Unit 3A The Nursing Process
Problem Solving
Identify the problem
Look for causes
Identify possible methods to solve (Plan)
Consider each
a. Advantages / disadvantages
Select
Carry out the plan (implement)
Consider the effectiveness or the ineffectiveness; revise as needed (evaluate)
ADPIE:
Assessment
Diagnosing
Planning
Intervention
Evaluation
Nursing Judgment
Critical Thinking
Clinical Reasoning
Nursing Judgment
Integration of best evidence into practice
Don’t take data for face value: investigate deeper, reason through data, and develop inferences.
Nursing Process (Methodical Process)
“problem-solving, critical thinking approach to patient care” or “solving problems in a systematic, patient-centered way”
Collecting data- Assessment — clutter data — Assessment
Diagnosing (problem identification) — Always based on Assessment
Planning
Goal setting (planning care) — Develop a plan for the best outcome
Planning interventions to achieve goal (must anticipate what will happen)
Implementing the planned interventions — Will change a patients outcome
Evaluating the effectiveness of the interventions to help achieve the goal- “Did our actions work”?
Characteristics of Nursing Process
Core and essence of nursing
Patient-centered, humanistic, holistic
Collaborative
Structured, yet flexible; useful in any setting
Organized, systematic, deliberate — Fluid and makes sense
Continuous
Dynamic
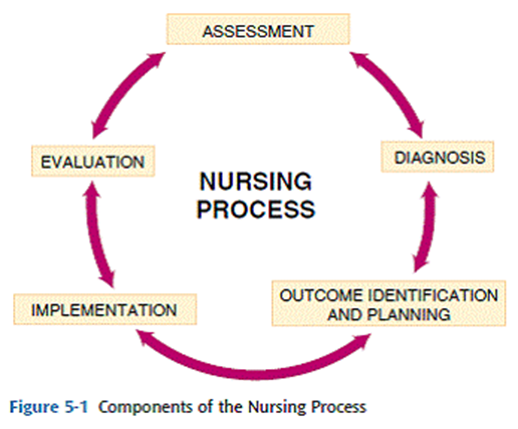
The steps are cyclical and interrelated: A constant cycle of evaluating and reassessing, modify the plan because the nursing process is always changing
Diagnosis may be actual or at risk for (potential diagnosis)
Ex; risk for falls
Collecting Data
Types
Subjective (statement)- Something that the patients can feel
Ex; patient is nervous
Ex; patient states they are in pain
Objective- What we can see
Ex; patient bp is 120/80
Ex; patient has a 4×6 cm lesion
Cues- A clear fact observable directly/verifying
Ex; patient is receiving O2 via nasal cannula
Ex; patient’s pulse is 102, regular, and bounding
Inferences- A small “hop” (assumption) conclusion
Ex; patient is in pain
Ex; patient’s family is aggravating
Three Steps of the nursing process:
Observing
Interviewing
Assessing
Assessment will never change a patient’s outcome
Sources
Patient (primary source)
Documents (secondary)
Chart/EMR (Electronic Medical/Health Record)
H&P (Medical History & Physical)
Admission Nursing Assessment
PCP orders (Primary care provider)
Progress Notes
Diagnostic test results
MAR (Medication Administration Records)
Concept cap/Kardex
Family and Interdisciplinary team members
Diagnosing- (Analyzing)
Analyze Data
Compare to standard- Comparing the data to the standard
Cluster using framework (Gordon’s Functional Health Patterns)
Formulate Nursing Diagnoses
Diagnostic labels based on “defining characters” (if actual diagnosis) — Defining characteristics that can lead to the problem
Ex; Activity Intolerance
R/T: compromised O2 supply
Secondary to: CHF (cognitive heart failure)- Underlying cause
Etiology based on “Related (or contributing factors)
Identify Nursing Diagnosis to act upon
Functional Health Pattern
Health perception-Health Management
Nutritional — Metabolic
Elimination
Activity — Exercise
Sleep — Rest
Cognitive — Perceptual
Self-Perception — Self Concept
Role — Relationship
Sexuality — Reproductive
Coping — Stress Tolerance
Value — Belief
These are Gordon’s Functional Health Patterns (Carpenito Nursing Handbook)- Used too organize Nursing Diagnosis
Nursing Interventions: “Are evidence based”
Planning / Implementing
Set patient centered SMART goals:
S - specific
Can’t set ambiguous goals
M - measurable
A - achievable
Don’t have sky-high goals
R - realistic
Ex; you can’t expect a patient to have 100% O2 saturation if they have a history of COPD
T - time frame
WIMC (while in my care — your shift! — short term goals)
Nursing care plans should be evidence based
Systematic reviews, randomized controlled trials, cohort studies, case-control studies, case series/case reports, editorials/expert opinion
Types of Interventions
Independent (without MD orders)
Ex; vitals, patient teaching
Dependent (MD orders needed)
Medication
Use nursing judgment » when medication has parameters
Ex; hold if BP is..
Collaborative / Interdependent
Working with physicians » must be patient advocate » help make decisions, make suggestions for patient care
Implementation
Carry out intervention » Doing, Delegating, Documenting
Delegate Intervention
Evaluating
Final Step (assessing patient’s response)
Determine:
Was the goal met? (partially or fully)- what can we modify? (REVIEW THE PLAN)
If not, why not?
Was the goal SMART
Should the plan be changed?
Documenting/Reporting- Always Document and report their findings
Requirements
Prompt
Care and response
Objective
Complete, yet concise- make sure data is complete
Relevant
If on paper — clear, legible, black ink
Corrected properly
Data, time, signature