The Biosphere - All Experiences
Ecology on a Living Planet
Our Living Planet: Stability and Change
biosphere: part of Earth in which all of life exists including land, water, and air/atmosphere
organisms:
interact w each other and physical components
respond to and change their environments
The Science of Ecology
ecology: scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment
Ecology and Economics
linked bc humans are a part of the biosphere → depend on ecological processes to provide essential water and food, which can also be bought and sold
Levels of Organization
(most specific → most broad)
species: a group of organisms that can breed and produce fertile offspring
population: a group of individuals of the same species that live in the same area
community: assemblage of different populations that live together in a defined area
ecosystem: all the organisms that live in a place, together with their nonliving environment
biome: a group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
Biotic and Abiotic Factors
an organism’s environment consists of the abiotic and biotic factors that affect it
Abiotic Factors
abiotic factors: physical or nonliving factors that shape an ecosystem
sunlight
heat
precipitation
humidity
wind / water currents
soil type
stable factors = stable environments, some change thru seasons
plantetarily → wind, ocean currents, and water overall determine the stability of ecosystems
Biotic Factors
biotic factor: any living part of the environment with which an organism might interact
important factors include predators, prey, competitors
planetary → predator and prey populations + human populations drive stability
Biotic and Abiotic Factors Together
ex: “muck” in shores of sand and pond has nonliving sand and mud particles, but it also has decaying organic material serving as food for bacteria → if it was ever living or containing living stuff, it’s biotic
abiotic conditions are shaped by organisms too → trees affect the sunlight and temp the “muck” experiences. trees also provide wind protection → impacts humidity. plant roots determine soil erosion. the type of decomposing oak leaves changes acidity of soil.
Global Systems
system: a network of relationships among parts, elements, or components that interact with and influence one another through the exchange of energy, matter, or information
the earth is divided into four spheres
biosphere
atmosphere: a thin layer of gases that surround earth
hydrosphere: all of the water (salt/fresh, liquid/ice/vapor) above and below Earth’s surface and in the atmosphere
geosphere: all of the rock at and below Earth’s surface
these parts often interact with each other
algae (biosphere) photosynthesize in the ocean (hydrosphere) and release oxygen into the air (atmosphere) for humans and animals to breathe, in which they live on the (geosphere)
Climate and Weather
