POA
BANK RECONCILIATION STATEMENT
Bank Reconciliation
The process of keeping a personal account of your transactions in a cashbook to ensure no errors in bank statement book
Types of Payments in B.R
UNPRESENTED CHEQUES
Cheques that are sent but have not been recorded by the recipient
LATE LODGEMENT
Delayed money deposit by a business into their accounts by the bank
STANDING ORDER
Instructions given by a business to a bank to pay specified amounts at given dates
DIRECT DEBIT
An authorization for regular withdrawals from a bank account to pay bills or expenses.
BANK CHARGES
Payments of the business for services provided by the bank.
CREDIT TRANSFER
A direct electronic transfer of funds from one bank account to another.
DISHONOURED CHEQUE
A cheque that a bank refuses to pay due to insufficient funds, stale-dated cheques, error on cheque
Items in Cashbook but not Bank Statement
Unpresented Cheques (CR)
Late Lodgement (DR)
Items in Bank statement but not Cashbook
Bank charges (CR)
Standing order (CR)
Direct debit (CR)
Dishonoured cheques (CR)
Interest (CR)
Credit Transfer (DR)
Errors
CASH BOOK ERRORS
Errors made during the writing up of the cash book. Should be corrected while cash book is being adjusted.
BANK ERRORS
Should not be corrected in the cash book. Instead, should be shown as adjustments at the bottom of the bank recon statement.
ACCRUALS & PREPAYMENT
Adjusting Entries
Entries made at the end of an accounting period to allocate revenue and expenses to the period they belong to as required by the Matching/Accruals Concept.
Balance Sheet Extract
Capital VS Revenue Expenditure
CAPITAL EXPENDITURE
Expenditure on non-current assets such as purchasing a non-current asset
