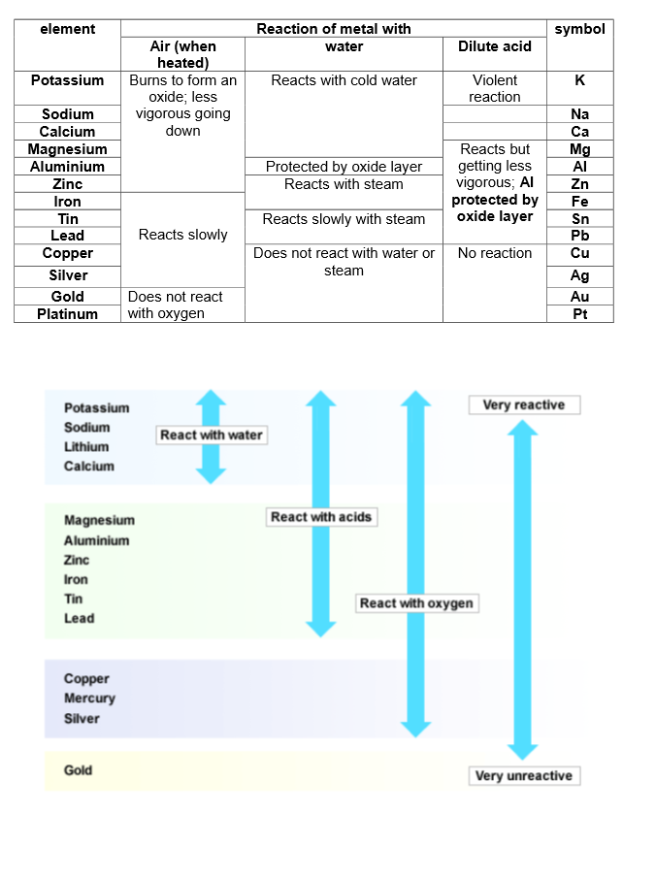
Metals of reactivity
Definitions:
Corrosion: The process by whihc the surface of most metals and alloys are attacked by Oxygen, water, acids and alkalis. Corrosion is a chemical reaction.
Tarnishing: The process by whihc most metals react slowly with Oxygen in the air to from a surface film of metal oxide (or in some cases metal sulphide)
Rusting: The formation of a loose flaky layer of hydrated iron (lll) oxide, on the surface of iron and steel. Rusting requires both water and Oxygen and is impossible if one of these 2 elements are not present.
Metals can be arranged in a metal reactivity series bases on the reaction of the metal and their compounds.
Reactions with oxygen:
Some metals react with oxygen in the air to form metal oxides.
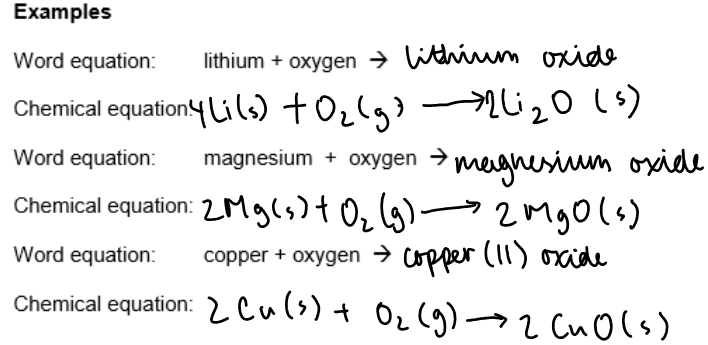
Why are potassium, sodium, lithium and barium stored under oil?
In order to prevent then from reacting with oxygen and water in the air.
Which metals do not react with oxygen?
Gold, platinum.
Metals form basic metal oxides whihc may dissolve in water tp form alkaline solutions; such as magnesium oxide dissolves in water to form a solution with a PH of 9.
Non-metals form acidic non-metal oxides whihc may dissolves in water to form acidic solutions; such as sulphur dioxide dissolves in water to form a solution with the PH of 2.
Reactions with water:
If metals react with water, they do so by displacing hydrogen as they are more reactive than hydrogen. The more readily they do this, the more reactive they are.
Reaction with cold water:
a. Group 1 - alkali metals:
Method:
A freshly cut piece pf metal is places in a trough of water. An indicator was added to the water when the reaction has ended.
