SCI 10 REVIEWER
☆ 2nd grading.
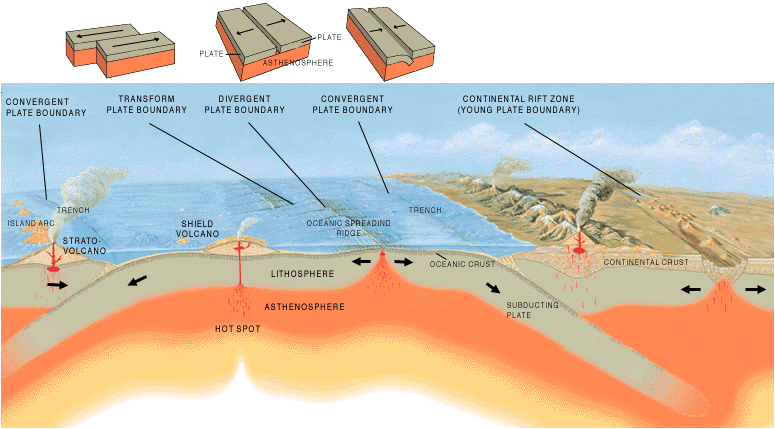
Lesson 1 - Plate Boundary Types
TERMINOLOGY:
PLATE TECTONIC THEORY
Explains how major landforms are created as a result of Earth’s subterranean movements.
- SUBTERRANEAN means ‘operating under the surface of the earth’
- It suggests that the Earth’s outer shell is divided into several parts that glide over the earth’s rocky inner layer.
- The lithosphere (outer shell) consists of tectonic plates. These plates ride on the asthenosphere.
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
A historical scientific theory that suggested that all continents were connected as one (a supercontinent) but separated and drifted away from each other over time.
- A supercontinent is one big, single piece of land. Alfred Wegener, the developer of the theory, named the supercontinent ‘Pangaea’.
- However, Scientists did not accept Wegener’s theory as it did not explain the mechanisms to why they drifted.
- This theory had been replaced with the theory we know of today: Plate Tectonic Theory.
LITHOSPHERE
Outer part of the earth. It consists of the crust and upper mantle.
- Oh so very cold compared to the earth’s asthenosphere.
- Has segments that vary in thickness. They tend to break into plates and move away, collide or slide past other plates due to mantle convection.
ASTHENOSPHERE
Layer under the lithosphere. It is the lower part of the upper mantle. It is semi-liquid.
- Consists of melted rocks.
PLATE BOUNDARY
The area where tectonic plates meet.
- See the three types in PLATE BOUNDARY TYPES
SUBDUCTION ZONE
A type of convergent plate boundary where at least one of the tectonic
plates sinks or bends beneath the other.
- In the ocean, a subduction zone can create an ocean trench. These are long, narrow dents on the seafloor.
PLATE BOUNDARY TYPES
There are 3 plate boundary types.
DIVERGENT BOUNDARY
- An area where two plates pull apart.
- An opening is created and a new crust is formed due to the magma that rises to the surface.
CONVERGENT BOUNDARY
- An area where two plates collide.
- If two plates are of equal density or weight, then, they push against each other and form a mountain chain
- If they are of unequal density, one plate sinks beneath the other and creates a subduction zone
TRANSFORM BOUNDARY
- An area where two plates slide past each other.
- Found in the ocean and creates a zigzag pattern between plates.
Lesson 2 - Mechanisms of Tectonic Plate Movement
TERMINOLOGY:
MANTLE CONVECTION
The process where heat from the Earth’s core is transferred upwards to the surface.
- It is thought that the heating of the mantle creates convection cells that activates this type of behaviour.
- Convection means the transfer of heat from one place to another in the form of liquid movement.
- This is commonly assumed to be the reason for tectonic plates movement.
MID-OCEAN RIDGES
Underwater mountain ranges that constantly create new variations of the Earth’s crust.
- This is possible due to the mid-ocean ridges acting as gaps for magma to reach the seafloor, solidify and form new oceanic crust.
ASTHENOSPHERE
Layer under the lithosphere. It is the lower part of the upper mantle. It is semi-liquid.
PLATE BOUNDARY
The area where tectonic plates meet.
- See the three types in PLATE BOUNDARY TYPES
SUBDUCTION ZONE
A type of convergent plate boundary where at least one of the tectonic
plates sinks or bends beneath the other.
- In the ocean, a subduction zone can create an ocean trench. These are long, narrow dents on the seafloor.
MECHANISMS OF PLATE MOVEMENT
There are two categories of forces (that causes plate movement).
DRIVING FORCES
- These forces propel or move the tectonic plates.
- There are 3 types of driving forces: ridge push, slab pull and suction.