REVENUE EXPENDITURE
Expenditure on the day-to-day running costs of an organization
DEPRECIATION
Define Depreciation
the decline in the the useful life of a fixed asset.
INCOME STATEMENTS (TRADING & PROFIT AND LOSS)
Purpose of Income Statement
Its purpose is to show how much profit or loss has been made over a period of time. The main purpose of the trading and profit and loss account (income statement) is for the owners to be able to see how profitably the business is being run
Gross Profit (Net Sales-Cost of Goods Sold)
The excess of sales over the cost of goods sold in the period.
Net Profit (Gross Profit-Total Exp)
What is left of the gross profit after all other expenses have been deducted
Format for Income Statement
Sales | xxx | |
|---|---|---|
Less Sales Return | xxx | |
Net Sales | xxx | |
Less Cost of Goods Sold | ||
Opening Stock | xxx | |
Add Purchases | xxx | |
Add Carriage Inwards | xxx | |
xxx | ||
Less Return Outwards | xxx | |
Costs of Goods Available for Sale | xxx | |
Less Closing Stock | xxx | |
Cost of Goods Sold | xxx | |
Gross Profit (Net Sales-Cost of Goods Sold) | xxx | |
Additional Revenue | xxx | |
Less Expenses | ||
Expenses | xxx | |
Last Expense | xxx | |
Total Expenses | xxx | |
Net Profit (Gross Profit-Total Exp) | xxx (Double Underline) |
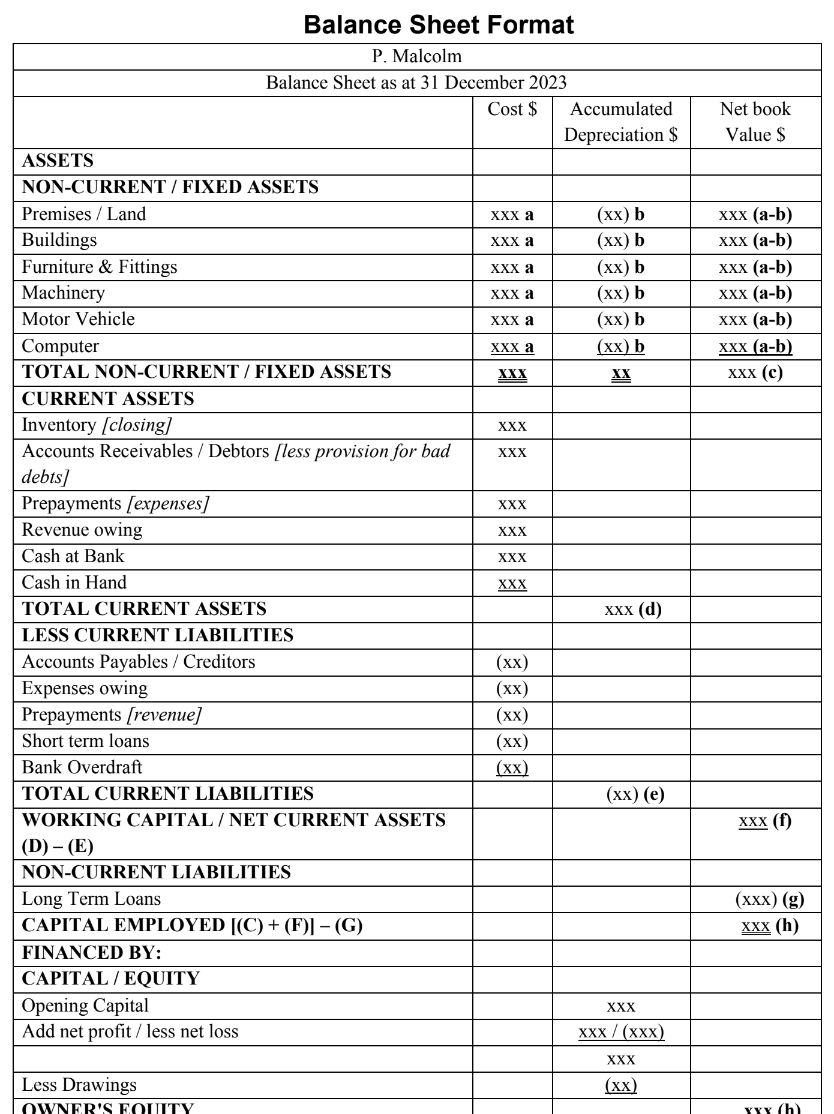
BALANCE SHEET (STATEMENT OF FINANCIAL POSITION)
Components of Balance Sheet
NON-CURRENT ASSETS
Furniture & Fittings
Vehicles
Land and Premises
Buildings
Machinery
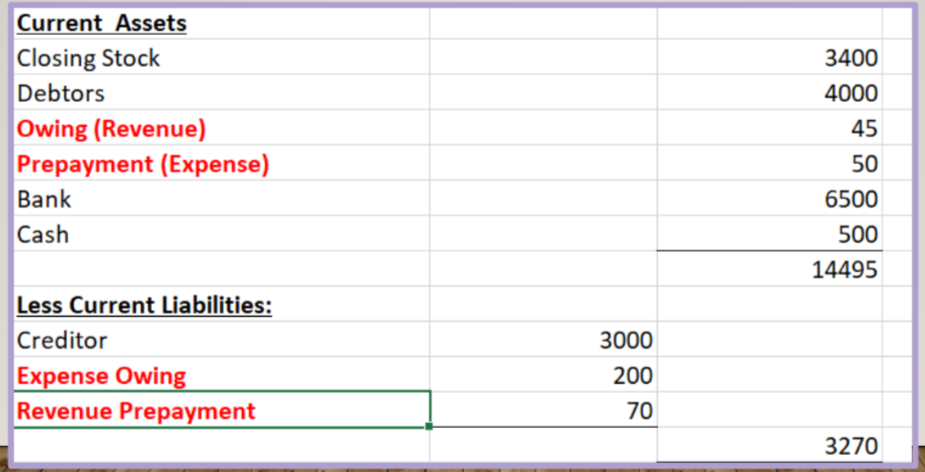
CURRENT ASSETS
Accounts Receivable/debtors
Cash in hand
Cash at bank
Inventory
Prepayment (Expense)
Accruals (Revenue)
CURRENT LIABILITIES
Bank Overdraft