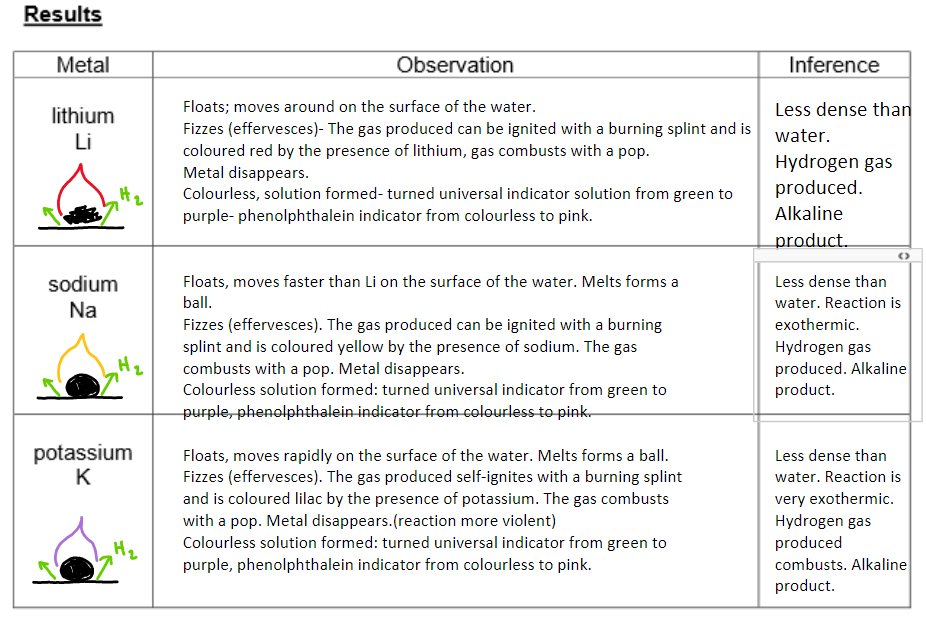
Conclusion:
Group 1 metals are called alkali metals because they react with water to form alkaline solutions.
The metal hydroxides formed dissolve in water, creating alkaline solutions with a pH greater than 12 (pH > 12).
All group 1 metals have similar chemical reactions due to having 1 electron in their outer shell.
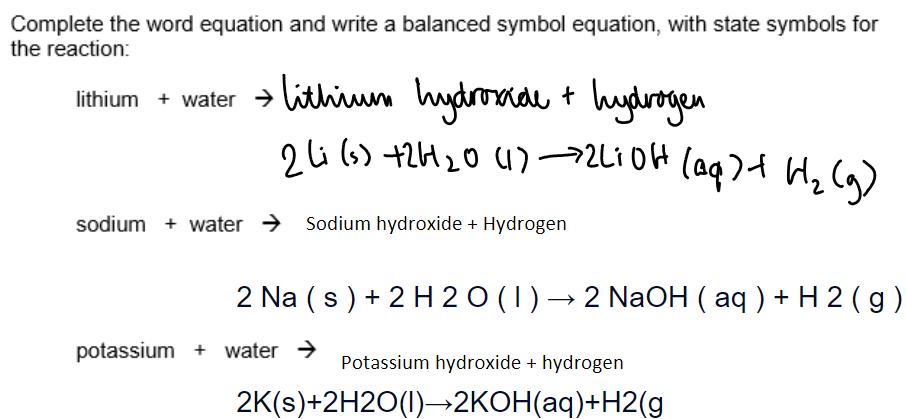
b. Group II - alkaline earth metals:
Magnesium reacting with cold water:
Method and results:
A piece of magnesium was placed in a beaker of water under an inverted funnel whihc had a test tube filled with water, placed over it. Any gas produced, was collected and tested for after 1 week.
