Mitosis and Meiosis
Vocabulary:
Cell: Smallest biological unit that exhibits the properties of life, all organisms have at least 1. Highly diverse, can divide to make replica. All have a plasma membrane, DNA, and ribosomes
Cell cycle: The life of a cell from the time it is formed until cell division into daughter cells
Daughter cell: The replica of a parent cell, two of these
Parent cell: Produces two daughter cells during replication
Mitosis: The most common form of unicellular division, asexual reproduction in prokaryotes and done for growth/development/renewal in eukaryotes. Makes identical copies of DNA, with the same number of chromosomes in daughter cells
Meiosis: Done for sexual reproduction in eukaryotes, produces gametes/spores. Daughter cells have half the genetic information as the parent cells, genetically different, has 2 rounds of division, reduction and equational
Gamete: Sex cell
Mitochondria: An organelle that contains its own genetic information
Genome: The complete set of genetic material in a cell
Chromatin: The form DNA takes during nondivisional stages, appear as thread-like fibers. Chromosomes have uncoiled and diffused into networks within the nucleus
Chromosome: The form DNA takes during cell division, a higher order structure that appears like a condensed X. One carries several hundred to a few thousand genes. Allow for DNA to be accurately copied
Histone Octamer: A set of 8 proteins that support chromatin structure, function as a unit. Made of 8 positively charged histones which bond to negatively charged DNA
Nucleosome: Formed by DNA entirely wrapping around a histone octamer, coils to form chromatin
Centrioles: Located in the cytoplasm of the centrosome in animal cells, spindle fibers used for the movement of chromosomes during cell division
Centrosome: Hold centrioles in animal cells
Binary fission: Asexual reproduction in some prokaryotes, a cell divides into two identical cells like with mitosis but doesn’t always use the same mechanisms as it
Diploid: A ploidy level of 2 (2n), two sets of chromosomes, with one inherited from each parent
Haploid: A ploidy level of 1 (1n), one set of chromosomes
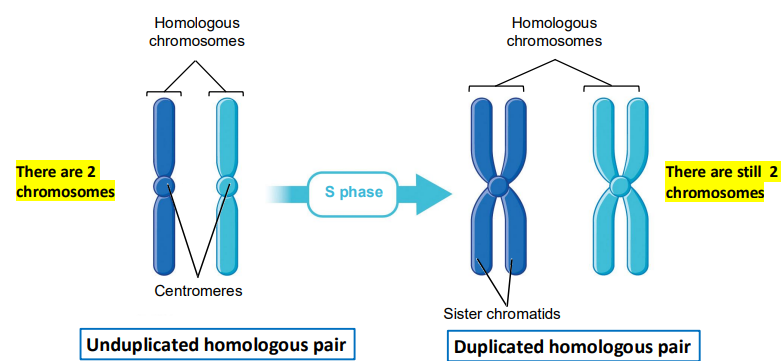
Homologous pairs: Exist for 2n organisms, 2 sets of the same chromosomal information. Have the same length, centromere position, and order or genes. Typically one from each parent. Not identical to one another, but carry genes for the same characteristic
Karyotyping: The process of pairing and ordering all chromosomes of an organism, thus providing a genome-wide snapshot of an individual’s chromosomes, can identify genetic problems as the cause of a disorder or disease
Autosomes: Chromosomes that are not involved in sexual reproduction, 1-22 in humans
Allosomes: Sex chromosomes, 23rd in humans. Can be X or Y in humans, with only portions being homologous. Play a role in sex determination
Centromere: A constricted region on a chromosome, establishes the appearance of one. This is where microtubules of the spindle attach
Metacentric: Describes a centromere in the middle
Submetacentric: Describes a centromere partially towards one end
Acrocentric: Describes a centromere very close to an end