Accounts Payable/creditors
Short term loan
Accruals (Expense)
Prepayment (Revenue)
WORKING CAPITAL
Formula: Total Current Assets - Total Current Liabilities
NON-CURRENT LIABILITIES
Long term Loan
Mortgage
CAPITAL EMPLOYED
Total Non-Current Assets+Working Capital
FINANCED BY:
Capital
Opening Balance
Add Net Profit
Less Drawings
Format of Balance Sheet (Sample) with provision for doubtful debts
Non-Current Asset | Cost | Depreciation | Net Book Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Land and Premises (Building) | xxx | xxx | xxx | |
Fixtures | xxx | xxx | xxx | |
(Total) | xxx | xxx | xxx | |
Current Asset | ||||
Closing Inventory | xxx | |||
Accounts Receivable | xxx | |||
Less provision for doubtful debts | (xxx) | |||
xxx | ||||
Bank | xxx | |||
(Total) | xxx | |||
Less Current Liabilities | ||||
Accounts payable | xxx | |||
Accruals | xxx | |||
(Total Current Liabilities) | (xxx) | |||
Working capital (Total Current Assets - Total Current Liabilities) | xxx | |||
(Add Working Capital + Total Non-Current Assets) | xxx Double underline | |||
Less non-current liability | ||||
Long term loan from … | (xxx) | |||
Capital Employed | xxx double underline | |||
Financed by: | ||||
Capital | ||||
Opening Balance | xxx | |||
Net Profit | xxx | |||
xxx | ||||
Less Drawings | (xxx) | |||
Owner’s equity | xxx double underline |
Simple Balance Sheet Format
TO NOTE
SALES RETURN ON TRIAL BALANCE
DEBITED: RETURN INWARDS
CREDITED: RETURN OUTWARDS
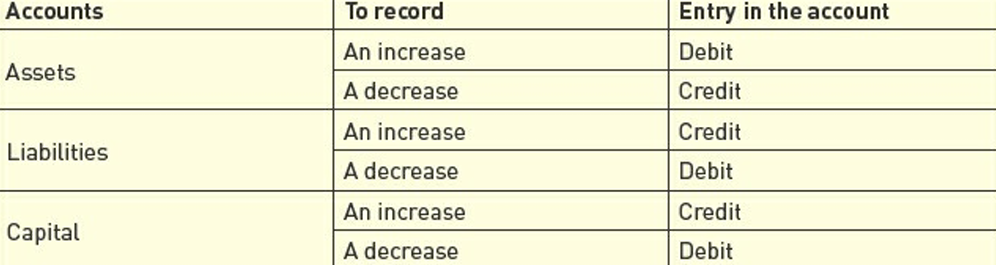
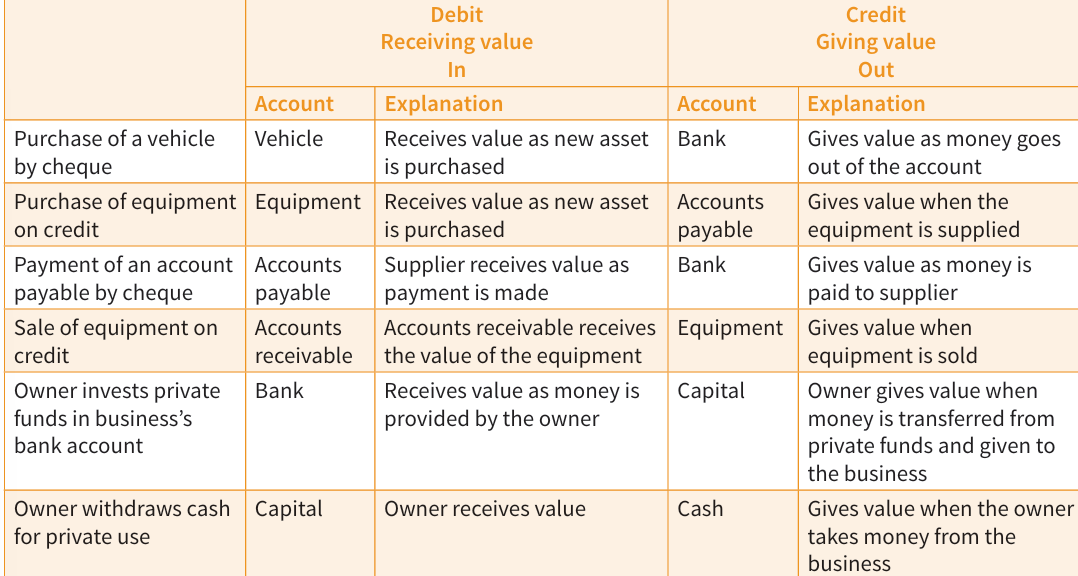
DOUBLE ENTRY SYSTEM
DEFINITION
A record-keeping system, where every transaction is recorded with at least two entries: a debit and a credit.
