
bio topic 4 : ch 5 & 6 notes
PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
plants
algae (protists)
certain bacteria
transform light into chemical energy
uses carbon dioxide and water as a starting material
release oxygen as a by-product
chemical produced via photosynthesis is stored in the BONDS OF SUGAR MOLECULES
organisms that generate their own organic matter from inorganic ingredients are called autotrophs
plants and other organisms that do this by photosynthesis are producers for most ecosystems are called photoautotrophs
chloroplasts are light-absorbing organelles & are the site of photosynthesis
the green color is from chlorophyll: a pigments in the chloroplasts that plays a central role in converting solar energy to chemical energy
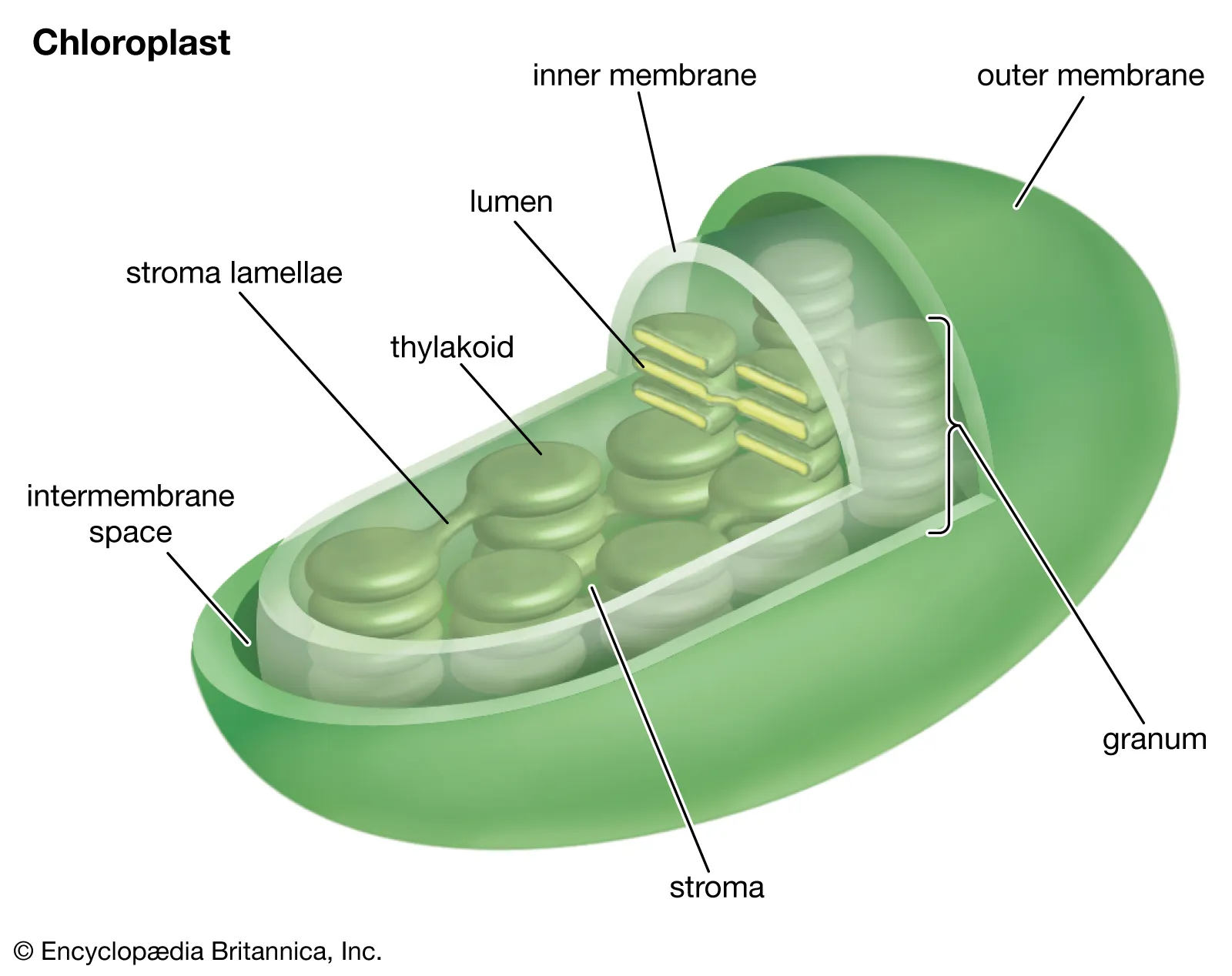
chloroplast has a double membrane envelope
the inner membrane encloses a compartment filled with stroma
stroma is the fluid between the thylakoid membrane and the two outer membranes of a chloroplast
suspended in the stroma are interconnected membranous sacs called thylakoids
each individual pancake is called a thylakoid
the thylakoids are concentrated in stacks called grana (singular, granum)
the chlorophyll molecules that capture light energy are built into the thylakoid
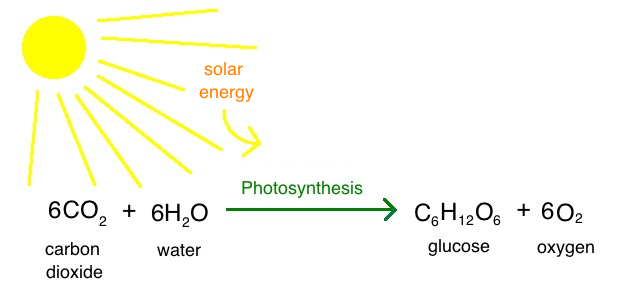
in the overall equation for photosynthesis, notice that the reactants of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide(CO2)
water (H2O)
ARE THE SAME AS THE WASTE PRODUCTS OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION
photosynthesis produces what respiration uses→ glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2)
*a multistep chemical pathway
NADPH stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, a molecule that acts as an electron donor/ carrier in all organisms
STEPS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
light reaction produce
1> ATP 2> NADPH 3> release oxygen
CO2 enters Calvin. ATP & NADPH used from light reaction > Calvin Cycle produces SUGAR
summary
in the light reaction, chlorophyll in the thylakoid membranes absorbs solar energy which is then converted to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH and water is split, providing a source of electrons and giving off O2 gas as a by-product
the Calvin cycle (happens outside the thylakoid membrane )uses the products of the light reactions (oxygen) to make sugar (cellulose) from carbon dioxide
