Translation
mRNA - messenger RNA
made from DNA in nucleus.. travels out of nucleus to find a ribosome
function: to carry instructions from DNA to ribosome
tRNA - transfer RNA
brings amino acids to the ribosomes; found in cytoplasm
function: to bring amino acids to ribosome
rRNA - ribosomal RNA
part of the ribosome; this is where proteins are made (can be found where protein synthesis takes place)
function: combine with proteins to make up ribosomes
Translation:
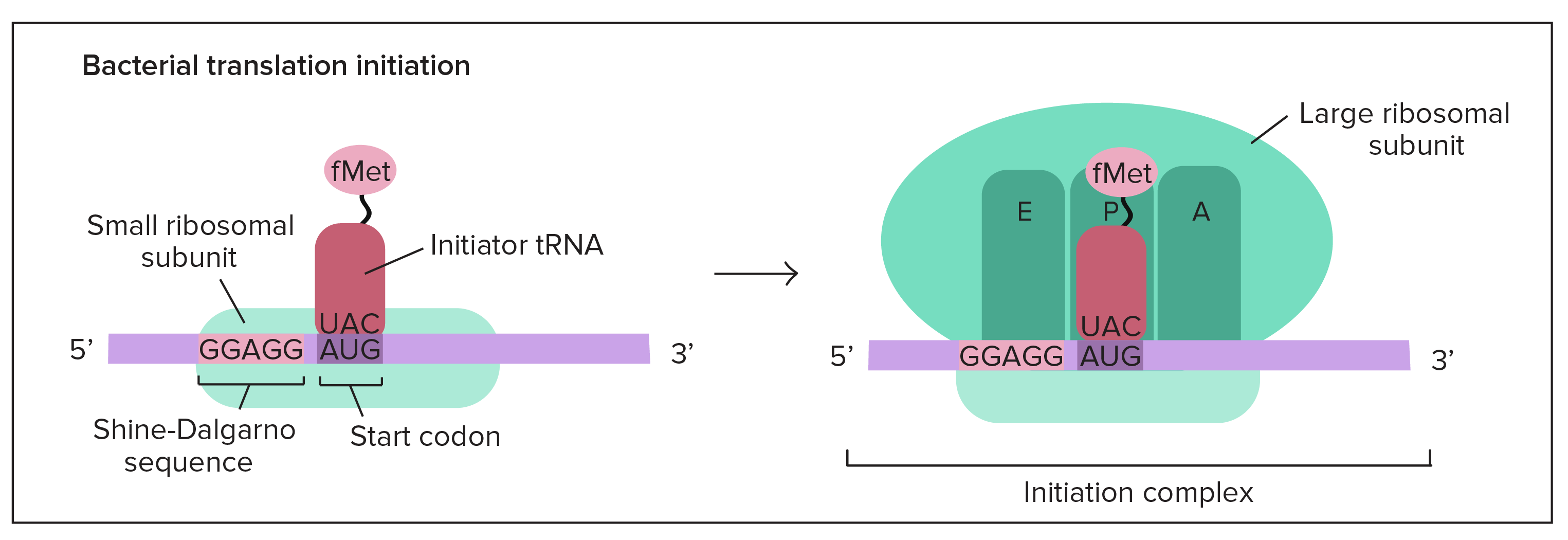
Initiation and Ribosomes
Ribosomes contain two subunits: small and large
Subunits: composed or proteins and rRNA molecules (created within the nucleolus and brought into the cytoplasm) Small unit(40s) + Large unit (60s) = 80s
the subunits combine with the mRNA to form the ribosome
mRNA leaves the nucleus through the nuclear pore
it enters the cytoplasm through initiation factors to find small units and bind to the 5’ end
travels along the mRNA until it locates a specific sequence of nucleotides(start codon) beginning with 5’ end(AUG) and ending with 3’ end.
Once it locates, the small subunits tell its signals to a tRNA molecule to go out and find a methionine molecule to bring it to AUG.
once it combines, the large subunit combines with the small subunit to complete the process of initiation.