Types of Accounts
Personal Accounts
Accounts receivable
Real Accounts
Assets, liability, capital
Nominal Accounts
Expenses and revenue
REVENUE
Income earned by the business, such as:
Rent Received
Interest Received
Discount Received
Reduction in Prov. for Bad Debt
Commission Received
EXPENSES
Costs of operating the business
Rent
Salary
Electricity
Utilities
Carriage
Motor Expenses
Insurance
Advertising
Miscellaneous
CASH BOOK
Define Cash Book
A book of original entry in which all cash and bank transactions are recorded.
Three Column Cashbook
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN TWO VS THREE COLUMN
Three column makes provision for discounts while two does not
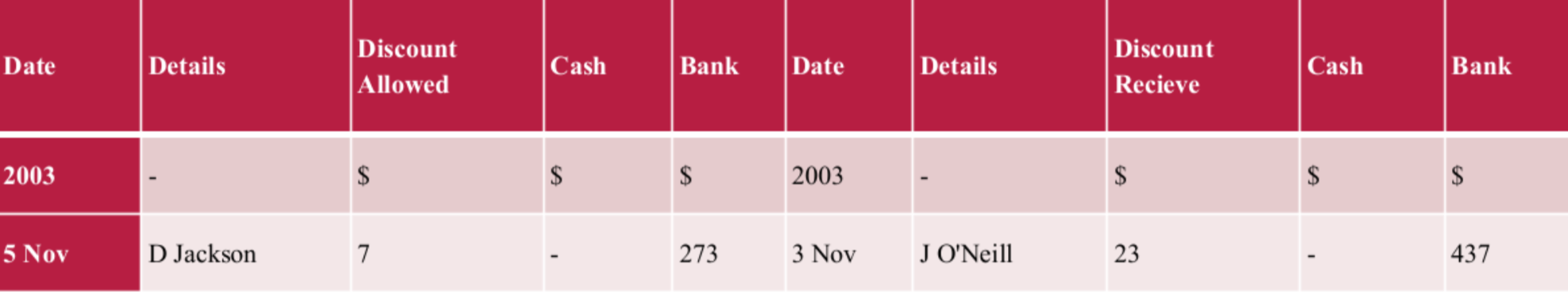
Contra Entry
An entry where a single transaction affects both the receipt and payment side of the cashbook. Both cash and bank columns are affected
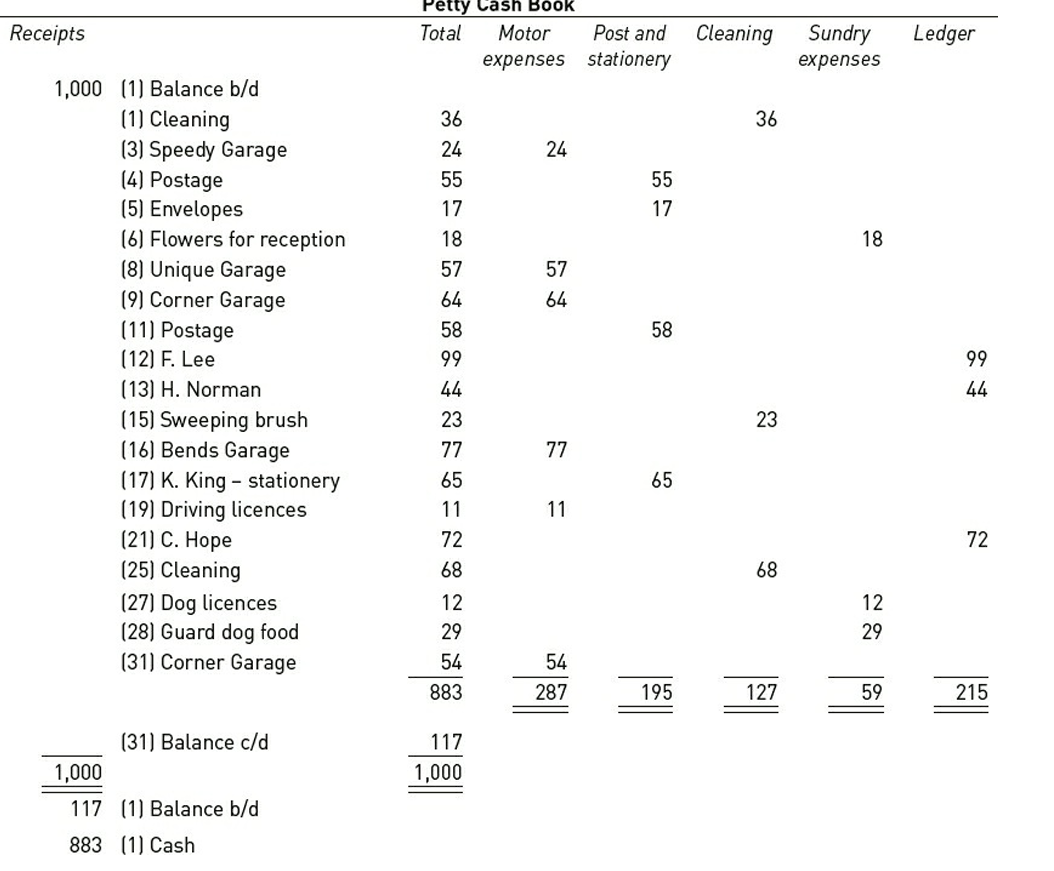
PETTY CASH BOOK
Define Petty Cash Book
A book of original entry that tracks small cash expenditures in a business
SOURCE DOCUMENT
Petty Cash Voucher
Imprest System
A system where the cashier gives the petty cashier enough cash to meet the needs of the next period
Petty Cash Book Example/Format
Receipt | Date | Detail | Voucher Number | Total | Petty expenses (Wages,etc) | Ledger Folio | Ledger Accounts |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 ^ 21.1 PG 342
^ 21.1 PG 342
SOURCE DOCUMENTS
Cash Book
Cash Receipt
Withdrawal Slip
Cheque Counterfoil
Bank Receipt
Pay-in-Slip
Debit and credit receipts
Cash Memo
Statement
Petty Cash Book
Petty Cash Voucher
Return Inwards/Outwards Journal
Credit Notes - INWARDS
Debit Notes - OUTWARDS
ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS
Definition
Fundamental rules that must be followed when preparing financial statements.
List of Concepts
ACCRUALS (MATCHING)
In order to calculate profit, income for a financial period is matched with expenses that relate to that accounting period, whether paid or not.
PRUDENCE (CONSERVATISM)
When there is doubt, asset and profit values should be understated rather than overstated.
CONSISTENCY
Accounting policies should be carried out in the same way year after year so that comparisons of performance can be made on a valid basis.
SEPARATE ENTITY
Only transactions affecting the financial position of the business are recorded in its books of accounts. The owner’s private financial affairs are not recorded.
HISTORICAL COST
Assets are normally shown at cost price
DOUBLE ENTRY/DUAL
For every transaction, giving of value and receiving of value occurs
MONEY MEASUREMENT
Accounting is concerned only with monetary transactions.