ATP generated by the light reactions provides the energy for sugar synthesis
the NADPH produced by the light reactions provides the high-energy electrons that drive the synthesis of the glucose from the carbon dioxide
thus, the Calvin cycle indirectly depends on light to produce sugar because it requires the supply of ATP and NADPH produced by the light reactions

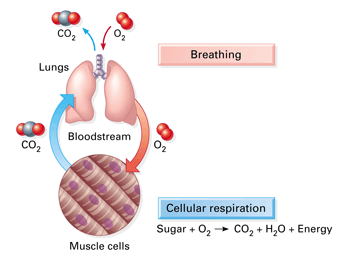
cellular respiration is a process of electron transfer. A “fall” of electrons from food molecules to oxygen to form water releases the energy that mitochondria can use to make ATP
the opposite occurs in photosynthesis: electrons are boosted “uphill” and added to carbon dioxide to produce sugar
cellular respiration: electrons are ‘carried’ by NADH and “fall” combining with oxygen to “make” water
sunlight is a type of energy called radiation, or electromagnetic energy
the distance between the crests of two adjacent waves is called a wavelength
the full range of radiation is called the electromagnetic spectrum
light behaves as waves
discrete packets of energy called photons, fixed quantities of light energy
the shorter the wavelength, the stronger the energy of a photon
when a pigment molecule absorbs a photon, one of the pigment’s electrons gains energy
this electron is now said to be “excited”
the excited state is highly unstable
an excited electron usually loses its excess energy and falls back to its ground state almost immediately
most pigments release heat energy as their light-excited electrons fall back to their ground state

some pigments emit light as well as heat after absorbing photons
a fluorescent light emitted ya glow stick is caused by a chemical reaction that excites electrons of a fluorescent dye
the excited electrons quickly fall back down to their ground state, releasing energy in the for of fluorescent light
in the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll molecules are organized with other molecules into photosystems
each photosystem has a cluster of a few hundred pigment molecules, including chlorophylls A & B and some carotenoids
how light reactions generate ATP & NADPH
photons of light excite electrons in the chlorophyll of the first photosystem
these photon are then trapped by the primary electron acceptor
this new photosystem then replaces the lost electrons by extracting new ones from water
this is the step that REALEASES O2