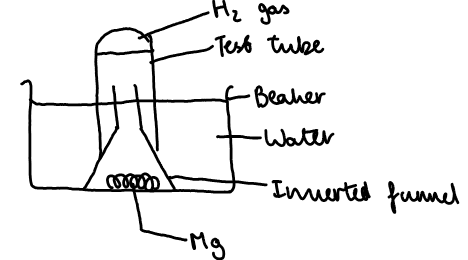
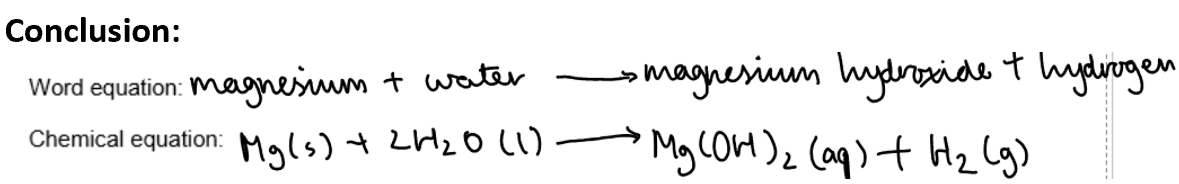
Calcium and barium reacting with cold water:
A small piece of calcium was places in a beaker under and upturned test tube of water and any gas produced is collect and tested for hydrogen. (goes out with a squeaky pop) Repeated with barium.
Results:
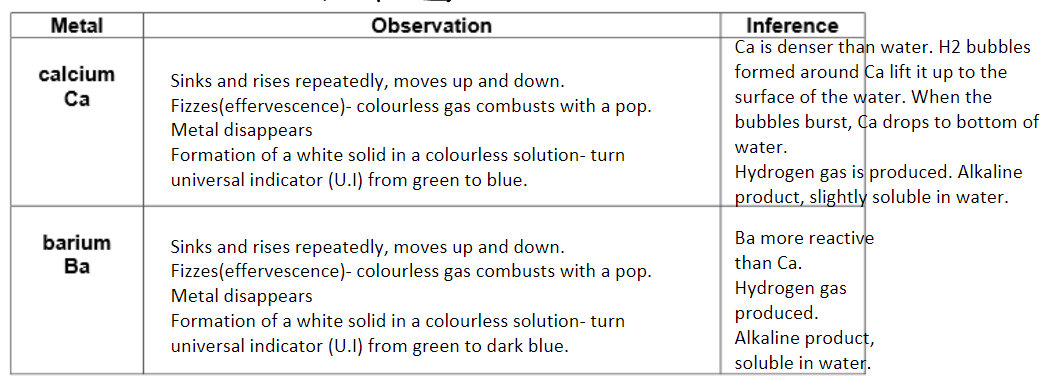
Conclusion:
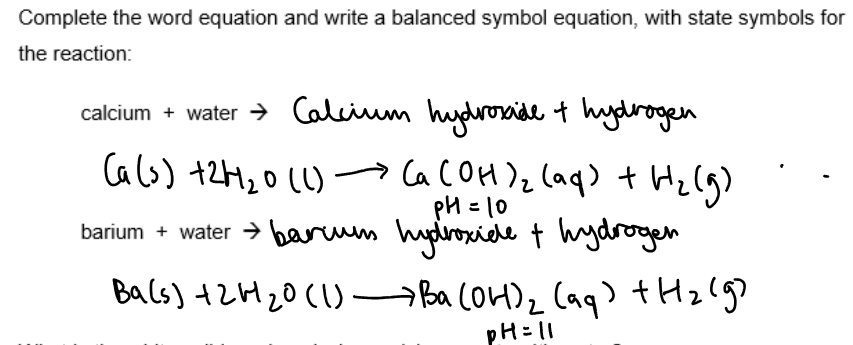
What is the white solid produced when calcium reacts with water?
Calcium hydroxide.
What is the Ph of the solution form when calcium reacts with water?
10.
Why is the solution alkaline?
Because of the hydroxide ions present.
