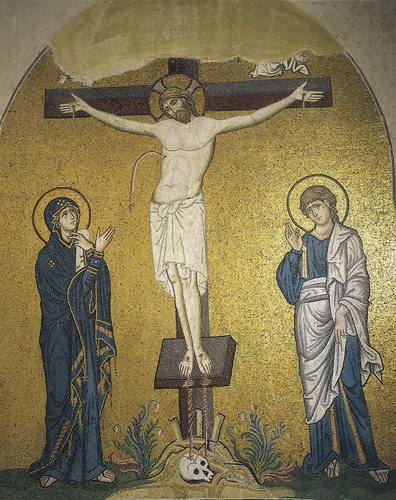
Mosaic
attempts to render bulk and body form in gold
“promise of a new life” “sacred/different” due to the gold coloring
nearly naked jesus: naked leans more towards shame, nudity is more so “praise” of the body
Eastern wall of the church
Jesus is a bit idealized/more muscular, taking some inspo from Greeks
Skull at bottom - Golgotha (Calvary), where Jesus was crucified and Adam was buried
Above was two angels holding a banner
Mary is always in blue which is representing the Queen of Heaven, she also has stars on her mantle - sometimes has red on to show Jesus’s death
Virgin of Compassion/The Vladimir Madonna

Pathos relief - the icon shows sadness because she is worried about Jesus’s future
Mary (blue & stars) and baby Jesus
Encaustic
Icons are like a talisman, Iconstasis (separates sanctuary from rest of church
Mary is foreshadowing
Byzantine faces: ¾ and elongated noses
Jesus looks like a little man, people struggling rendering babies
Cathedral of Saint Basil
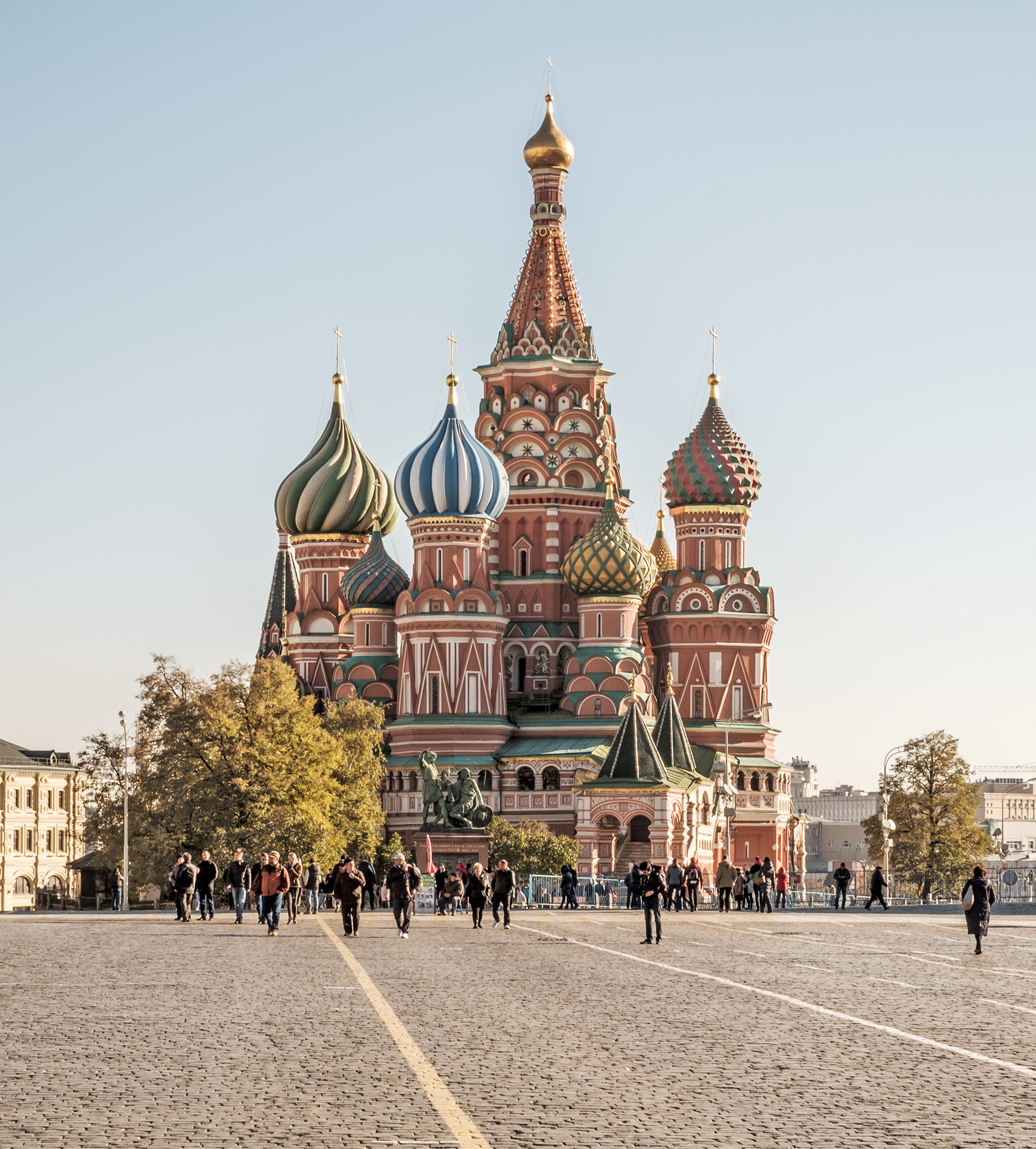

Commermerated the victory over the mongols
Patron was Ivan the Terrible (murdered his own son and blinded the builder so he could never build another building again)
Brick and painted onion dome (cupolas)
Kremlin is Russian for “fortress”
Meant to stand out
The Old Testament Trinity Prefiguring the Incarnation

tempera on wood
figures framed by halos and wings
¾ byzantine face
linear drapery, no body lines
Russian because of the vivid colors
No clear view where the head ends and neck begins