> light reactions —> produce 1.ATP 2. NADPH 3. release O2

the mechanism of ATP production during the light reactions is similar to cellular respiration
an electron transport chain pumps hydrogen ions across a membrane
ATP synthesis (enzyme) uses the energy stored by the H+ gradient to make ATP
the main difference is that food provides the high-energy electrons in cellular respiration, whereas light-excited electrons flow down the transport chain during photosynthesis
with each turn of the cycle
inputs:
CO2 from the air & ATP and NADPH produced by the light reactions
the Calvin cycle constructs an energy-rich sugar molecule called glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) using
carbon from CO2
energy from ATP
high-energy electrons from NADPH
plant uses G3P as the raw material to make
glucose
other organic compounds
know that ATP and NADPH are used from light reactions
carbon dioxide gas enters Calvin cycle
glucose is made in Calvin cycle
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
focused on the mitochondria
muscles need energy to work
muscles cells obtain this energy from the sugar glucose through a series of chemical reactions that depend upon a constant input of oxygen (O2)
when you work too hard and your body demands more oxygen, your muscles switch to “emergency mode” and they break down GLUCOSE very inefficiently and produce LACTIC ACID as a by-product
plants are autotrophs → make their own food
producers
we are heterotrophs → cannot make organic molecules from inorganic ones (need others to feed)
consumers
chemical ingredients for photosynthesis are
CO2 passes from the air into a plant via tinny pores
H2O is absorbed from the soil by the plant’s roots
chloroplast use light energy to rearrange the atoms of these ingredients to produce sugars, most importantly glucose (C6H12O6)
O2 is a by-product
plants use carbon dioxide to release oxygen plants make glucose (cellulose , starch)

both animals and plants use organic products of photosynthesis as a source of energy
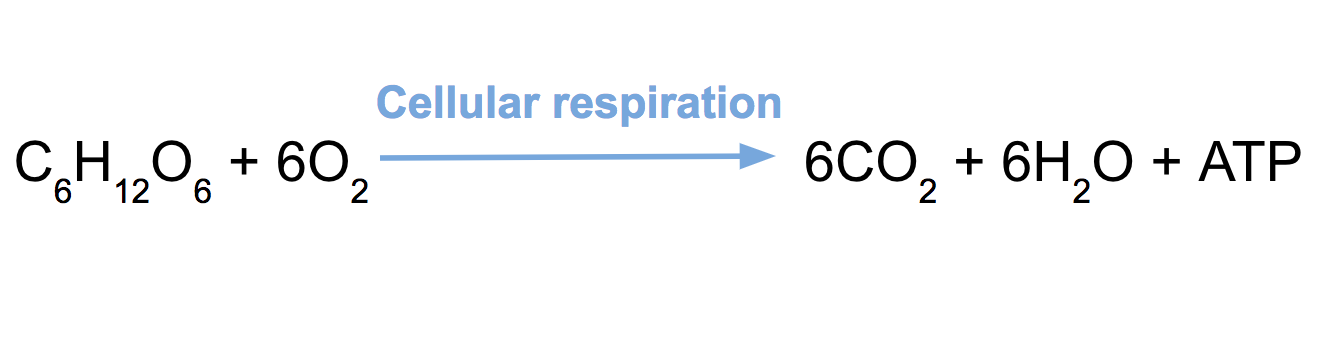
cellular respiration used O2 to convert energy stored in chemical bonds of organic fuels called ATP
cells use ATP for all their work
this takes place in the mitochondria
WASTE PRODUCUTS of cellular of respiration are CO2 and H2O; the same ingredients for photosynthesis
plants store chemical energy via photosynthesis and then harvest this energy via cellular respiration