Once the pre MRNA undergoes post transcriptional modifications it becomes mRNA
mRNA then travels to the nucleus through the cytoplasm.
when it reaches the cytoplasm with the help of initiation factors, the small subunits bind to the 5’ end of the mRNA until it reaches the start codon
signals for the tRNA to bring methionine to bind to the start codon - known as the charged tRNA complex
2. Elongation
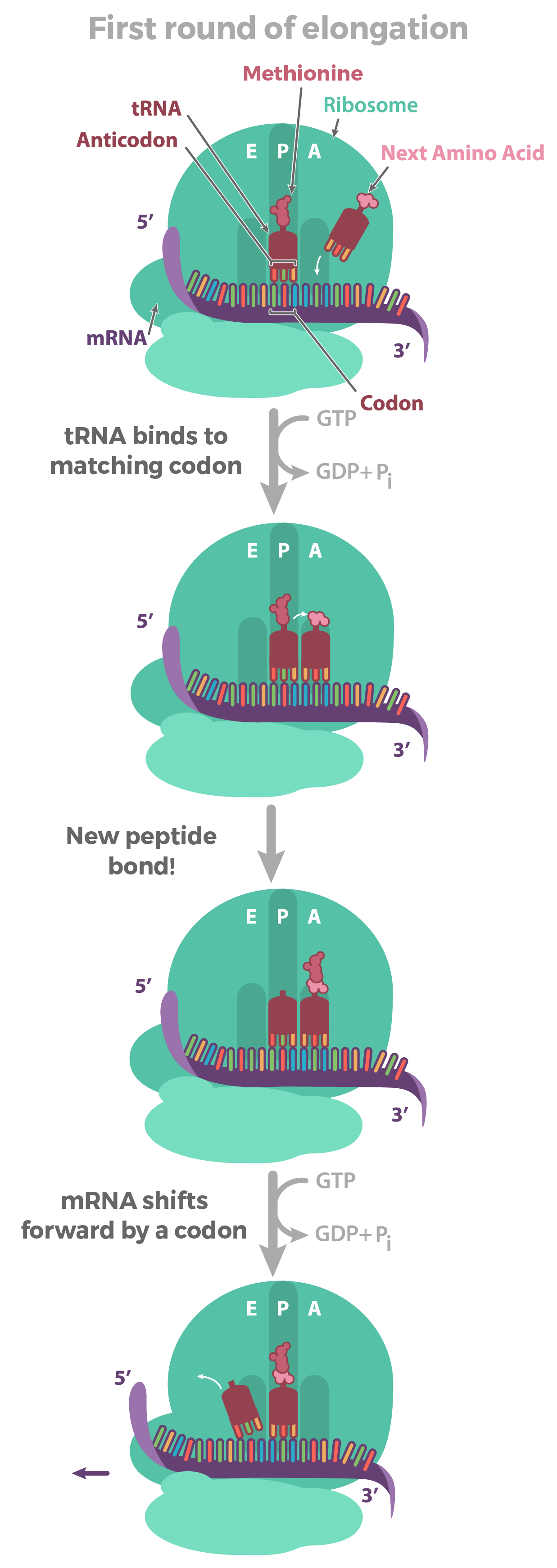
the charged tRNA molecule that carries the methionine amino acid is found within the P Site of the ribosome.
The ribosome begins moving along the mRNA molecule, before the movement takes place another tRNA molecule must find the approrpaite amino acid and bring it to the A site of the ribosome.
A peptide bond is formed between teh amino acids of the A and P site by the help of an enzyme known as peptide transferase, when the bond is formed the amino acid detaches from the tRNA in the P-site.
the tRNA molecule that is empty in the P site is then moved three nucleotides to the E site(exit site) in the 5’ to 3’ direction but the charged tRNA with the growing polypeptide change moves to the P site
This sliding process is known as Translocation
Once the A-site is emtpy, the process repeats until the chain is complete
Termination:
There is a stop codon known as UAA, UGA, OR UAG sequence
a protein called release factor will bind to A site intead of a tRNA molecule to break off the polypeptide chain from the tRNA.
A site contains the stop codon.