GOING CONCERN
This concept implies that the business will continue to operate for the foreseeable future.
REALIZATION
Revenue can only be recognized after it has been earned.
MATERIALITY
Determines whether the omission/misstatement of information in a financial report would impact a reasonable user's decision making
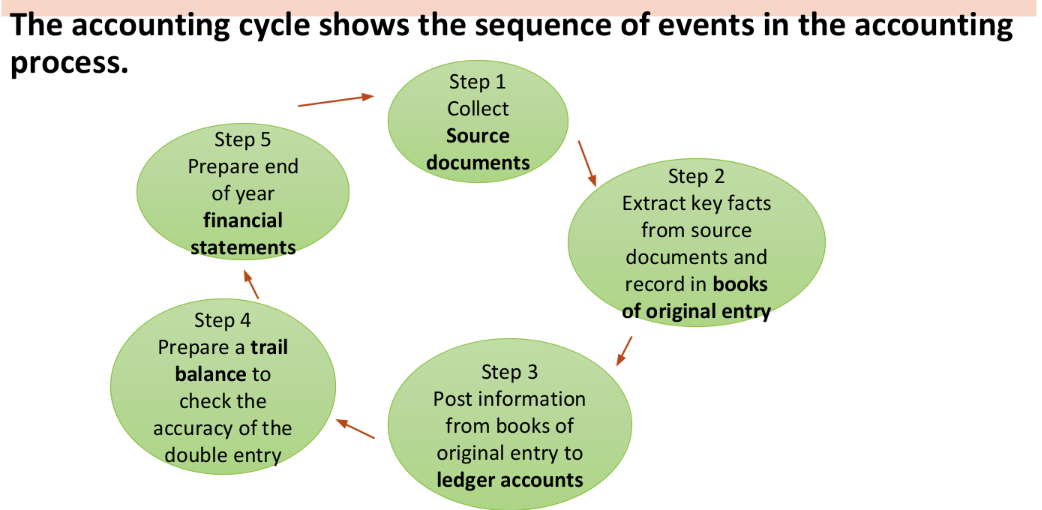
Accounting Cycle
ETHICS
Factors that Influence Ethical Views
CULTURE
What is immoral or illegal in some cultures is acceptable behaviour in others. Thus, ethics can differ in different cultures.
LAW
Illegal behaviour is unethical even when the law differs between countries. A company’s code of ethics always states that an employee must abide by local laws of the country.
CONSEQUENCES
Individuals react to ethical or unethical behaviour based on the consequences.
CODE OF ETHICS
When there is a code of ethics, behaviours are judged based on the code
Principles of Ethics
INTEGRITY
A professional accountant should be straightforward and honest in all professional and business relationships.
OBJECTIVITY
Professional accountants must stay unbiased, avoid conflicts of interest, and resist outside influence to make ethical decisions.
PROFESSIONAL COMPETENCE AND DUE CARE
A professional accountant needs to be independent, unbiased, and informed about industry updates to offer competent services. They must act diligently and follow technical and professional standards when working with clients or employers.
CONFIDENTIALITY
A professional accountant must keep information confidential from professional and business relationships, only sharing with proper authority or when required by law. They should not use this information for personal gain or benefit others.
PROFESSIONAL BEHAVIOUR
A professional accountant must follow laws and regulations, maintaining ethical behavior to uphold the profession's reputation. This includes ensuring the firm's ads are truthful and not misleading.
Application of Ethical Principles
treat people with respect and courtesy
act responsibly and honestly
ensure confidentiality
be accountable for your actions
be trustworthy
apply technical skills and competence
comply with legal requirements and organisation laws and regulations
avoid conflicts of interest.
Inappropriate Applications of E.P
not working in the best interests of your employer
being dishonest and untrustworthy
disregarding confidentiality
undermining colleagues
causing conflict
intimidation or harassment of colleagues to gain an advantage in a particular area
accepting bribes or gifts in return for a favour.