plants make more than they need for fuel → the rest can be stored (starch in potatoes)
people eat the plants and take advantage of their photosynthetic abilities
cellular respiration is AEROBIC (requires oxygen) harvesting of chemical energy from organic fuel molecules
the man way that chemical energy is harvested from food and converted to ATP
glucose is the basic food for all cells (MONOsaccharide)
table sugar = DIsaccharide
3 stages of cellular respiration (GCCET)
glycolysis
citric acid cycle
electron transport
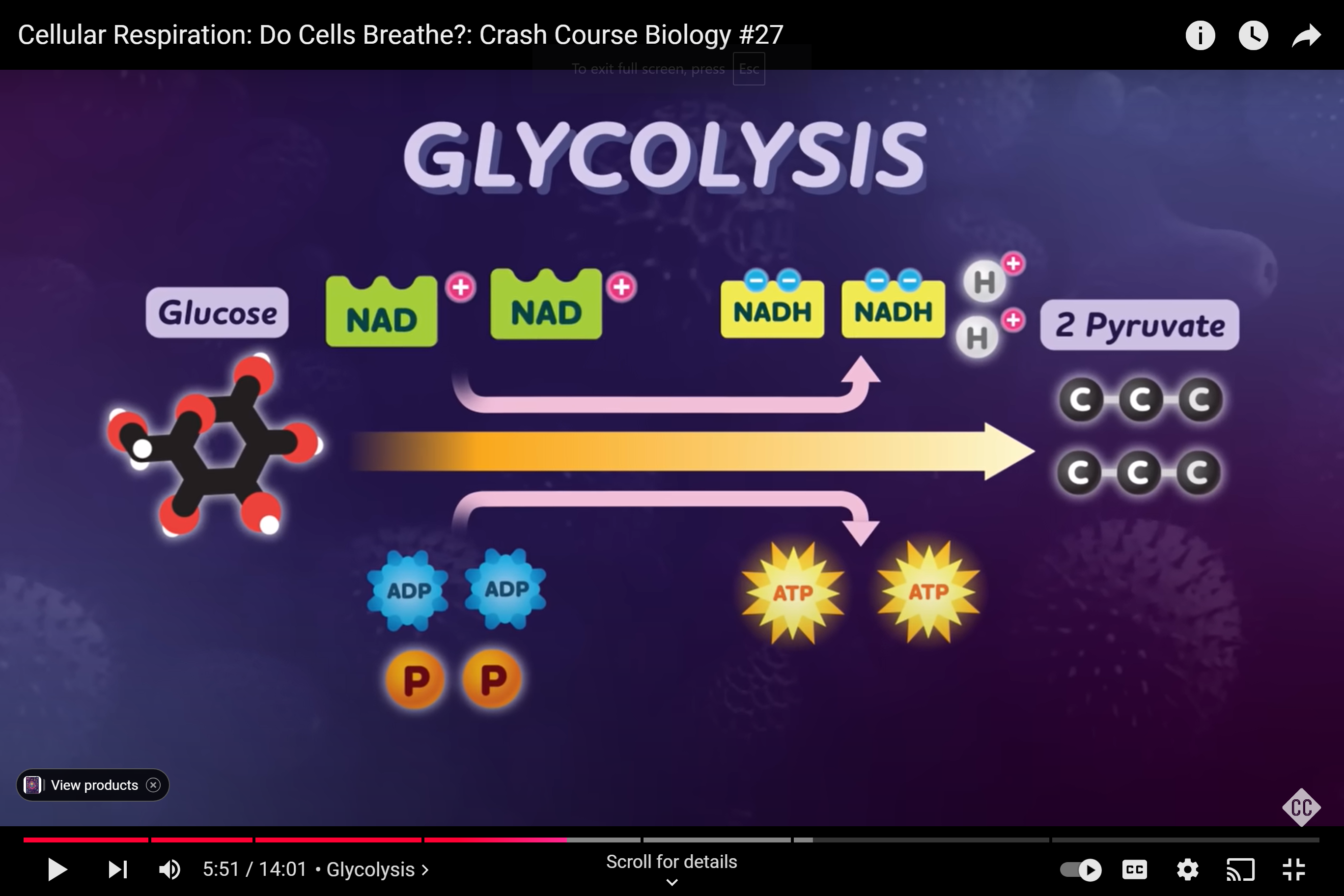
glucose (6 carbons) is split into 2 molecules called pyruvic acid (usually located in the cytoplasm/outside the mitochondria ) (2 ATP)
citric acid cycle (inside the mitochondria) uses enzymes that are dissolved in the fluid within mitochondria and completes the breakdown of glucose all the way to CO2 (which is then released as a waste product (second step: CO2 is released as waste) (2ATP)
3 carbon molecules then donate high-energy electrons to NAD+; forming NADH
electron transport chain (ETC): (inside the mitochondria) electrons from NADH are combined with oxygen {hydrogens, electrons, and oxygen combine to form water} (the MOST/ nearly 30 ATP)
2+2+30 = 34 about 34 ATP is produced from each GLUCOSE molecule within this process
*the NADH that is used in the ETC, oxygen uses the electrons from NADH (oxygen is an electron ACCEPTOR)
the overall effect of all this transfer of electrons during cellular respiration is a “downward” trip for electrons
from glucose
to NADH
to am electron transport chain
to oxygen
FERMINTATION
LACTIC ACID FORMATION
anaerobic process (does not require oxygen) to harvest food energy
relies on glycolysis to produce ATP
glycolysis does NOT require oxygen / produces only 2 ATP molecules for each glucose
the addition of electrons to pyruvic acid produces a waste product called lactic acid
the lactic acid by-product is eventually transported to the liver, where liver cells convert it back to pyruvic acid
human muscles do NOT undergo alcoholic fermentation but instead produce lactic acid under no oxygen conditions
the buildup of lactic acid causes muscle fatigue
lactic acid produced by YEAST using lactic acid formation is used to produce
cheese, sour cream, yogurt, soy sauce, olives, cabbage, etc.
can perform alcoholic fermentation to produce O2 and ethyl alcohol instead of lactic acid
CO2 released in alc. drinks is responsible for bubbles in champagne , beer, & wine