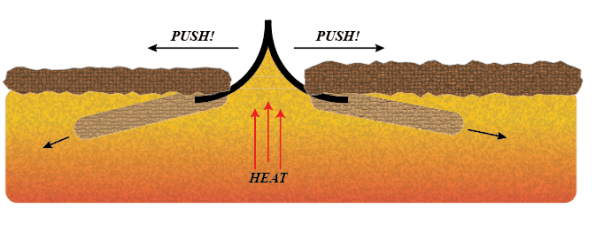
RIDGE PUSH: A force that pushes mid-ocean ridges apart to create a gap for magma to fill the gap and create a new crust.
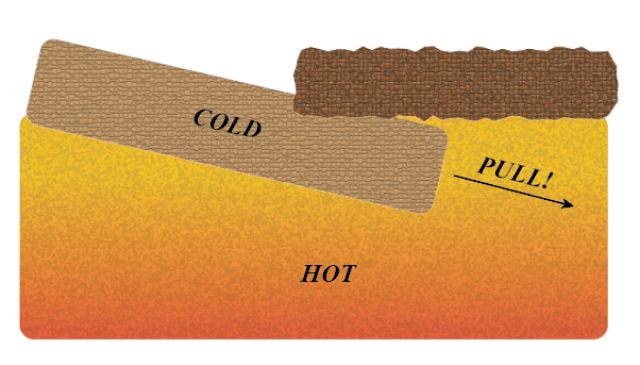
SLAB PULL: It occurs in subduction zones where denser or heavier plates sink down. Due to the weight, it continues to sink until the entirety of the plate is fully dragged down back into the mantle.
SLAB SUCTION: It is a process related to slab pull. However, this creates the force or effect that causes slab pull to occur.
- It’s like a vacuum and slab pull is the force that takes action to suck various items or crumbs inside, but in this case, it is tectonic plates and the mantle.
RESISTING FORCES
- These forces slow down or oppose the movements of the driving forces. They act as limits to prevent total destruction.
- There are 4 types of resisting forces: slab resistance, transform fault resistance, collisional resistance and drag force.
SLAB RESISTANCE: A resistance that occurs when a tectonic plate subducts into the Earth’s mantle. It is like pushing a heavy object into thick, sticky substances (like slime or lava).
- The heavy object does not fully sink into the substance due to the heavy viscosity/thickness of the substance.
TRANSFORM FAULT RESISTANCE: A resistance that occurs when tectonic plates grind or slide past each other.
- Ideally, both tectonic plates should glide past the other with ease. However, some plates move in opposite directions that cause bumps or temporary obstacles.
COLLISIONAL RESISTANCE: A resistance that occurs when tectonic plates collide or converge with the other.
- It is similar to magnets. If you hold two magnets with the same poles or side facing each other and try to push it, the force pushes them apart. It is similar to collisional resistance for tectonic plates.
DRAG FORCE: A resistance that occurs when a tectonic plate moves over the asthenosphere.
- It is similar to the feeling when you move your hand or yourself in water. Due to the resistance, you are unable to run or move as swiftly as you normally would. This is what a drag force feels like.
Lesson 3 - Land Formations on Plate Boundaries
TERMINOLOGY:
MANTLE CONVECTION
The process where heat from the Earth’s core is transferred upwards to the surface.
- It is thought that the heating of the mantle creates convection cells that activates this type of behaviour.
- Convection means the transfer of heat from one place to another in the form of liquid movement.
- This is commonly assumed to be the reason for tectonic plates movement.
PRIMORDIAL HEAT
One of the three sources of heat.
- Also known as old heat
- These are heat that was trapped during the formation of the Earth. It’s warmth that has stuck around since the Earth was born (poetic :00000).
RADIOACTIVE ISOTOPES
One of the three sources of heat.
- Tiny particles in the Earth that give off heat as they change.
- Acts like an ongoing heater inside the Earth.
TIDAL FRICTION
One of the three sources of heat.
- Heat from the Earth’s movements caused by the Moon’s pull.
- It’s like when you adjust your sitting position while on the couch because your ass feels kinda off (loooooolzers). That creates some warmth.
- A more serious explanation is that the gravitational pull from the Moon causes tides in the ocean. The rotational energy created from the earth is converted into heat.
LITHOSPHERE
Outer part of the earth. It consists of the crust and upper mantle.
- Oh so very cold compared to the earth’s asthenosphere.
- Has segments that vary in thickness. They tend to break into plates and move away, collide or slide past other plates due to mantle convection.
ASTHENOSPHERE
Layer under the lithosphere. It is the lower part of the upper mantle. It is semi-liquid.
- Consists of melted rocks.