USERS OF ACCOUNTING INFO
Internal Users
OWNER
To create informed decisions in order to gain a profit to their business
MANAGER
To make informed decisions to improve the business
EMPLOYEES
A sound business with a good working environment will help to keep employees’ morale high and will be able to attract high-calibre new staff
External Users
BANK
To determine if a business is eligible to take/repay bank loans
INVESTORS
Private individuals, companies or banks, which will want to monitor the performance of the business to ensure that they will get a return on their investment
CUSTOMERS
To ensure the good/service is of high quality to purchase
SUPPLIERS
This group will need to be sure of the financial stability of the business before accepting orders
TYPES OF BUSINESS ORGANIZATIONS
SOLE TRADER
An individual trading alone in his or her name, or under a recognised trading name. He or she is solely liable for all business debts but when successful takes all the profits.
PARTNERSHIP
A group of more than two people and a maximum of twenty, carrying on a particular business to make a profit.
LIMITED COMPANIES
A private limited company is a legal entity which must have at least one shareholder and one director who may be the sole shareholder. The liability is limited to the amount that they have agreed to invest.
A public limited company is a legal entity with limited shareholder liability, but, unlike a private company, it can ask the public to subscribe for its shares.
NON-TRADING ORGANIZATIONS
Clubs, associations and other non profit-making organisations are normally run for the benefit of their members to engage in a particular activity and not to make a profit.
COOPERATIVE SOCIETIES
A business entity created to enhance the economic well-being of its members and society by offering goods or services.
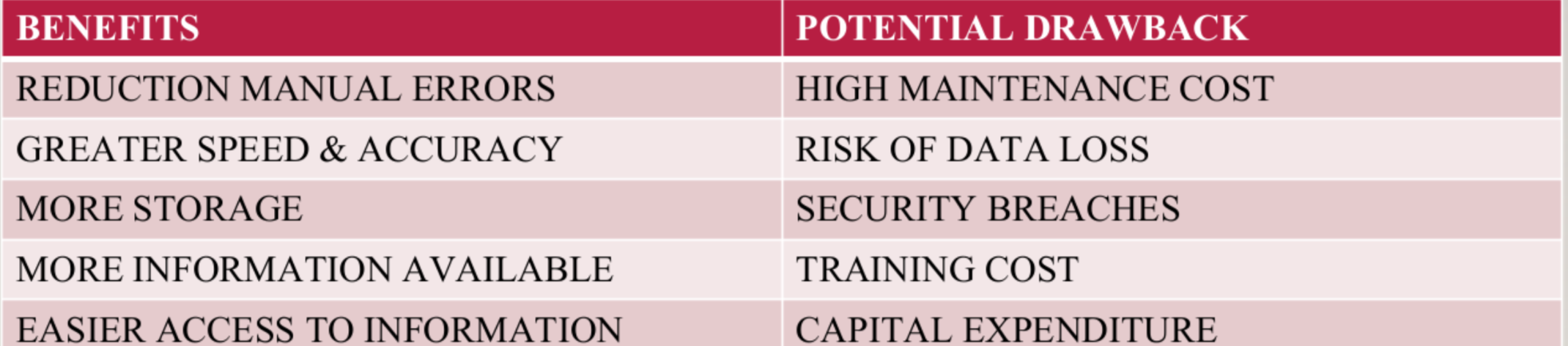
ACCOUNTING TECHNOLOGY
Accounting Software
QUICKBOOKS
FRESHBOOKS
SAGE
MICROSOFT DYNAMICS
NetSuite ERP
Advantages & Disadvantages
Jobs
Accounts Clerk
Financial Analyst
Auditing Clerk
Bookkeeper
Tax Professional
STUDYING CHECKLIST
Account Software/ Computer Software/ Computerized Accounting ( jobs, benefits, advantages and disadvantages)
Types of businesses organizations
Users of accounting information (Internal and external)
Ethical principles
Accounting Concepts ( should be able to apply them)
Ledgers/ T- accounts
Source documents (return inwards and return outwards)
Double Entry System
Petty Cash Book
Cash Book
Income Statements
Financial Position / Balance sheet (current assets)
Bank reconciliation