Reaction with steam:
a. Reaction with magnesium with steam:
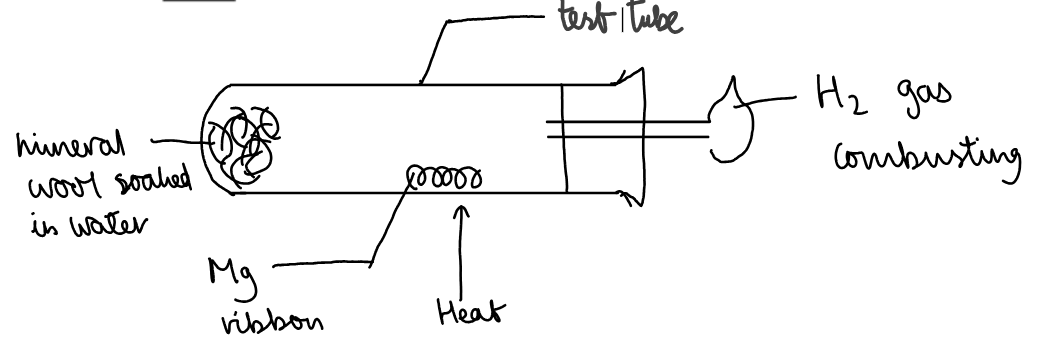
Results:
The magnesium ribbon burnt with a bright white flame. The colourless gas produced was ignited at the end of the delivery with a splint and combusted with a yellow flame. A white solid formed.
Conclusion:
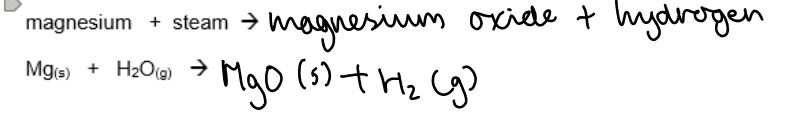
b. Reaction of Zinc with steam:
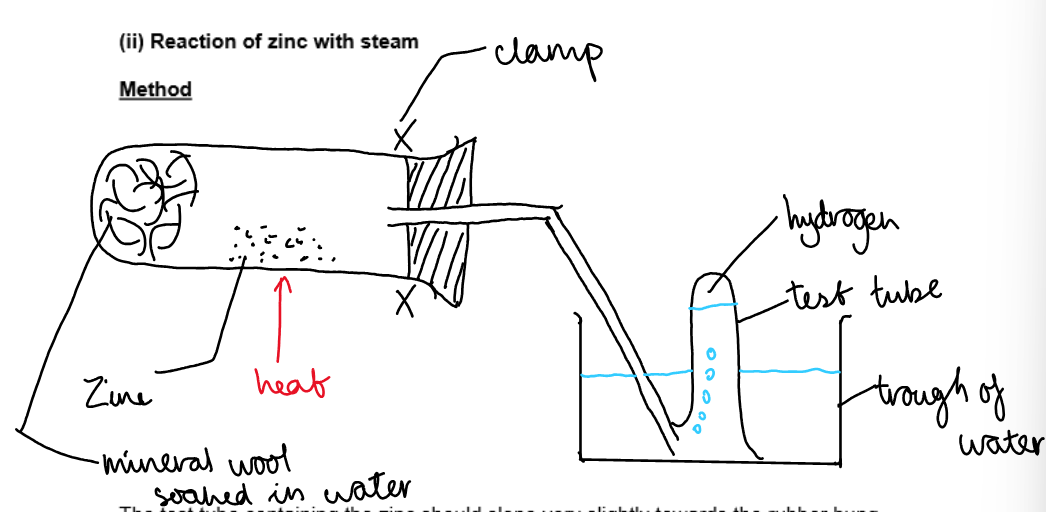
The test tube containing the zinc should slope very slightly towards the rubber bung. Why?
In order to prevent water that is formed from the condensation of steam running back into the hot test tube and cracking it.
The first few bubbles were allowed to escape, why?
Because it would not have been pure hydrogen.
Mention a safety precaution:
Before heating is stopped, the apparatus must be lifted out of the water to prevent suck-back.
Results:
A colourless gas was produced whihc combusted with a squeaky pop. A yellow solid was formed whihc turned white on cooling.
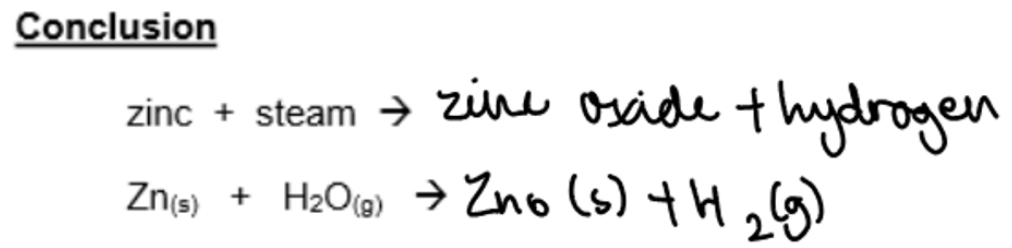
C. Reactions with steam:
Method: same method as reaction of zinc with steam.