CO2 release bubbles from fermenting yeast causes bread dough to rise
BOTH ANAEROBIC AND AEROBIC RESPIRATION START WITH GLYCOLYSIS (FERMINTATION & CELLULAR RESPIRATION)
GLYCOLYSIS IS THE UNIVERSAL ENERGY-HARVESTING PROCESS OF LIFE
When both stages of photosynthesis have been completed, the energy of light ends up in which of the following?
Sugar molecules
Photosynthesis releases the oxygen we breathe from which molecule?
Water
In photosynthesis, carbon atoms from carbon dioxide end up in which molecule?
Sugar
What is the source of the inorganic carbon fixed by photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide
Which of the following occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast?
The Calvin cycle
How does energy move between the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
In the form of ATP and NADPH
In photosynthesis, what is the function of light-dependent reactions?
To transform light energy into chemical energy
A molecule that absorbs the energy in specific wavelengths of light is called which of the following?
A pigment
Light-dependent reactions store chemical energy in which of the following?
ATP and NADPH
What is the ultimate source of the electrons that are transferred during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
Water
Excited electrons have more energy than non-excited electrons. Electrons in the photosystems of plants are excited by light.
In carbon fixation, what inorganic molecule is "fixed" to RuBP?
Carbon dioxide
What source of energy is used in the Calvin cycle?
ATP and NADPH
The CO2 used in carbon fixation enters the plant through which of the following?
Stomata
How many carbon atoms make up RuBP?
5
What role does the enzyme RuBisCo play in the Calvin cycle?
Catalyzes the reaction between CO2 and RuBP
Which step of cellular respiration is responsible for making the most ATP molecules?
The electron transport chain
In fermentation, what molecule is converted to lactate (lactic acid)?
Pyruvate
What factor determines whether pyruvate is processed by cellular respiration or by fermentation?
Oxygen levels in the cells
Both aerobic respiration and fermentation begin with
glycolysis
Where in the cell does fermentation take place? Select all that apply.
The cytosol
Which step of fermentation is responsible for the majority of ATP production?
Glycolysis
Which of the following compounds is NOT produced during glycolysis?
