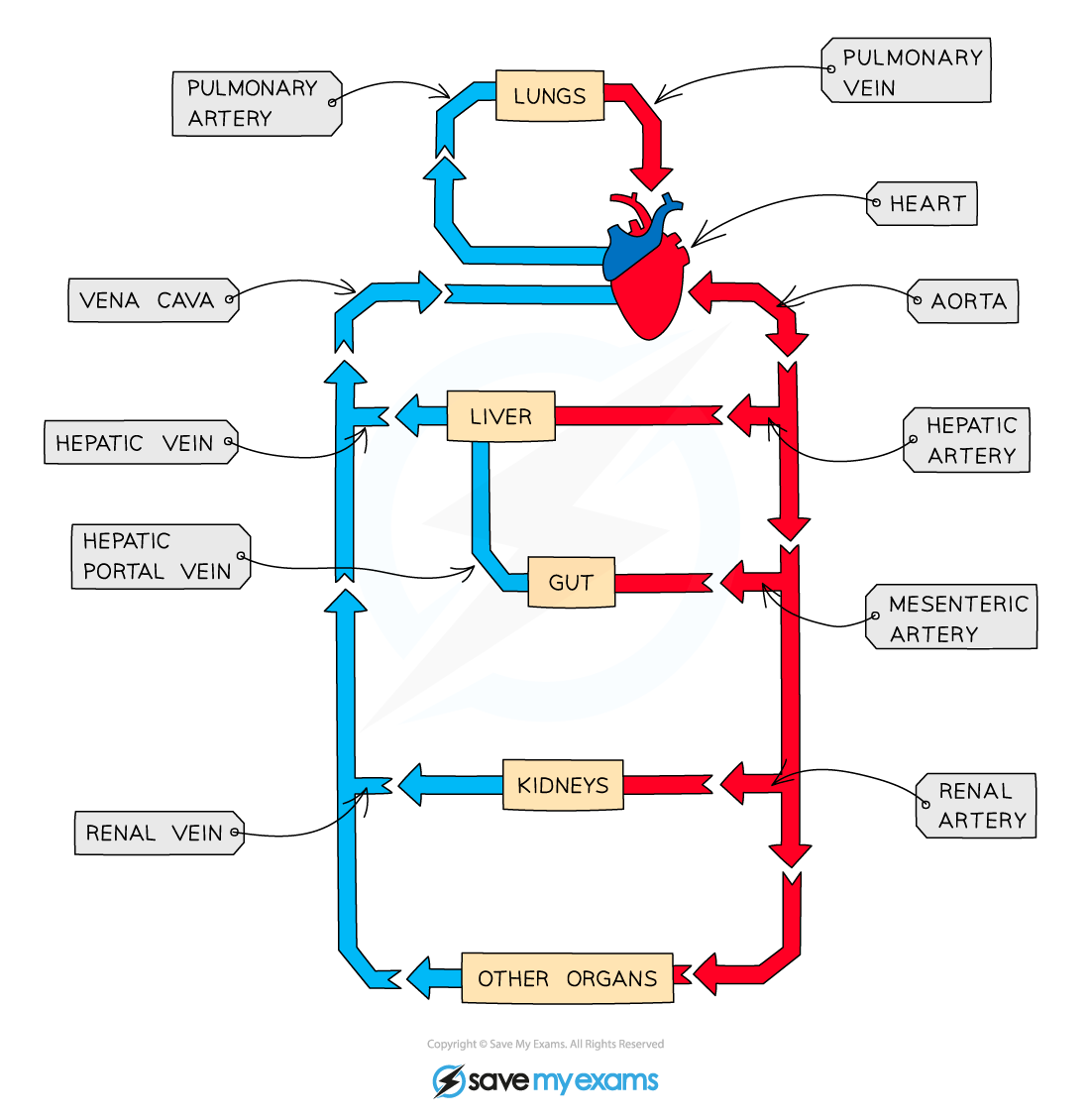
Heart
Order of blood transfer
Deoxygenated Blood enters through the
1) Vena Cava
2) Right Atrium
Tricuspid Valve
3) Right ventricle
Semilunar Valve
4) Pulmonary Artery
Oxygenated Blood enters through the
5) Pulmonary Vein
6) Left Atrium
Bicuspid Valve
7) Left Ventricle
Semilunar Valve
8) Aorta
Blood Vessels
Arteries
Elastic fibres and thick walls allow even higher pressure for transporting blood
Small lumen for higher pressure
High Pressure so that the arteries can handle the high velocity that the blood is travelling away from the heart at
Aorta has blood under highest pressure as it’s going all over the body
Veins
Elastic fibres and thin walls
Large lumens
Low Pressure
Valves to prevent backflow of blood
Capillaries
Thin wall - Only one cell think
Very small luman
Low Pressure
Permeable Wall
Capillaries adaptations for exchange:
Permeable walls for diffusion
Walls are once cell think so a short diffusion distance
Blood Components
Plasma - Carries plasma components. (Vitamins, minerals, hormones, urea)
Red Blood Cells - Carry Oxygen.
Platelets - Form blood clots
Structure and function of RBC:
Biconcave shape so a large surface area for diffusion of oxygen
No nucleus so more space for haemoglobin to carry oxygen
Normal Blood:
55% Plasma
5% White Blood Cells and platelets
40% Red Blood Cells
Aneamic Blood:
75% Plasma
5% White Blood Cells and platelets
20% Red Blood Cells
Anaemia
Iron Deficiency
Symptoms:
Shortness of breath
Tiredness
This is due to less iron to make haemoglobin in red blood cells. Red blood cells carry oxygen to cells around the body for respiration to produce energy. If less red blood cells due to anaemia then less energy produced causing symptoms of tiredness.
High Altitude Impact On Exercise
High altitudes have low oxygen levels
Causes the body to produce more red blood cells
This makes people more efficient at transporting oxygen in red blood cells to muscle cells needed for aerobic respiration
White Blood Cells
White blood cells fight disease.
There are two types:
Phagocytes : Large white blood cells that engulf pathogens. They send digestive enzymes that break down the pathogen and then release it when it’s done
Lymphocytes : Produce antibodies that stick to antigens (something your immune system doesn’t recognize) on pathogens to destroy them
Coronary Heart Disease
When coronary arteries become blocked with plaque (fat), it causes a lack of oxygen and then a heart attack.
Risk factors include:
Diet high in saturated fat
High blood pressure
Inactivity
Smoking
Diagram of circulatory system