changes in weather and climate determine the success/failure of crops and the stability of populations and communities
weather: day-to-day conditions of the atmosphere, including the temperature, precipitation, and other factors
climate: average year-to-year conditions of temperature and precipitation in an area over a long period of time
these determine the type of organisms that grow in ecosystems
climate is influenced by solar energy, latitude, and wind and ocean currents
Latitude and Solar Energy
solar radiation hits Earth at diff angles and at diff times bc Earth is curved and tilted on its axis, causing seasons
equator → sun directly overhead (not spreading out)→ little changes in daylight
poles → sunlight spreads out as winter sun drops lower → shortest winter days
EQUATOR has most solar energy
climate zones are produced by uneven distribution of heat/sunlight, tilted axis = seasons
polar zones: between 66.5 and 90 degrees north and south latitude; very cold winters, barely warm summers
temperate zones: between 23.5 and 66.5 degrees north and south latitude; hot summers, cold winters
tropical zones: 2; between 23.5 north and 23.5 south latitudes near the equator; warm/hot throughout year
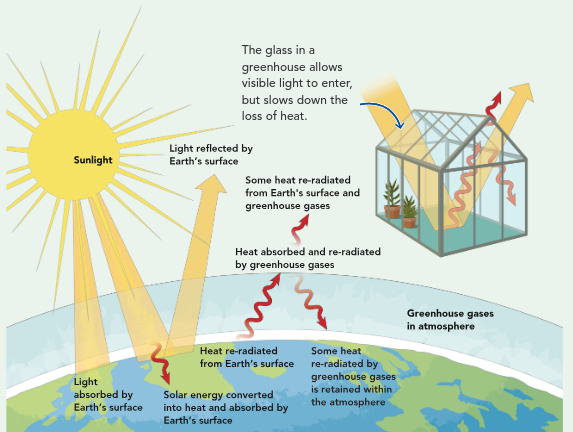
Solar Energy and the Greenhouse Effect
Earth’s avg temp is determined by amount of heat trapped in biosphere and the amount lost to space
controlled by concentration of three gases - carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor → greenhouse gases trap heat
greenhouse effect: the process in which certain gases (carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor) trap sunlight energy in Earth’s atmosphere as heat
part of their nutrient cycles → impacted by natural and human-caused changes
concentrations increase → earth heats, concentrations decrease → earth cools
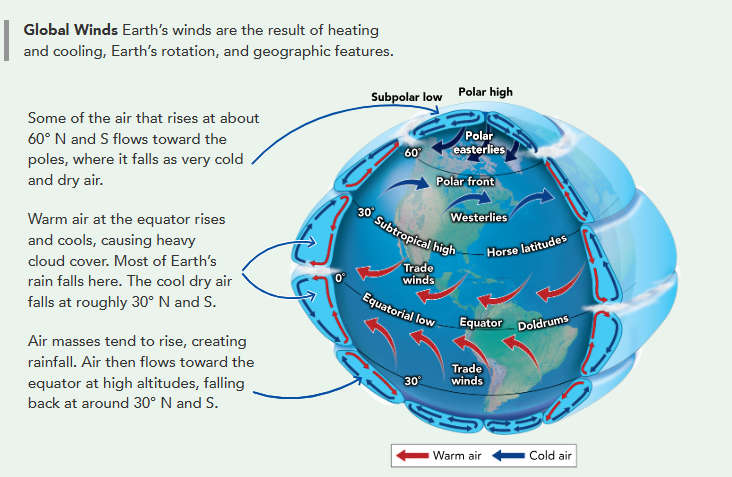
Heat Transport in the Biosphere
unequal distribution of heat = global wind and ocean currents
warm rises, cool sinks
→ Global Winds
heated area in warm areas expand and lose density → spreads north and south, losing heat → air cools and becomes denser, sinking → rinse and repeat
between places where are rises and sinks, air travels over the surface, creating winds
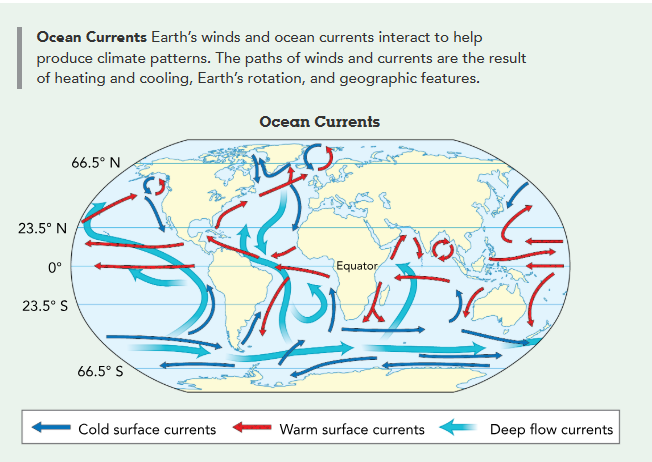
→ Ocean Currents
similar to wind process
cold water sinks cs its dense, but: some areas rise tho thru upwelling → surface waters r moved by winds, creating heat in currents → air passing over warm currents pick up heat → water cools
overall, wind and water currents determine humidity, temperature, ocean salinity, etc. and affect land and marine organisms
Energy Flow and Ecosystem Stability
Primary Producers
autotroph: organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food from inorganic compounds; also called a producer
