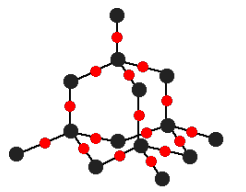
2.2J Covalent Network Structures
Covalent Network Structures
Covalent network structures are giant 3D networks of atoms linked by covalent bonds.
Allotropes of an element have different bonding and structural patterns, and so have different physical and chemical properties
e.g. O2 and O3
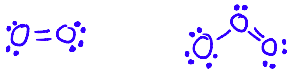 Allotropes of Carbon
Allotropes of Carbon
Carbon has 4 allotropes
Diamond
Graphite
Graphene
Fullerenes
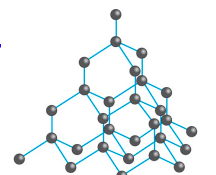
Diamond
Each carbon shares electrons with 4 other carbons
High melting points
Very hard
Non-conductive
Insoluble in H2O
Tetrahedral
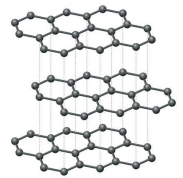
 Graphite
Graphite
Layered structure, sheets attract one another through L.D. forces
Each carbon bonds with 3 other carbons
Remaining electron is “spare”, can become delocalized
High melting point
Soft, slippery feel
Insoluble in H2O
Conducts electricity
 Graphene
Graphene
Similar structure to graphite but single-layer only
Conducts electricity
Conducts heat
Very flexible
High melting point
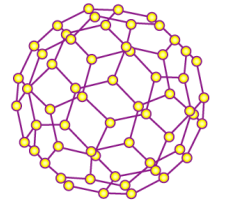
 Fullerene (C60)
Fullerene (C60)
Each carbon bonds with 3 other carbons to form a sphere.
Semi-conductor
Low thermal conductivity
Low melting point
 Silicon
Silicon
Like carbon, silicon has 4 valence electrons
Silicon dioxide forms covalent network structures
Oxygen acts like bridge connecting silicon atoms
Physical Properties
High melting point
Hard
Non-conductive
Insoluble