Results: a colourless gas was produced which combusted with a squeaky pop. Iron glowed red hot.
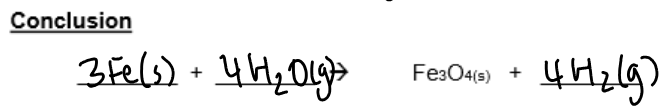
Name 2 metals that do not react with water/steam:
Copper, silver, gold, platinum.
Give an example to illustrate this lack of reactivity:
Copper being used in domestic hot water pipes as it doesn't react.
Write a general equation for the reaction of a metal with steam:

Reactions with dilute HCL and HSO:
Metals can also displace hydrogen from an acid; the more readily they do this, the more reactive they are. It is easier to displace hydrogen from an acid than from water.
Method: A small piece of metal was placed in 2cm cubed of dilute acid and any gas produced is collected and tested.
Results:
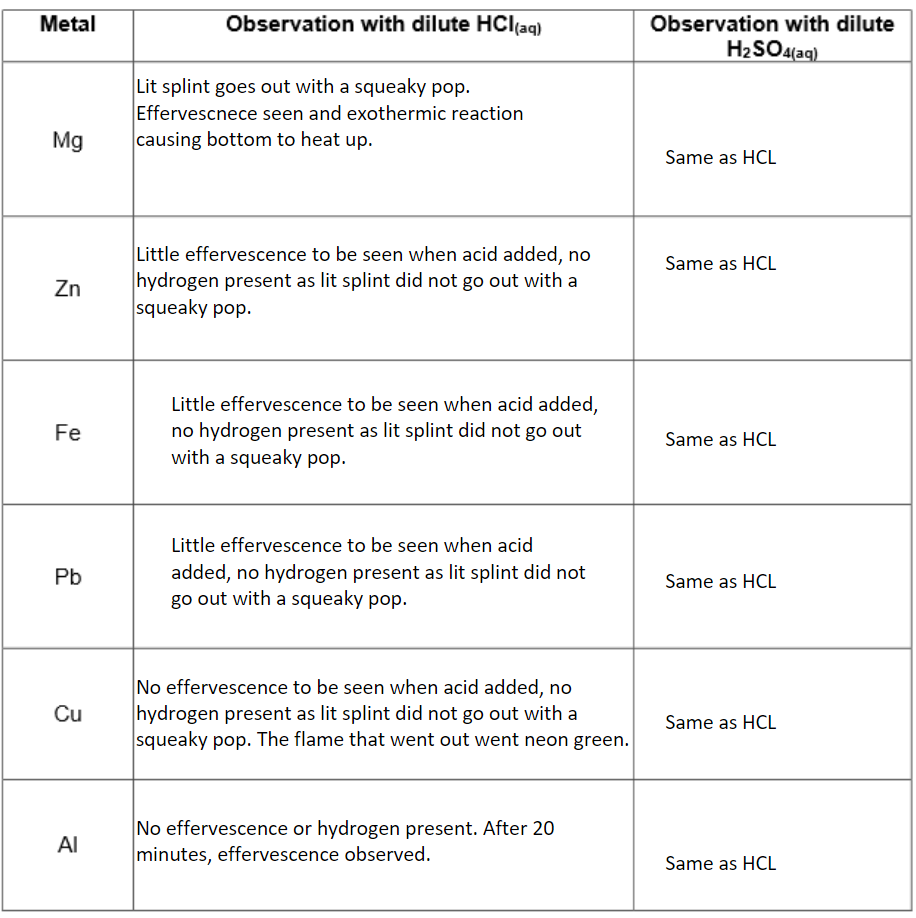
Conclusion:
Which metals displace hydrogen from dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid?
Copper.
Which metals do not react with dilute hydrochloric acid and dilute sulphuric acid?
Magnesium, zinc, iron, lead, copper.