ATP
Pyruvate
Glucose
NADH
Some of the ATP produced during aerobic cellular respiration is produced via substrate-level phosphorylation.
Which of the following molecules carry electrons from the citric acid cycle to the electron transfer chain? Select all that apply.
NADH
FADH2
In a molecule of sugar, where is energy stored?
In high-energy electrons in molecular bonds
Energy removed from sugar molecules is transferred to the ETC by which of the following?
Electron carriers
Which stage of cellular respiration releases energy from electrons in slow, controlled steps?
The ETC
Which of the following are outputs of the aerobic respiration of sugar? Select all that apply.
ATP
Water
Heat
Which of the following steps contribute electron carriers to oxidative phosphorylation? Select all that apply.
Pyruvate oxidation
Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis
Potential energy in the form of an electrochemical gradient is transformed into ATP during oxidative phosphorylation.
bio topic 4 : ch 5 & 6 notes
PHOTOSYNTHESIS:
plants
algae (protists)
certain bacteria
transform light into chemical energy
uses carbon dioxide and water as a starting material
release oxygen as a by-product
chemical produced via photosynthesis is stored in the BONDS OF SUGAR MOLECULES
organisms that generate their own organic matter from inorganic ingredients are called autotrophs
plants and other organisms that do this by photosynthesis are producers for most ecosystems are called photoautotrophs
chloroplasts are light-absorbing organelles & are the site of photosynthesis
the green color is from chlorophyll: a pigments in the chloroplasts that plays a central role in converting solar energy to chemical energy

chloroplast has a double membrane envelope
the inner membrane encloses a compartment filled with stroma
stroma is the fluid between the thylakoid membrane and the two outer membranes of a chloroplast
suspended in the stroma are interconnected membranous sacs called thylakoids
each individual pancake is called a thylakoid
the thylakoids are concentrated in stacks called grana (singular, granum)
the chlorophyll molecules that capture light energy are built into the thylakoid
in the overall equation for photosynthesis, notice that the reactants of photosynthesis
carbon dioxide(CO2)
water (H2O)
ARE THE SAME AS THE WASTE PRODUCTS OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION
photosynthesis produces what respiration uses→ glucose (C6H12O6) and oxygen (O2)
*a multistep chemical pathway
NADPH stands for nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, a molecule that acts as an electron donor/ carrier in all organisms
STEPS OF PHOTOSYNTHESIS
light reaction produce
1> ATP 2> NADPH 3> release oxygen
CO2 enters Calvin. ATP & NADPH used from light reaction > Calvin Cycle produces SUGAR
summary
in the light reaction, chlorophyll in the thylakoid membranes absorbs solar energy which is then converted to the chemical energy of ATP and NADPH and water is split, providing a source of electrons and giving off O2 gas as a by-product
the Calvin cycle (happens outside the thylakoid membrane )uses the products of the light reactions (oxygen) to make sugar (cellulose) from carbon dioxide
ATP generated by the light reactions provides the energy for sugar synthesis
the NADPH produced by the light reactions provides the high-energy electrons that drive the synthesis of the glucose from the carbon dioxide
thus, the Calvin cycle indirectly depends on light to produce sugar because it requires the supply of ATP and NADPH produced by the light reactions


cellular respiration is a process of electron transfer. A “fall” of electrons from food molecules to oxygen to form water releases the energy that mitochondria can use to make ATP
the opposite occurs in photosynthesis: electrons are boosted “uphill” and added to carbon dioxide to produce sugar
cellular respiration: electrons are ‘carried’ by NADH and “fall” combining with oxygen to “make” water
sunlight is a type of energy called radiation, or electromagnetic energy
the distance between the crests of two adjacent waves is called a wavelength
the full range of radiation is called the electromagnetic spectrum
light behaves as waves
discrete packets of energy called photons, fixed quantities of light energy
the shorter the wavelength, the stronger the energy of a photon
when a pigment molecule absorbs a photon, one of the pigment’s electrons gains energy
this electron is now said to be “excited”
the excited state is highly unstable
an excited electron usually loses its excess energy and falls back to its ground state almost immediately
most pigments release heat energy as their light-excited electrons fall back to their ground state

some pigments emit light as well as heat after absorbing photons
a fluorescent light emitted ya glow stick is caused by a chemical reaction that excites electrons of a fluorescent dye
the excited electrons quickly fall back down to their ground state, releasing energy in the for of fluorescent light
in the thylakoid membrane, chlorophyll molecules are organized with other molecules into photosystems
