Copy of Unit Review: Physical Geography
Unit Review: Physical Geography
CGC1D1f: Issues in Canadian Geography
Mrs. Tricanico
Test Format:
K/U - 20 marks
A: 10 multiple choice questions - 10 marks
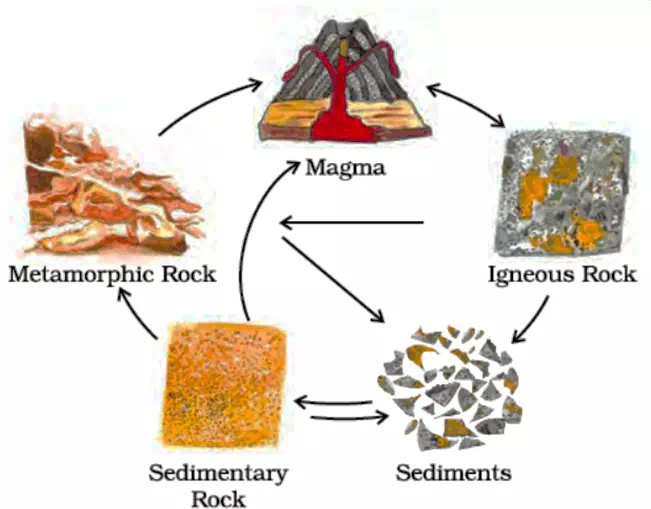
B: Complete a chart (rock cycle - choose the type of a rock described) - 6 questions - 6 marks
EX:
| The rock type that is made by cooling magma | Igneous Metamorphic Sedimentary |
|---|
C: Definitions - Matching - 4 questions - 4 marks
T/I - 10 marks
Short answers - 2 questions - 5 marks per question - Make sure you make 5 unique points for each question for full marks.
A - 10 marks
Be able to share detailed information about a landform region in Canada selected by you. Your answer will need to include ALL of the following:
- Where is it located in Canada? ( /1 mark)
- When (era) and how was it formed (geologic history)? ( /2 marks)
- How has its appearance changed over time? ( /2 marks)
- What economic industries take place there today? What natural resources and rock types are found in the region? ( /3 marks)
- Why is this region worth visiting / settling in? ( /2 marks)
- Lawrence Lowlands. It is located between Quebec City and Windsor,Ontario. Major cities are Toronto, Montreal, Quebec City and Ottawa.
- The St. Lawrence Lowland was formed almost 500 million years ago. It lies on sedimentary rocks which are some 450 million years old and which formed during the Cambrian period of the Paleozoic era. The topography of the Lowlands is the result of weathering and erosion by rivers of the nearby flat-lying early sedimentary rock.
- The lowlands are low, flat lands with rolling hills. The St. Lawrence Lowlands
were created almost 500 million years ago. There was an ice age and when the ice age was done all the glaciers started melting. From 13,000 to 10,000
years ago the St. Lawrence Lowland rose rapidly as much as somewhere around 20 meters per century in response to the disappearance of the ice mass.
- People living within this region tend to build manufacturing plants close to the bodies of water, for hydro power, close to where the minerals are found and close to people for more workers.This region provides all of these necessities for successful manufacturing in Canada.Farming is another popular industry here. This region has the 2nd largest area in Canada used for farming because of its rich soil, flat land and the climate is good.This is a very important region for growing crops in Canada.The St. Lawrence Lowlands mine iron, zinc, coal, silver, copper and lead.The lowland bordering the St. Lawrence River in Quebec and are floored with sedimentary rocks
- Bec the warm climate, excellent soils, flat land, transportation routes and development of cities
Please Review the Following: (at least the highlighted eras)
| ERA & YEARS AGO | SIGNIFICANT GEOLOGICAL EVENTS | SIGNIFICANT BIOLOGICAL EVENTS |
|---|---|---|
| (Name of the era):(600 Million- 4.6 Billion MYA) | Preambriam shieldsCanadian shield Brazilian shield African shield Australia shield | First single- celled and multi-celled organisms |
| **(Name of the era):**230 Million -600 Million MYA) | ||
| (Name of the era): \n The mesozoic era**(65 Million -230 Million MYA)** | Rocky mountains formedInnuitian mountains Shallow seas in that interior north america | Age of reptiles First birds and mammals First flowering plants |
| (Name of the era):(65 Million MYA - Present) |
Define the following terms:
- Pangaea: the hypothetical supercontinent (or sentences together before the separated
- continental drift: the movement of tectonic plates resulting in continents separating
- Weathering: the breaking down/ dissolving of rocks/ Minerals on earth due to weather and climate
- Erosion: water, wind, rain etc, wearing down the surface of the earth (ex.rocks)
- divergent tectonic plate movement: tectonic plates moving away from each other
- convergent tectonic plate movement: tectonic plates moving towards each other
- glaciation:the covering of a surface with ice
- permafrost - the soil that is permanently frozen
What are the forces of erosion?
Wind, rain, running water
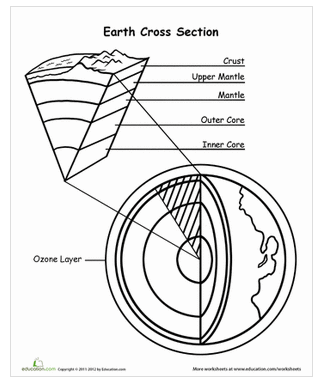
What does each of the following layers of the earth consist of?
crust (continental) - granite
crust (oceanic) basalt
outer core - made of iron & nickel (liquid molten metals)
inner core- dense ball of solid metal like iron and nickel
What is created by the movement of tectonic plates?
- Earthquakes
- Volcanic eruptions
- Tsunamis
- Mountains
- Avalanches
Which type of soil remains frozen all year?
Permafrost
Which landform region are we located in?
St. lawrence lowlands
What type of rocks contain fossilized remains of plant and animal life. We also find fossil fuels such as oil, natural gas and coal?
sedimentary rock
What type of rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust?
igneous rocks
How is each of the following types of rock made?
igneous is made from magma cooling
Sedimentary is made from sediments ( sand,etc) compacted together after igneous rocks are heated and compacted
Metamorphic is made from sedimentary rocks cooling
Unit Review: Physical Geography
CGC1D1f: Issues in Canadian Geography
Mrs. Tricanico
Thinking - Reflect on these questions:
Why is it important to study physical geography?
- We are surrounded by it everyday
- Need to know about the world we live in
- It influences why people live where they live
- It influences the way countries make money
- Influences how people make their money
- Need to conserve our natural diversity
What do the movement and melting of glaciers, as well as the melting of the permafrost, indicate? Why should we be aware of it?
- It indicates global warming
- This means the earth is getting warmer
- We should be aware of it because it is affecting the animals that we need
- We can help by reducing our carbon footprint
- We can do this by recycling and reusing are waste