Telocentric: Describes a centromere at the end
Q arm: The long armed sister chromatid
P arm: The short armed sister chromatid
Allele: A single form of one gene, one on each homologous chromosome
Locus: Where a given gene is located on a chromosome
Biparental inheritance: Inheritance from two parents, each have influence
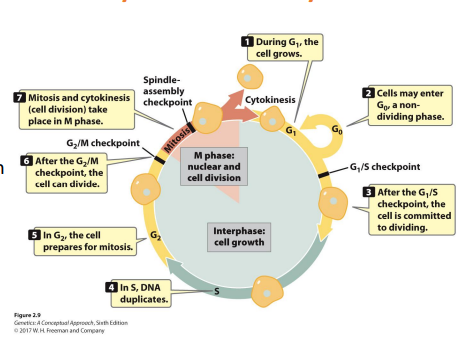
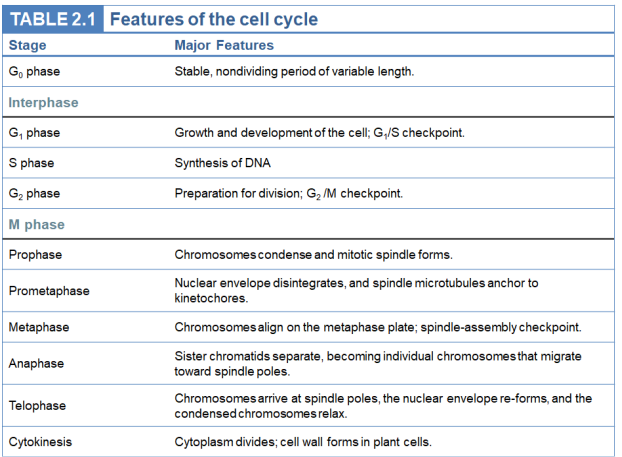
Interphase: Part of the cell cycle, extended, between cell divisions and includes DNA synthesis and chromosome replication. Subdivided into S, G1 and G2 phases
S phase: Part of interphase, when DNA is synthesized
M phase: The part of the cell cycle where the cell divides
Cytokinesis: Division of cytoplasm
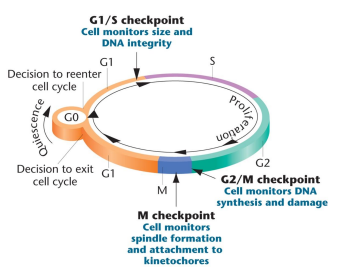
G0: A point in the G1 phase where cells withdraw from the cell cycle and enter a nondividing but metabolically active state
Phase checkpoints: Exist to check and regulate cell cycling, key transition points
G1 Checkpoint: After this, the cell is committed to dividing
G1 phase: Part of the cell cycle when the cell carries out whatever it is specialized to do functionally
G2 phase: Part of the cell cycle, when it makes new organelles, gains nutrients, prepares for mitosis, and replicates centrosomes. The nuclear envelope is still present, and chromosomes aren’t condensed. Has 2 centrosomes
Sister chromatid: An identical copy formed by the DNA replication of a chromosome, two copies are joined together by a centromere, can be one half of a duplicated chromosome
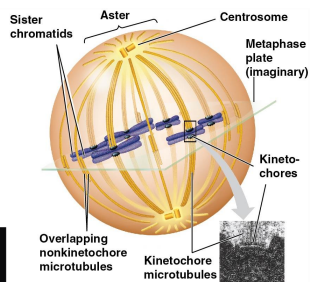
Kinetochore: During cell division, help attach the microtubules of the spindle to the centromere. A protein complex associated with the centromeres, the point of attachment
Cohesins: Proteins that attach sister chromatids along their arms
Zygote: A fertilized egg
Karyokinesis: The partitioning of genetic material to daughter cells
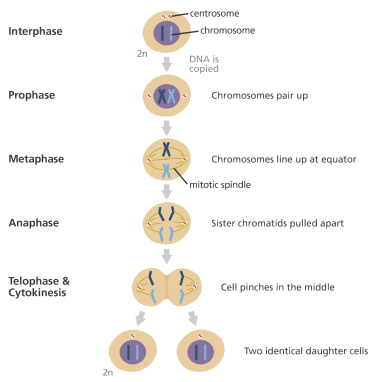
Prophase: Part of mitosis where chromosomes condense and mitotic spindles assemble. Chromatin begins to condense into sister chromatids, centrioles moved to opposite poles, spindle networks begin to form, the nuclear envelope begins to break down
Prometaphase: Part of mitosis, chromosome movement. They continue to condense, the nuclear envelope dissolves and spindles attach to the chromosome. Centrioles reach opposite poles and microtubules span across the cell. By the end of this phase, asters extend and make contact with the plasma membrane
Mitotic spindle: An assembly of microtubules organized around the centrosome, assembly begins at the centrosome and extends towards the cell’s midplane
Kinetochore microtubules: Attach to kinetochores during prometaphase, have one end near the centrosome region and the other end anchored to the kinetochore
Metaphase plate: Divides the cell into two parts, where chromosomes land between two poles when guided by spindles
Aster: A radial array of short microtubules that extends from each centrosome
Metaphase: Part of mitosis where chromosomes line up along the metaphase plate, centrosomes are at opposite poles and sister chromatids ate attached at the kinetochore to a spindle, they are aligned at the equatorial plane by the spindle fibers