Complete the following general equations:
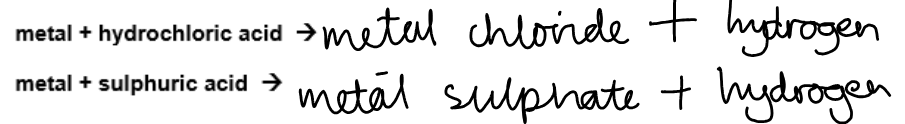
Write a balanced symbol equation with state symbols for each reaction:
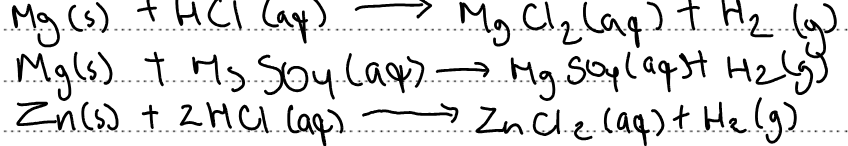
Metal displacement reactions:
Method:
Pour 2cm cubed of magnesium sulphate solution into 4 test tubes in a test tube rack.
Add a sample of each metal listed in the table below to separate test tubes of magnesium sulphate solution
Leave the test tubes for a few minutes. Look at the surface of the metal to see if there is a deposit or a colour change in the solution.
Clean the test tubes and repeat steps 2 and 3 using each of the other solutions in turn.
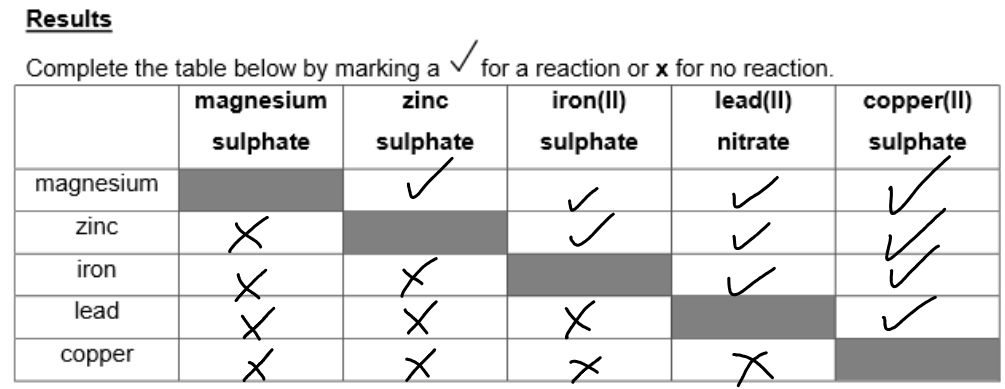
Conclusion:
A more reactive metal will displace a less reactive metal from a solution of its ions.
Which metals are displaced by magnesium?
Z, I, L, C.
Which metals are displaced by zinc?
I, L, C.
Which metals are displaced by lead?
C.
Which metals are displaced by copper?
None.
Write balanced symbol equations with state symbols for the reactions that happen.
