Dispute Resolution
Managing Wildlife Conservation Conflict
Definitions
Conflict: expressed struggle between at least 2 interdependent parties who perceive incompatible goals, scarce resources, and interference from others in achieving goals
what are some scarce resources in conflict over wildlife management?
intangible
tangible
Is human-wildlife conflict a reasonable idea?
Only with high level animals, like dolphins, baboons, etc
We tend to anthropomorphize wildlife when wildlife aren’t fighting with us, they’re just surviving
Case study: cat colony management
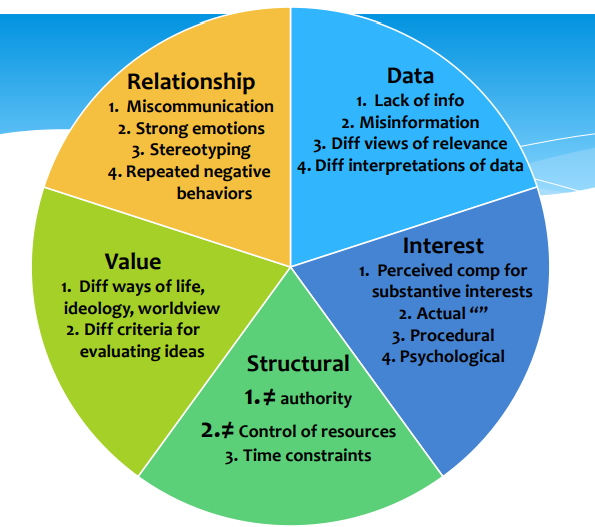
Value
Diff ways of life, ideology, worldview
Diff criteria for evaluating idea
Data
Lack of info
Misinformation
Diff views of relevance
Diff interpretations of data
Interest
Perceived comp for substantive interests
Actual ““
Procedural
Psychological
Structural
does not equal authority
does not equal control of resources
time constraints
Relationship
Miscommunication
Strong emotions
Stereotyping
Repeated negative behaviors
Relationship Conflict Interventions
Control expression of emotions: ground rules, caucuses, etc
Promote constructive expression of emotions by legitimizing feelings and creating a clear process
Clarify perceptions (build positive ones)
Improve quantity and quality of communication
Encourage problem-solving attitudes
Data Conflict Interventions
Build consensus on what data are important
Agree on a process to collect data
Create rules for using outside opinions and breaking deadlocks
Value Conflict Interventions
Avoid defining conflict based on values
find a superordinate goal that parties share
Allow mutually agreed upon disagreement
Create ‘spheres of influence’ where one party’s values dominate
Structural Conflict Interventions
Define and occasionally change roles
Replace destructive behavior patterns
Reallocate power (ownership/control)
Make decision-making process more fair/acceptable
Shift from coercion to persuasion
Modify physical and environmental relationships among parties
Change time constraints
Change from positional to interest-based bargaining
Stakeholders can be problematic in terms of managing conflict.
Interest-based Conflict Interventions
Interest not positions
Develop objective criteria for solution development
Create solutions that address needs for all parties
Create ways to ‘expand the pie’
Develop trade-offs for interests of different strengths
Bargaining
Position Based Bargaining
positions: statements by a party about how an issue can or should be handled
used when the resource being negotiated is limited, a party wants to maximize his share in a fixed sum pay off
Set target point, set bottom line, consider 1-2 for opponents, considers position between your 1-2, determine if any positions meet interests of opponents, move to positions that offer opponents more benefits as needed
Costs: damages relationships, kills creativity, promotes rigid positions, produces compromise when it isn’t needed
Benefits: reduce premature concessions, useful in fixed sum resources, does not require trust to work
Interest-Based Bargaining
interests: specific needs, conditions or gains that a party must have met in an agreement for it to be considered satisfactory (procedural, relationship, substance)
used when interests of the negotiators are interdependent
ID interests that must be met, speculate on 1 for opponents, educate each other, frame problem in a manner that is win win
Costs: requires some trust, requires negotiations to disclose info and interests
Benefits: produces solutions that meet specific interests, builds relationships, promotes trust
Methods for Conflict Resolution
Divided by who controls: process, issues, and outcome
Self-negotiation (parties control all three)
Fact-finding (third party share all three with parties)
Mediation (the facilitator only shares control over the process with parties)
Arbitration (third party controls process and outcome and shares control over issues)
Litigation (once it starts, third party controls all three)