EARTH’S CRUST
The outermost layer of the Earth.
- The thinnest, coolest layer among the three main layers (crust, mantle and core).
- Composed of various rocks.
DIFFERENT LAND FORMATIONS ON BOUNDARIES
Plates move in different directions along the lithosphere and asthenosphere all the time, but no gaps are ever made. There are three categories of land formations: Divergent, Convergent and Transform.
The landforms that these boundaries create depend on the type of plates.
DIVERGENT
RIFT VALLEY
- Two CONTINENTAL plates
MID-OCEAN RIDGES AND VOLCANOES
- Two OCEANIC plates
CONVERGENT
FOLDED MOUNTAINS
- Two CONTINENTAL plates
MID-OCEAN RIDGES AND VOLCANOES
- OCEANIC and CONTINENTAL plates
DEEP-OCEAN TRENCH
- Two OCEANIC plates
VOLCANIC ISLAND ARC
- Two OCEANIC plates
TRANSFORM
TRANSFORM FAULTS
- Basically the movements of TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES.
- When one plate slides past another but, when the plates get stuck due to friction and suddenly release, it creates an earthquake.
- There are various types of faults, a total of 6.
NORMAL FAULTS: It is simply pulling the Earth’s crust apart (like two pieces of bread).
- This fault often creates valleys and is seen in areas where the Earth’s crust is stretching.
REVERSE FAULTS: It is the opposite of NORMAL faults. It is squeezing or pushing the earth’s crust together.
- This fault often forms mountains and are seen in areas where the crust is being compressed.
STRIKE-SLIP FAULTS: It is when tectonic plates move past each other (transform boundary movement, yerknow).
- Often causes earthquakes
OBLIQUE-SLIP FAULTS: This fault’s tectonic plates move like a boat on water. It moves up and down while moving forward side-by-side.
R-LATERAL FAULTS: This simply describes the sense of movement of the fault. This fault moves right.
L- LATERAL FAULTS: Like the above, this fault moves left.
THE FORMATION OF THE PHILIPPINE ARCHIPELAGO
In summary, there were several incidents of subduction and collision of oceanic plates that are located along the Pacific Ring of Fire. The subduction process led to volcanic activity and created volcanic island arcs that are known as the ‘Philippine Island Arc System’.
Lesson 4 - Lines of Evidence that Support Plate Movement
TERMINOLOGY:
PLATE TECTONIC THEORY
Explains how major landforms are created as a result of Earth’s subterranean movements.
- SUBTERRANEAN means ‘operating under the surface of the earth’
- It suggests that the Earth’s outer shell is divided into several parts that glide over the earth’s rocky inner layer.
- The lithosphere (outer shell) consists of tectonic plates. These plates ride on the asthenosphere.
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY
A historical scientific theory that suggested that all continents were connected as one (a supercontinent) but separated and drifted away from each other over time.
- A supercontinent is one big, single piece of land. Alfred Wegener, the developer of the theory, named the supercontinent ‘Pangaea’.
- However, Scientists did not accept Wegener’s theory as it did not explain the mechanisms to why they drifted.
- This theory had been replaced with the theory we know of today: Plate Tectonic Theory.
EVIDENCES OF PLATE MOVEMENT
Both theories above suggest that the Earth is constantly moving. While Continental Drift Theory proposed that each continent propelled through the ocean floor, Plate Tectonic Theory gained more credibility for proposing that the Earth is broken into seven large and many smaller plates.
There are a total of 5 pieces of evidence of plate movement.
SEISMIC AND VOLCANIC
- Earthquakes and volcanic activity occur along plate boundaries.
- Earthquakes are caused by the release of energy when tectonic plates interact and move and Volcanic eruptions are related with plate subduction.
COMPLEMENTARY COAST
- Coastlines of some continents appear to fit together like puzzle pieces.
- This heavily suggests that continents were once connected and have since drifted apart.
FOSSILS
- Fossils of plants and animals are found on continents that have long been separated. For example, a fossil of an extinct Mesosaurus was found in both South America and Africa.
GEOLOGICAL EVIDENCE
- Similar rock formations and mountain ranges are found on different continents. For example, the Appalachian Mountains in North America align with the Caledonian Mountains in Scotland.
MAGNETIC POLARITY
The Earth’s magnetic field has an invisible giant needle (like on a compass). This needle sometimes flips and the north pole becomes the south pole, and vice versa.
- This is called reverse polarity if the north pole faces south, and if north faces north, it is called normal polarity.
- Recall the mid-ocean ridges and the new earth crust that is formed there. These are the stripes on the ocean floor and align themselves with the current magnetic field. Meaning, it aligns in the direction where the invisible giant needle is facing and solidifies.