Separase: An enzyme that degrades cohesin
Shugoshin: A protein that protects cohesin from separase at the centromere
Anaphase: The part of mitosis where sister chromatids separate from each other, migrating to opposite poles as fibers shorten through the use of motor proteins and ATP. Cohesion proteins are cleaved by separase, disjunction occurs. Cytokinesis may begin but not finish here
Disjunction: Centromeres separate and sister chromatids are pulled apart
Telophase: Part of mitosis where the nuclear membrane reforms and chromosomes unwind to their interphase state
Daughter nuclei: Where DNA is stored in the new cells after mitosis, this region begins to form as the nuclear membrane reforms and chromosomes relax during telophase
Cleavage furrow: Created by animal cells by actin fibers contracting to the center, this region pinches the cell into two daughter cells
Cell plate: Formed in plant cells during mitosis by fusing vesicles, will split parent cell into two daughter cells
Cell control system: Dictates sequential events of the cell cycle, regulated internally and externally, consists of various checkpoints. Uses cyclins (cdc) and cyclin dependent kinases (cdk)
Cell cycle checkpoints: G1/S, G2/M, and M. Where the cell monitors internal/external signals as well as checking mitosis for errors, where the cell decided whether to proceed with division
CDKs: Proteins that regulate the synthesis are destruction of cyclin proteins, which are key in checkpoints for the cell
Cyclin: Proteins that regulate the cell cycle, bind to kinases to activate them at appropriate times in the cell cycle
CDC mutations: Errors in cell replication, this led to the discovery of the checkpoints
Kinase: A kind of enzyme that adds a phosphate, used in energy transfer and cell cycle regulation
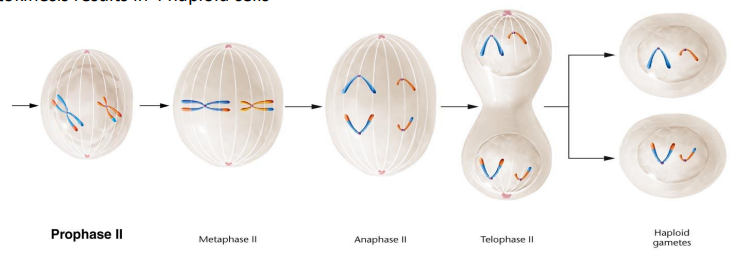
Meiosis I: General stage of meiosis where homologous chromosomes separate, brings the ploidy number down, results in 2 daughter cells
Meiosis II: General stage of meiosis where sister chromatids separate, ploidy number doesn’t change, results in 4 total daughter cells
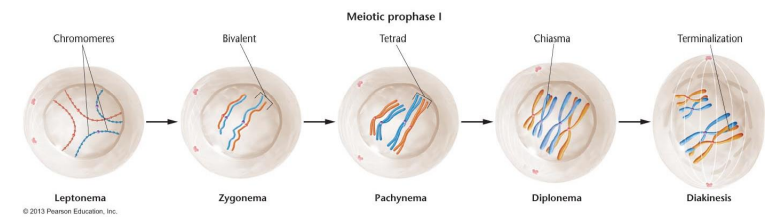
Bivalent: Refers to the synapsed homologous chromosomes, typically earlier in the process before all 4 chromatids are visible
Tetrad: Homologous chromosomes that have replicated and are synapses, has 4 chromatids
Dyad: One chromosome that consists of 2 sister chromatids, present in the products of meiosis I
Monads: One chromosome after meiosis II, sister chromatids are separated at the centromere, each sister chromatid is this
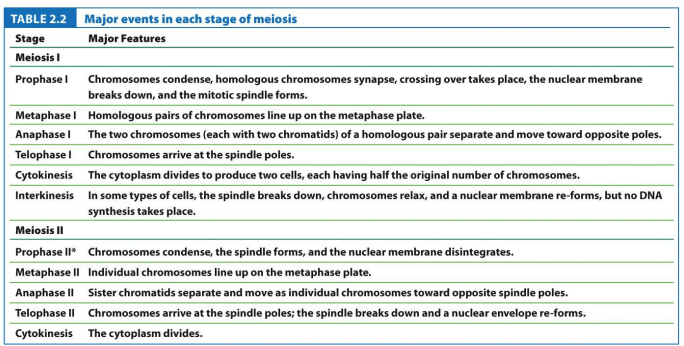
Prophase I: Part of meiosis, has 5 substages of leptonema, zygonema, pachynema, diplonema, and diakinesis. After this stage each tetrad is present at the equatorial plate
Leptonema: Part of prophase I, chromosomes appear as long single threads, unassociated with one another
Zygonema: Homologous chromosomes pair up with one another and match genes, forming bivalents
Synapsis: The pairing of matched chromosomes in zygonema
Pachynema: Part of prophase I, where each bivalent becomes shorter and thicker and splits into two sister chromatids (tetrad) except at the centromere, where crossing over occurs