each photosystem has a cluster of a few hundred pigment molecules, including chlorophylls A & B and some carotenoids
how light reactions generate ATP & NADPH
photons of light excite electrons in the chlorophyll of the first photosystem
these photon are then trapped by the primary electron acceptor
this new photosystem then replaces the lost electrons by extracting new ones from water
this is the step that REALEASES O2
> light reactions —> produce 1.ATP 2. NADPH 3. release O2

the mechanism of ATP production during the light reactions is similar to cellular respiration
an electron transport chain pumps hydrogen ions across a membrane
ATP synthesis (enzyme) uses the energy stored by the H+ gradient to make ATP
the main difference is that food provides the high-energy electrons in cellular respiration, whereas light-excited electrons flow down the transport chain during photosynthesis
with each turn of the cycle
inputs:
CO2 from the air & ATP and NADPH produced by the light reactions
the Calvin cycle constructs an energy-rich sugar molecule called glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (G3P) using
carbon from CO2
energy from ATP
high-energy electrons from NADPH
plant uses G3P as the raw material to make
glucose
other organic compounds
know that ATP and NADPH are used from light reactions
carbon dioxide gas enters Calvin cycle
glucose is made in Calvin cycle
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
focused on the mitochondria
muscles need energy to work
muscles cells obtain this energy from the sugar glucose through a series of chemical reactions that depend upon a constant input of oxygen (O2)
when you work too hard and your body demands more oxygen, your muscles switch to “emergency mode” and they break down GLUCOSE very inefficiently and produce LACTIC ACID as a by-product
plants are autotrophs → make their own food
producers
we are heterotrophs → cannot make organic molecules from inorganic ones (need others to feed)
consumers
chemical ingredients for photosynthesis are
CO2 passes from the air into a plant via tinny pores
H2O is absorbed from the soil by the plant’s roots
chloroplast use light energy to rearrange the atoms of these ingredients to produce sugars, most importantly glucose (C6H12O6)
O2 is a by-product
plants use carbon dioxide to release oxygen plants make glucose (cellulose , starch)

both animals and plants use organic products of photosynthesis as a source of energy
cellular respiration used O2 to convert energy stored in chemical bonds of organic fuels called ATP
cells use ATP for all their work
this takes place in the mitochondria
WASTE PRODUCUTS of cellular of respiration are CO2 and H2O; the same ingredients for photosynthesis
plants store chemical energy via photosynthesis and then harvest this energy via cellular respiration
plants make more than they need for fuel → the rest can be stored (starch in potatoes)
people eat the plants and take advantage of their photosynthetic abilities
cellular respiration is AEROBIC (requires oxygen) harvesting of chemical energy from organic fuel molecules
the man way that chemical energy is harvested from food and converted to ATP

glucose is the basic food for all cells (MONOsaccharide)
table sugar = DIsaccharide

3 stages of cellular respiration (GCCET)
glycolysis
citric acid cycle
electron transport

glucose (6 carbons) is split into 2 molecules called pyruvic acid (usually located in the cytoplasm/outside the mitochondria ) (2 ATP)
citric acid cycle (inside the mitochondria) uses enzymes that are dissolved in the fluid within mitochondria and completes the breakdown of glucose all the way to CO2 (which is then released as a waste product (second step: CO2 is released as waste) (2ATP)
3 carbon molecules then donate high-energy electrons to NAD+; forming NADH
electron transport chain (ETC): (inside the mitochondria) electrons from NADH are combined with oxygen {hydrogens, electrons, and oxygen combine to form water} (the MOST/ nearly 30 ATP)
2+2+30 = 34 about 34 ATP is produced from each GLUCOSE molecule within this process
*the NADH that is used in the ETC, oxygen uses the electrons from NADH (oxygen is an electron ACCEPTOR)
the overall effect of all this transfer of electrons during cellular respiration is a “downward” trip for electrons
from glucose
to NADH
to am electron transport chain
to oxygen
FERMINTATION
LACTIC ACID FORMATION
anaerobic process (does not require oxygen) to harvest food energy
relies on glycolysis to produce ATP
glycolysis does NOT require oxygen / produces only 2 ATP molecules for each glucose
the addition of electrons to pyruvic acid produces a waste product called lactic acid
the lactic acid by-product is eventually transported to the liver, where liver cells convert it back to pyruvic acid
human muscles do NOT undergo alcoholic fermentation but instead produce lactic acid under no oxygen conditions
the buildup of lactic acid causes muscle fatigue
lactic acid produced by YEAST using lactic acid formation is used to produce
cheese, sour cream, yogurt, soy sauce, olives, cabbage, etc.
