INVERSE FUNCTIONS
def. reverts the x and y values of a function, values must be one to one to have an inverse function
e.g.
has an inverse function
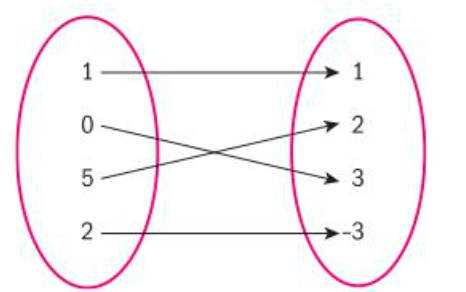
does not have an inverse function
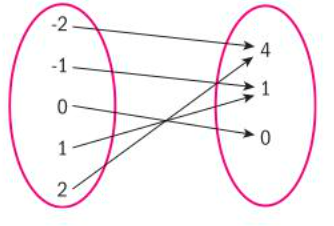
swaps the x and y values
domain and range are swapped
e.g. f = 3<x<8, f-1 = 3<y<8
regular function and inverse function will intersect at x=y
x and y intercepts are swapped
e.g. f = (0,3) (5,0), f-1 = (0,5) (3,0)
GRAPHING INVERSE FUNCTIONS
E.g.1
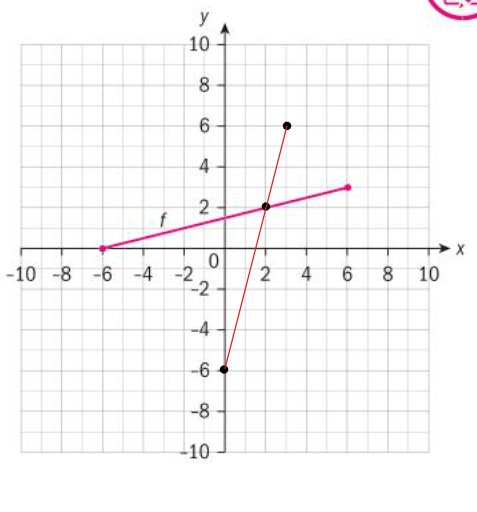 regular points = (-6,0), (2,2) and (6,3)
regular points = (-6,0), (2,2) and (6,3)
inverse points = (0,-6), (2,2) and (3,6)
E.g.2
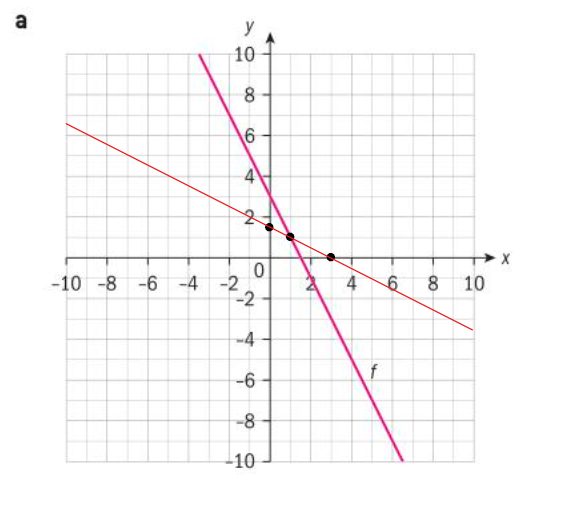
regular points = (0,3), (1,1) and (1.5,0)
inverse points = (3,0), (1,1) and (0,1.5)
E.g.3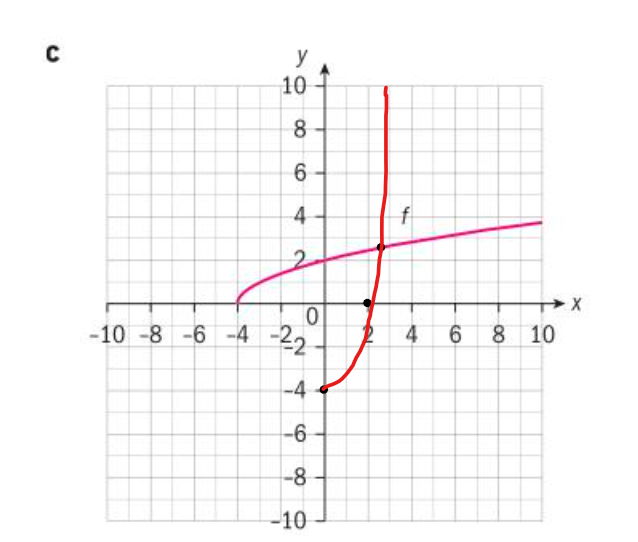 regular points = (-4,0), (0,2) and (2.5,2.5)
regular points = (-4,0), (0,2) and (2.5,2.5)
inverse points = (0,-4), (2,0) and (2.5,2.5)
IMPORTANT POINTS
y-intercept
x-intercept
point where x = y - e.g. (2,2) or (1,1) or (-4,-4)
Oxford IB Textbook : Exercises 5G and 5H