IB ITGS - 1. Introduction
What is ITGS?
- Information Technology in a Global Society is the study of how developments in IT affect people and society.
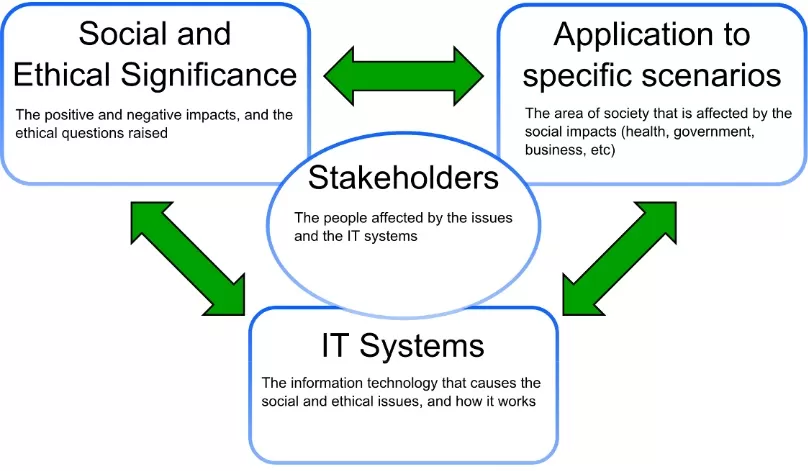
The ITGS triangle
There are four core aspects of ITGS:
- Social and ethical significance
- IT systems
- Application to specific scenarios
- Stakeholders
Strand 1: Social and ethical significance
- Issues of social and ethical significance can arise whenever IT is used. These issues have social impacts on stakeholders.
- These issues are:
- Reliability refers to how well a computer system works: if it functions as intended or fails and crashes.
- Integrity refers to the correctness of data.
- Security is concerned with protecting IT systems from unauthorized users.
- Privacy is the ability to control how data about us is used.
- A person becomes anonymous if they hide their identity and have total privacy.
- Intellectual property refers to creations of the mind.
- Copyright law is designed to protect intellectual property from unauthorized reproduction.
- Authenticity involves a user proving their identity to gain access to a computer.
- Digital divide and equality of access: IT has not developed at the same rate for everybody in all parts of the world. There are often individuals who lack access to technology.
- Surveillance involves using IT to monitor people.
- Globalization and cultural diversity: IT has helped to reduce global boundaries and speed up the global spread of news and culture.
- Policies are rules designed to control the way people use IT, often in the form of laws.
- Standards and protocols are technical rules that hardware and software designers should follow.
- People and machines concerns the way that humans interact with IT.
- Digital citizenship involves being a good citizen in a digital world.
Strand 2: Applications to specific areas
- Business and employment: many businesses make heavy use of IT to develop, advertise, and sell their products and services.
- Education and training: the availability of vast amounts of information for free on the Internet has opened up new educational possibilities for many people.
- Environment: robot vehicles and satellite technology have allowed us to explore and map Earth’s surface.
- Health: IT has helped advance healthcare in daily tasks. It also raises health concerns, such as addiction.
- Home and leisure: IT has changed the way we use our leisure time and the way that we interact with friends.
- Politics and government: governments have used IT to increase efficiency and transparency, as well as promote political campaigns.
Strand 3: IT Systems
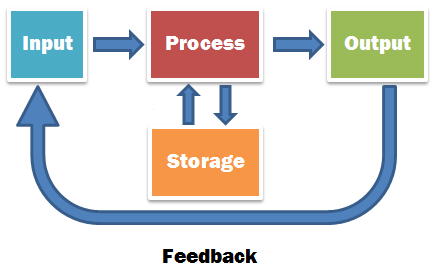
All IT systems take data as input and process it according to programmed instructions into output.
A system will also store data and communicate with other systems via networks.
They consist of:
- Hardware: to input, process, and output data.
- Software: to control the hardware.
- People: to use the system.
- Data: on which the system performs work.