can perform alcoholic fermentation to produce O2 and ethyl alcohol instead of lactic acid
CO2 released in alc. drinks is responsible for bubbles in champagne , beer, & wine
CO2 release bubbles from fermenting yeast causes bread dough to rise
BOTH ANAEROBIC AND AEROBIC RESPIRATION START WITH GLYCOLYSIS (FERMINTATION & CELLULAR RESPIRATION)
GLYCOLYSIS IS THE UNIVERSAL ENERGY-HARVESTING PROCESS OF LIFE
When both stages of photosynthesis have been completed, the energy of light ends up in which of the following?
Sugar molecules
Photosynthesis releases the oxygen we breathe from which molecule?
Water
In photosynthesis, carbon atoms from carbon dioxide end up in which molecule?
Sugar
What is the source of the inorganic carbon fixed by photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide
Which of the following occurs in the stroma of the chloroplast?
The Calvin cycle
How does energy move between the light-dependent and light-independent reactions of photosynthesis?
In the form of ATP and NADPH
In photosynthesis, what is the function of light-dependent reactions?
To transform light energy into chemical energy
A molecule that absorbs the energy in specific wavelengths of light is called which of the following?
A pigment
Light-dependent reactions store chemical energy in which of the following?
ATP and NADPH
What is the ultimate source of the electrons that are transferred during the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis?
Water
Excited electrons have more energy than non-excited electrons. Electrons in the photosystems of plants are excited by light.
In carbon fixation, what inorganic molecule is "fixed" to RuBP?
Carbon dioxide
What source of energy is used in the Calvin cycle?
ATP and NADPH
The CO2 used in carbon fixation enters the plant through which of the following?
Stomata
How many carbon atoms make up RuBP?
5
What role does the enzyme RuBisCo play in the Calvin cycle?
Catalyzes the reaction between CO2 and RuBP
Which step of cellular respiration is responsible for making the most ATP molecules?
The electron transport chain
In fermentation, what molecule is converted to lactate (lactic acid)?
Pyruvate
What factor determines whether pyruvate is processed by cellular respiration or by fermentation?
Oxygen levels in the cells
Both aerobic respiration and fermentation begin with
glycolysis
Where in the cell does fermentation take place? Select all that apply.
The cytosol
Which step of fermentation is responsible for the majority of ATP production?
Glycolysis
Which of the following compounds is NOT produced during glycolysis?
ATP
Pyruvate
Glucose
NADH
Some of the ATP produced during aerobic cellular respiration is produced via substrate-level phosphorylation.
Which of the following molecules carry electrons from the citric acid cycle to the electron transfer chain? Select all that apply.
NADH
FADH2
In a molecule of sugar, where is energy stored?
In high-energy electrons in molecular bonds
Energy removed from sugar molecules is transferred to the ETC by which of the following?
Electron carriers
Which stage of cellular respiration releases energy from electrons in slow, controlled steps?
The ETC
Which of the following are outputs of the aerobic respiration of sugar? Select all that apply.
ATP
Water
Heat
Which of the following steps contribute electron carriers to oxidative phosphorylation? Select all that apply.
Pyruvate oxidation
Citric acid cycle
Glycolysis
Potential energy in the form of an electrochemical gradient is transformed into ATP during oxidative phosphorylation.
 Knowt
Knowt