MRU - An introduction to externalities
private cost: the cost paid by the consumer or the producer
external cost: a cost paid by bystanders, by people other than the consumer or the producer
social cost: the cost to everyone, the private cost plus the external cost
externalities: external costs or external benefits
- costs or benefits that fall on bystanders
social surplus = consumer surplus + producer surplus + bystander's surplus
- when there are significant externalities, the market will not maximize social surplus
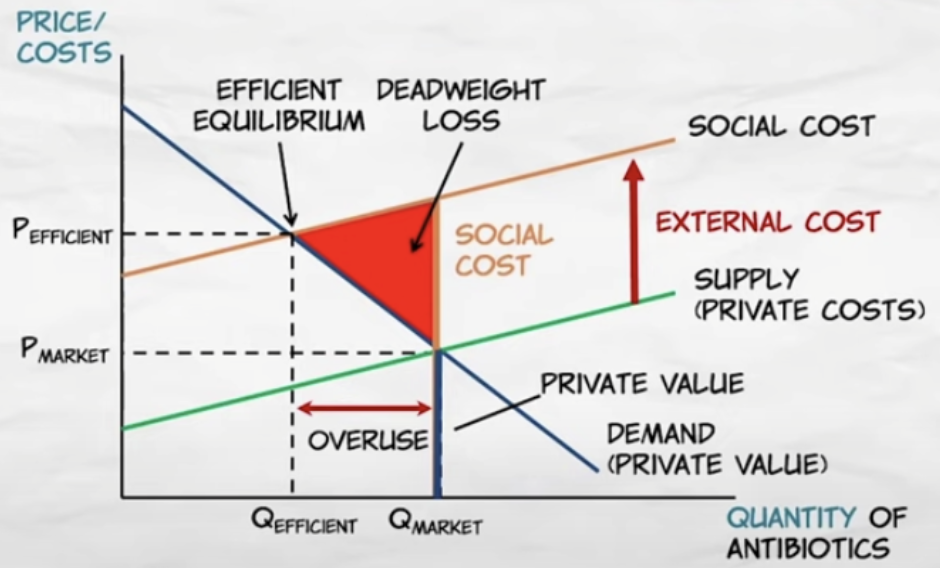
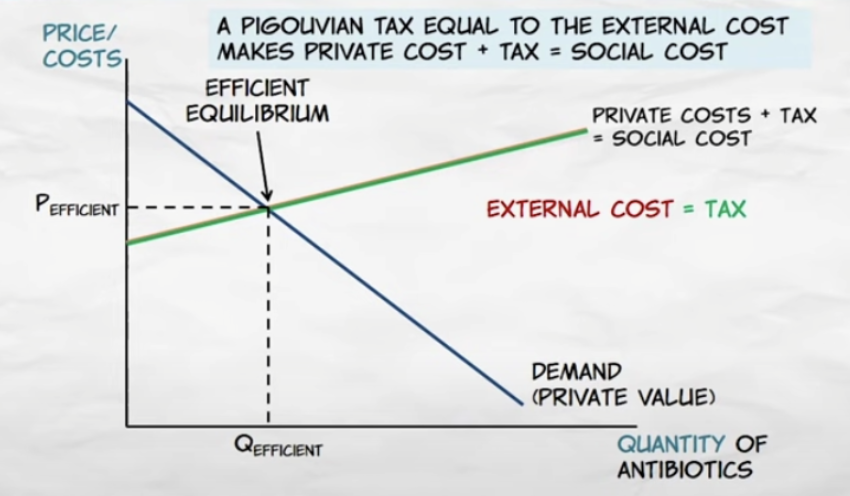
when there are external costs, output should be reduced to maximize social surplus
for determining the efficient level of output, who bears the cost is irrelevant
when other people bear some of the costs, the price is too low and antibiotic users purchase too many antibiotics
one of the solutions is
- Pigouvian tax: a tax on a good with external costs