Crossing over: The exchange of genetic material between non-sister chromatids during the synapsis and tetrad formation. Source of major genetic diversity
Diplonema: Part of prophase I, within tetrads a pair is relaxed and they start to move apart
Chiasma: Where chromatids are still intertwined, physical evidence of crossing over
Diakinesis: Part of prophase I, where the nucleus and nuclear envelope break down and centromeres attach to spindle fibers
Metaphase I: Part of meiosis I, where independent assortment occurs and where tetrads align on the metaphase plate
Independent assortment: The orientation of homologous pairs to the poles is random, source of genetic diversity, has 2^chromosomes possibilities
Terminal chiasmata: A major factor in holding non-sister chromatids together at the metaphase plate
Anaphase I: Part of meiosis I, cohesin is degraded between sister chromatids (but not at the centromere), homologous chromosomes undergo disjunction, effectively reducing the number of chromosomes in half
Nondisjunction: An error in anaphase I, where a gamete way have an abnormal number of chromosomes
Telophase I: Part of meiosis I, where cytokinesis occurs and results in 2 haploid daughter cells. The nuclear membrane reforms and the nuclei enter interphase
Random fertilization: Increases genetic diversity, any two gametes from a given set of parents can come together
Meiosis II: General stage of meiosis equational to mitosis, where sister chromatids from a dyad are separated to opposite poles, resulting in 4 total daughter cells with a haploid number, one member of each homologous chromosome
Telophase II: Part of meiosis II, where one member of each pair of homologous chromosomes is present at each pole, monad chromosomes. Cytokinesis occurs and forms 4 total haploid cells
Gametogenesis: Varies between females and males, generates haploid gametes
Spermatogenesis: Gametogenesis in males, done in testes and forms sperm. Yields 4 viable gametes, starts during puberty
Oogenesis: Gametogenesis in females, done in the ovary and forms eggs. Begins in utero, restarts at puberty and continues through menopause. Only yields 1 ovum, 3 polar bodies are discarded, this is because the daughter cells receive equal genetic material, but not equal cytoplasm
Primary polar body: The daughter cell that in oogenesis receives cytoplasm, undergoes meiosis I and II, then develops into an ovum
Fungi life cycle: Haploid vegetative cells arise via meiosis, proliferate via mitotic cell division
Plant life cycle: Alternates between haploid and diploid, sporophyte stage is 2n, gametophyte is 1n, “alternation of generations”
For humans, somatic cells are formed via mitosis, and gametes via meiosis
When arranging a karyotype, the largest chromosome is given the number 1, second largest 2, and so on with the last number being sex chromosomes. The short arm of a chromosome is on top, and the long on the bottom
Chromosomes are made up of 2 chromatids joined at the centromere, while chromatids separate from each other during mitosis to form two new chromosomes
During anaphase, there are nonkinetochore microtubules that are responsible for elongating the cell. They overlap extensively and push against each other