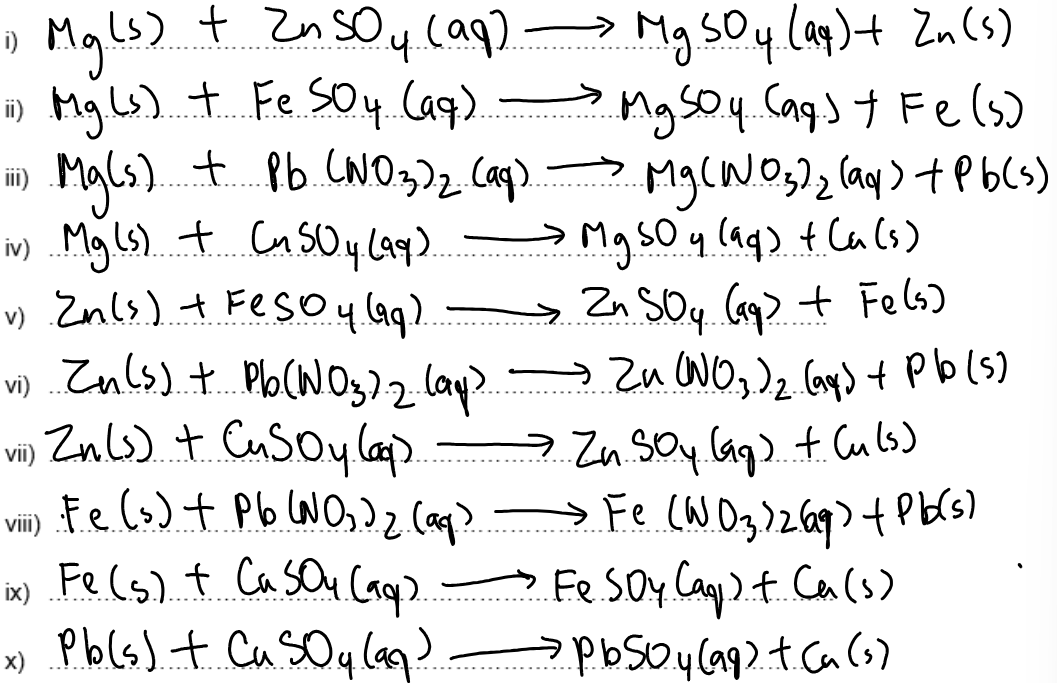
Complete the following chemical equations and suggest what observations you would make during these reactions.

Observations: Colourless solutions turn blue and silver fur forms over a pink brown solid.
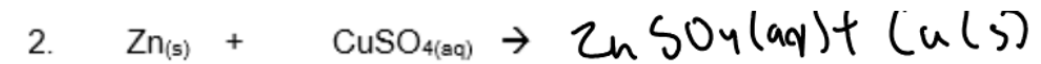
Observations: Blue colour of solution fades to colourless. Pink brown solid forms over grey solid.
Aluminium:
Why Aluminium Appears Unreactive but Is Actually Reactive:
Aluminium is above zinc in the reactivity series but seems unreactive due to a protective aluminium oxide layer.
This layer blocks oxygen, water, and metal ions from reaching the metal — known as the passive layer effect.
If scratched off, aluminium reacts quickly.
The oxide layer is basic and reacts with acids in a neutralisation reaction, eventually exposing the reactive aluminium.
Why You Shouldn’t Cook with Fruit Juices in Aluminium Pans:
Acids in fruit juice react with and remove the oxide layer.
Exposed aluminium then reacts with acid and water, which can be unsafe.
Effect of Mercury Chloride on Aluminium:
Mercury chloride removes the oxide layer.
Exposed aluminium reacts with air and water vapour, forming a white ‘moss’ of aluminium oxide and hydroxide.
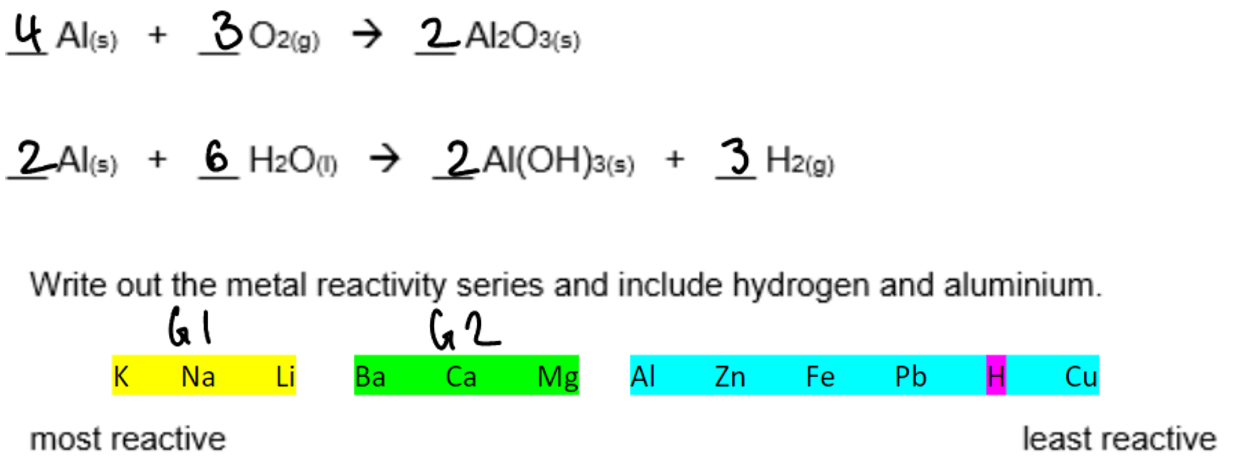
The reactivity series: VERY IMPORTANT!