primary producers: first producer of energy-rich compounds that are later used by other organisms
Energy from the Sun
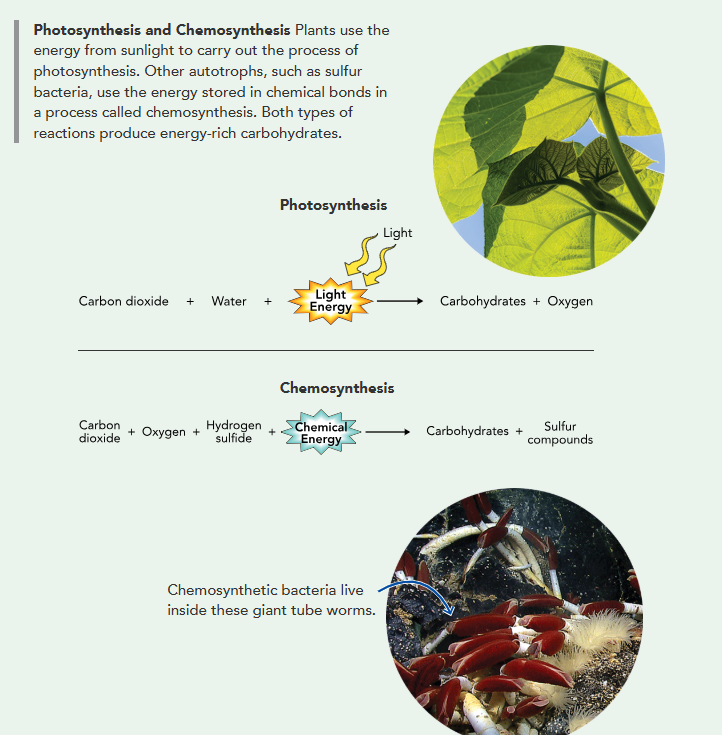
photosynthetic primary producers (algae, plants, bacteria) get solar energy and use photosynthesis to convert carbon dioxide and water into carbs and oxygen
land → plants; freshwater → plants, algae, bacteria; sunlit water → algae; tidal flats → other kind of photosynthesis w bacteria
Life Without Light
deep dark oceans → water from vents has inorganic compounds like hydrogen sulfide
chemosynthesis: process in which chemical energy is used to produce carbohydrates
chemosynthetic bacteria around vents live in worms and clams and supply host w carbs
studies underwater helped us realize chemosynthetic primary producers are common and live in many areas
bacteria thrive in deep dark areas
Consumers
heterotrophs: organism that obtains food by consuming other living things; also called a consumer
consumers: organism that relies on other organisms for its energy and food supply; also called a heterotroph
decomposer: chemically break down organic matter, producing dead and decaying plant/animal matter
mushroom
herbivore: obtain energy and nutrients by eating plant leaves, roots, seeds, or fruits.
detritivore: chew or grind detritus particles into smaller pieces
carnivore: kill and eat other animals
omnivore: eat both plants and animals
scavenger: animals that consume carcasses of other animals that have been killed by predators or have died of other causes
Food Chains and Food Webs
food chain: a series of steps in an ecosystem in which an organism transfer energy by eating and being eaten
can be big or small
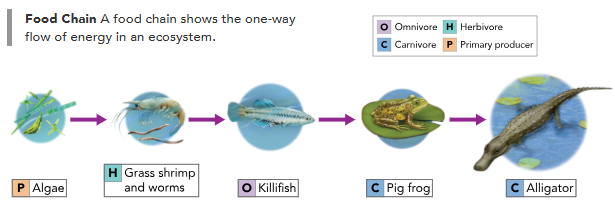
Food Webs
food web: network of complex interactions formed by the feeding relationships among the various organisms in an ecosystem
→ Food Chains within Food Webs
lots of food chains make up a food web
→ Decomposers and Detritivores in Food Webs
decomposers release nutrients into soil for primary producers
without detritivores, nutrients would remain locked in dead organisms
Food Webs and Ecosystem Stability
difficult to determine stability bc it changes based on seasons, but think of 2 things:
the amount the system varies from its average state (variability)
the ability of the system to recover from different kinds of disruptions (resilience)
stability = function and energy flow of ecosystem
diversity can affect variability and resilience
i.e. only one primary producer → environment changes → single food chain horribly disrupted
multiple producers → “taking over niches” species
ecosystems can pretty easily adapt and recover from short-term natural events
Food Webs and Disruptions
long-term manmade disruptions like climate change or habitat destruction can permanently transform ecosystems
Trophic Levels
trophic level: each step in a food chain or food web
1st = primary, rest = consumers
ecological pyramid: illustration of the relative amounts of energy or matter contained within each trophic level in a given food chain or food web
1) Pyramids of Energy
only 10% of the energy that enters any trophic level is available to organisms at the next level because ts organisms mostly spend energy on processes such as respiration, movement, growth, reproduction, released as heat
2) Pyramids of Biomass and 3) Numbers
biomass: total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level
kind of determined by energy available
primary producers have most mass, higher consumers have least mass
number of organisms at each trophic level → number pyramid similar to biomass pyramid most ecosystems
exceptions: consumers r smaller than the organisms they feed upon, like mosquitos on deer or insects biting trees
same biomass, upsidedown number pyramid
Trophic Levels and Ecosystem Stability
structure determined by interactions between food chains
climate change → more extreme weather events like droughts or floods → disrupt flow of energy and cycling of matter, same for human-caused disruptions
Cycles of Matter
Recycling in the Biosphere
essential nutrients: chemical substance that an organism needs to sustain life
CHNOPS = carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, phosphorus, sulfur
Biogeochemicals
biogeochemical cycles: process in which elements, chemical compounds, and other forms of matter are passed from one organism to another and from one part of the biosphere to another
elements are recycled through all spheres biologically, chemically, and geologically
→ Biological Processes
activities of living organisms → eating, breathing, burning food, eliminating waste products
→ Geological Processes
volcanic eruptions, forming n breaking rock, major movements below surface
→ Chemical and Physical Processes
forming clouds n precipitation, water flow, lightning
→ Human Activity
mining burning fossil fuels, clearing land, burning forests, fertilizers
The Water Cycle
mostly hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, sometimes biosphere
water travels into atmosphere as water vapor from ocean and lakes (evaporates)
condenses to form clouds
precipitation falls
runoff of water goes back to ocean and lakes
some groundwater, some transpirtation
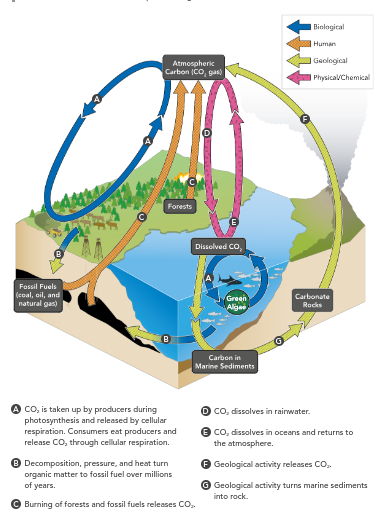
The Carbon Cycle
carbon is important bc:
makes up DNA and RNA
living tissues, ecosystems, ecosystem stability'
calcium CARBONate is important for animal skeletons and some rocks
CARBON dioxide is important for the atmosphere, dissolves in ocean
exchanges thru atmosphere and oceans:
plants take in CARBON dioxide thru photosynthesis, use carbon to build carbs
CARBs pass thru food webs to consumers
animals use CARBON calcium and oxygen to make their skeletons
organisms release CARBON dioxide thru cellular respiration
organisms die → decomposers break down into carbon
geologic forces carbon concentration → carbon rock
carbon dioxide released to atmosphere by volcanoes
reservoirs found in ocean, rock, fossil fuels
important for greenhouse gas effect
carbon-containing compounds of ancient organisms can become
coal'
oil
natural gas
“fossilized carbon” removed from atmosphere by photosynthesis
human activities like burning coal and trees
disrupts cycle, releases co2 into atmosphere
more co2, more heat trapped, higher temps, affects ecosystem stability
The Nitrogen Cycle
nitrogen has many uses:
amino and nucleic acids
makes up atmosphere
ammonia, nitrate, and nitrite found in soil, waste, decaying matter
most nitrogen isn’t usable, so:
nitrogen fixation: process of converting nitrogen gas into nitrogen compound that plants can absorb and use
bacterias do this
consumers eat producers → new nitrogen compounds
decomposers release nitrogen from dead animals
lightning causes atmospheric nitrogen fixation, humans do industrial fixation for fertilizers
denitrification: process by which soil bacteria converts nitrate into nitrogen gas
sm human activities disturb ts
lots of fertilizers end up in soil and rivers → adding excess nitrogen and nutrients
encourages more algae and plant growth bc usually not tm nitrogen, but disrupts ecosystem stability
burning fossil fuels also release nitrous oxide into atmosphere → winds carry, contribute to acid rain, affects stability
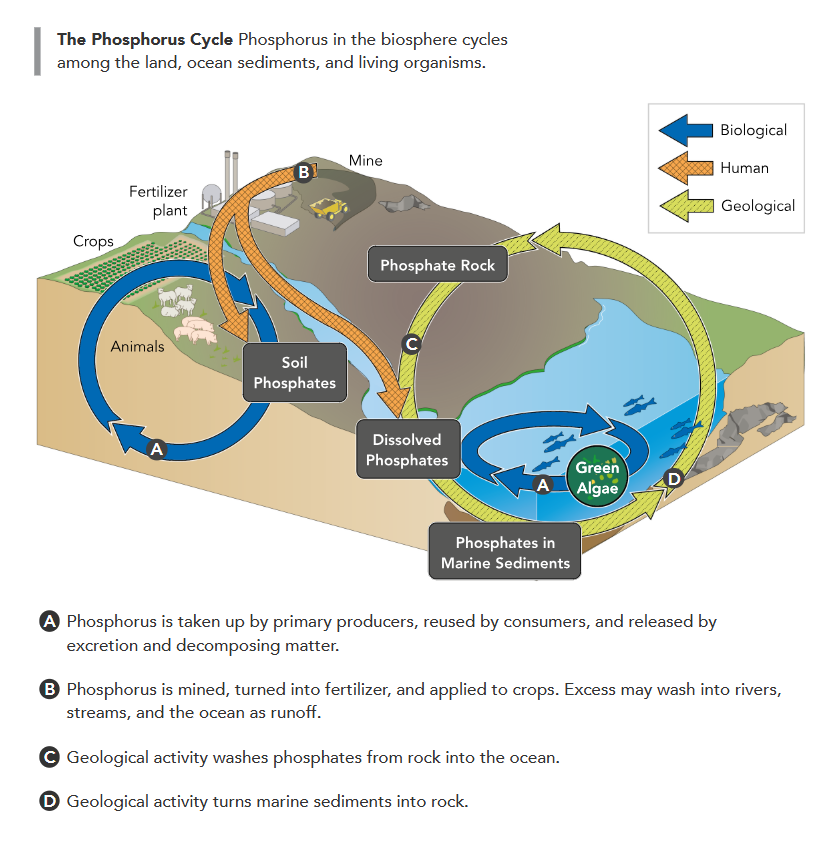
The Phosphorus Cycle
phosphorus is important cs:
important for DNA and RNA
DOESNT cycle through atmosphere
phosphate rock or dissolved in fresh/salt water
phosphate released as rocks wear down
cycles bw organisms and soil on land → plants bind into organic compounds
dissolved phosphate moves into oceans → aquatic organisms use it for biological compounds
humans use for fertilizer → disruptions
Nutrient Limitation
“The rate at which primary producers create organic material, the long-term survival of species, and ecosystem stability are all dependent on changing resource bases that can be limited.”
even if sunlight and water r abundant, shortage of one thing like nutrients could affect stability
limiting nutrient: single essential nutrient that limits productivity of an ecosystem
Nutrient Limitation in Soil
nutrients work like a gear system - if ur deficient in one, the ecosystem is cooked
ts explains why farmers use fertilizers bc they have many necessary nutrients for plants
no carbon cs atmosphere
tm affects environment tho
Nutrient Limitation in Aquatic Systems
usually nitrogen is the limiting nutrient esp for algae and plants
fresh water → phosphorus is limiting
heavy rain causes fertilizers to run into ocean → disrupts natural delivery, abnormal excess growth of algae and plants in water
algal bloom → grow and reproduce far beyond normal rates