- This creates a permanent recording of the Earth’s magnetic changes.
In relation to plate movement, these stripes and patterns signify the age of the seafloor.
- Wider stripes represent older crust.
- The matching patterns in direction of these stripes also signify the direction of the tectonic plates moving away from the mid-ocean ridges.
Lesson 5 - Volcanoes and Earthquakes
TERMINOLOGY:
VOLCANO
An opening on the earth’s surface that allows warm material to escape from the inside of the earth. When these materials escape, it causes an eruption
- Volcanoes can be active, dormant, or extinct
- ACTIVE: Has erupted recently or is erupting as of the moment. It is capable of erupting at any time.
- DORMANT: Has erupted in the past and might erupt again in the future. It’s stagnant, almost like taking a break.
- EXTINCT: Has not erupted in a long time or is inactive.
EARTHQUAKE
A sudden shaking of the ground due to the movement of plates beneath the surface.
- The result of release of energy in the Earth’s crust.
FOCUS
The point underground where an earthquake starts.
EPICENTER
The point on the Earth’s surface above the focus. It is where the earthquake is felt the strongest.
MAGMA
Warm liquid within the earth that can rise to the surface.
MOUNTAIN BELTS
A big chain or family of mountains. They are grouped together in a line or series.
- Formed due to the collision or converging plates; The land is pushed upward to create all mountains.
ANTICLINES
A fold in the Earth’s crust where the rock layers bend upward in an arch or dome shape.
SYNCLINE
The opposite of ANTICLINE. It bends downward.
VOLCANO AND EARTHQUAKE RELATION
Both Volcanoes and Earthquakes connect through plate boundaries and movements. Most earthquakes happen at the edge of tectonic plates and it is where most volcanoes can be found too.
MOUNTAIN SYSTEMS
Idk kung anong purpose sng mountain system pero whatever the bible says ig
The Circum- (hoy bad) Pacific System
- A chain of volcanoes that is often called the PACIFIC RING OF FIRE
THE ANDES
- It is a mountain line in South America. It is the longest continental mountain range
THE CARIBBEAN CHAIN
- It is a mountain range along the coast of Venezuela. It is a remnant from when the Caribbean Sea was subducted beneath Venezuela.
THE NORTH AMERICAN CORDILLERA
- It is a mountain range that extends from Mexico to Alaska
VOLCANOES AND ISLAND ARCS SURROUNDING THE NORTHWEST PACIFIC
BASIN
- It is a mountain range that extends from mainland Alaska, along the Aleutian Islands and then down to the peninsula of Kamchatka in Siberia and along the Kuril Islands to JAPAN!#!#!@$$@
- DEFINITION OF PENINSULA: A piece of land that juts out from a larger landmass and is mostly surrounded by water. - thank u google ^_^
The Alpine-Himalayan/Thetyan System
- A chain of volcanoes that lie between Africa, Arabia and India on the South; Europe and Asia on the North.
- The various ranges of the A-H System formed at different times, rates and plates. They all consist of different types of rocks.
THE HIMALAYAN CHAIN
- Contains the highest peaks on Earth
- Begins at the western end of the Sunda Island Arc
- Can be subdivided into 3 parallel belts:
- TETHYS Himalayas - NORTH
- LESSER Himalayas - SOUTH
- Great Himalayas
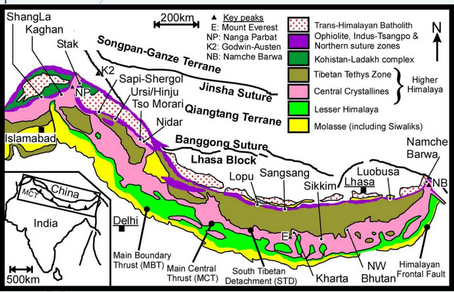
THE ZAGROS AND BITLIS MOUNTAINS
- Arabian Peninsula
- Collided with Iran and Turkey at the Zagros and Bitlist sutures
- DEFINITION OF SUTURES: a boundary where two tectonic plates collided and the result had led a merging of continental plates
THE WESTERN SEGMENT
- Involves more than just a collision of the African continent and parts of Europe
- After Africa had moved away from Europe, a new ocean floor (Tethys) had formed
- However, during the Cretaceous period, the divergence ceased and Africa and Europe began to converge
- This change is the reason to why many mountain ranges are different from the other
The Pacific Ring of Fire
- The plates within this belt are constantly sliding past, colliding or moving above/below the other.
- It is home to the deepest ocean trench: The Mariana Trench
- The tectonic activity is also the result of 90% of the world’s earthquakes
- Many of the world’s active volcanoes are located around the edges of the Pacific Ocean or Pacific Ring of Fire