Identification of an unknown metal:
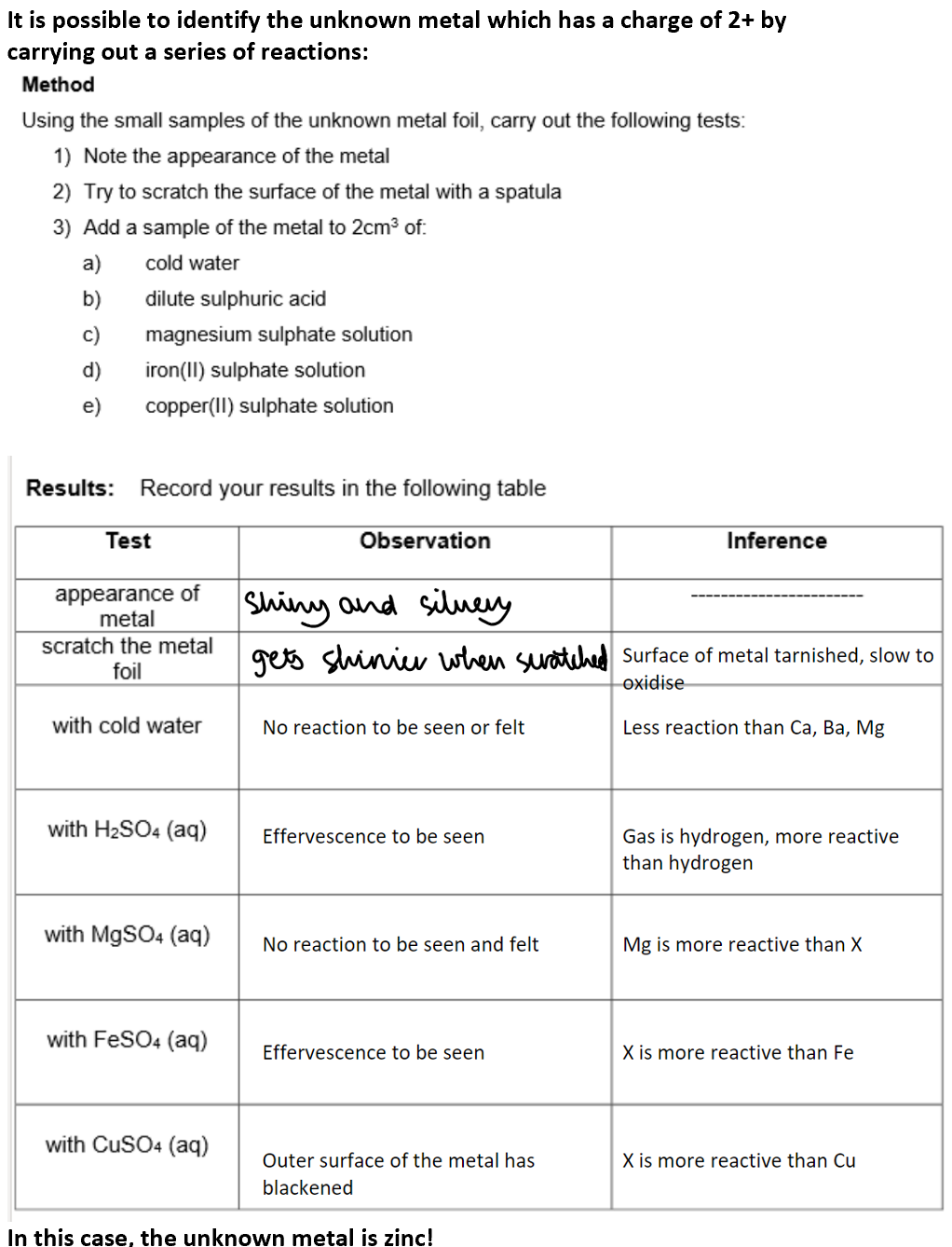
Summary: