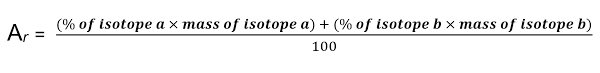Principles of Chemistry IGCSE Edexcel (States of Matter Pt. 1.1-1.4)
Chemistry IGCSE- Principles of Chemistry
}}1.1 States of Matter}}
The three States of Matter
The three states are solids, liquids and gases
The state changes occur at the meting point and boiling point
| Solid | Liquid | Gas |
|---|---|---|
| Regular arrangement | Randomly arranged | Randomly arranged |
| Vibrate around a fixed position | Move around eachother | Move quickly in all directions |
Changes of state
- The amount of energy needed for interconversion of state depends on the strength of forces between particles —>
This is a physical change involving changes in forces between the particles of the substances
Evaporation vs Boiling:
Both happen when a liquid changes into a gas
- %%Evaporation%% only occurs at the surface of liquids; where high energy particles can escape from liquids at low temperatures
- Evaporation occurs over a range of temperatures
- %%Boiling%% requires heat energy which transforms into kinetic energy
- It only occurs at a specific temperature which is unique to each pure liquid
Melting:
- Requires heat energy which transforms into kinetic energy, allowing particles to move
- Occurs at a specific temperature that is unique to each pure solid
Freezing:
- Is the reverse of melting and happens at the exact same temperature as the melting point
Condensation:
- When a gas is cooled, particles lose energy so when they bump together, they lack the energy to bounce away and instead group together to form a liquid
Diffusion and Dilution:
Diffusion and Dilution experiments support a theory that all matter (solids, liquids and gases) is made up of tiny, moving particles; the kinetic theory of matter
Diffusion-
- Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
- Therefore, particles must be able to move freely (in fact, diffusion cannot occur in solids)
Solutions:
| Solvent | Liquid in which solute dissolves |
|---|---|
| Solute | Substance that dissolves in a liquid to form a solution |
| Saturated solution | A solution with the maximum concentration of solute dissolved in the solvent |
}}1.2 Elements, compounds and mixtures}}
Pure substances and mixtures:
Element:
A substance made up from only one type of atom (eg. Sodium)
Compound:
A substance made from two or more elements that are chemically bonded together (eg. Carbon Dioxide)
Mixture:
Two or more elements or compounds physically combined together (eg. Salty water)
Chemical properties of each substance are not altered
Separation and Purification Techniques
Simple distillation:
- Separating a %%solvent from a solution%% (eg. Water from salty water)
Fractional distillation:
- Separating a liquid from a %%mixture of liquids%% (eg. Ethanol from ethanol and water or fractions from crude oil)
- Works as liquids have different boiling points so, when heated, liquid with lower boiling point will evaporate first, condense and be collected.
Paper chromatography:
- Separating %%mixtures of soluble substances%% (eg. Food colourings, inks, dye)
- Used to help identify substances
- Separation depends of the solubility of substance
Practical- Investigating the compositions of inks using chromatography
Method:
Draw a start line in pencil across the chromatography paper (approx 1-2 cm from bottom)
Use a pipette to add small dots of ink across the line and label them
Place the paper into a container with water (solvent) reaching just underneath the start line
Allow the solvent to move through the paper, remove the chromatogram before it reaches the top
Draw a line in pencil marking the solvent front
Analysis and results:
Measure distance travelled by each spot and record in a table
Calculate Rf value
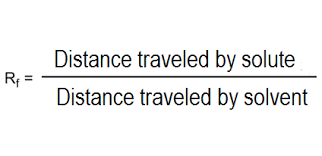
}}1.3 Atomic Structure}}
- All substances are made of atoms
- An atom is made up of protons, neutrons and electrons
| Subatomic Particle | Relative mass | Relative charge | Position |
|---|---|---|---|
| Proton | 1 | +1 | Nucleus |
| Neutron | 1 | 0 | Nucleus |
| Electron | Almost 0 | -1 | Shells |
Atomic and Mass number
Atomic number:
- Number of protons in atom’s nucleus
- Unique for every element
Mass number:
Total number of protons and neutrons in atom’s nucleus
Usually different but can be the safe across different elements
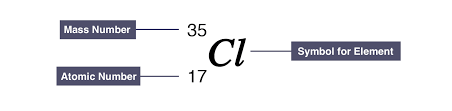
Isotopes
- Isotopes are atoms of an element that have the %%same number of protons%%, but %%different number of neutrons%%
Relative atomic mass
- It is the weighted average of the relative atomic masses of the isotopes in that element
- Their symbol is Ar
Calculating Ar