Global Challenges OCR Physics A
Physics on the Move
Speed is the rate at which an object covers distance. It is calculated as the distance traveled divided by the time taken. Speed is a scalar quantity and is typically measured in units like meters per second (m/s) or kilometers per hour (km/h).
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity of an object with respect to time. It is a vector quantity and can be calculated using the formula: acceleration = (final velocity - initial velocity) / time taken.
Speed and acceleration are used in various real-world applications. Speed is crucial in transportation for calculating travel time, while acceleration is important in designing vehicles for efficient performance.
Examples include using speed limits for road safety and optimizing acceleration in sports cars for quick acceleration.
Human Reaction Time: humans have a delay between their observation and acting which is around 0.25 seconds.
This can play a role when driving
The greater the speed of the vehicle, the greater the distance travelled during the same reaction time.
Dangers involved with braking hard
Increased risk of skidding
Potential loss of control
Wear on tires and brakes
Rear-end collisions
Strain on suspension components
Energy On Earth
Fossil Fuels
Derived from decomposed organic matter
Non-renewable due to long formation timescales
Combustion generates thermal energy for electricity
Nuclear Fuels
Uranium and plutonium
Energy released through nuclear fission
Concerns about safety and waste disposal
Biofuels
Derived from organic materials
Renewable and carbon-neutral
Used for electricity generation
Wind
Kinetic energy of wind converted to electricity
Renewable and harnessed through turbines
Hydroelectricity
Gravitational potential energy of water
Efficient and reliable
Electricity generated through turbines
Trends in the use of Energy Resources
Energy consumption was very low before 1850.
Sharp rise in coal use in the late 1800s due to the industrial revolution.
Extraction of fossil fuels and crude oil increased from the early 1900s.
Nuclear power has risen since the late 1900s.
Renewable energy usage has increased recently, with hydroelectric and wind being prominent.
The National Grid
Electrical power transferred at high voltages from power stations via overhead power lines.
Step-up transformers increase potential difference to reduce energy loss.
Step-down transformers decrease potential difference for domestic use.
Domestic Electricity Supplies
Mains electricity is AC at 50Hz and 230V.
Direct electricity (DC) is constant and provided by batteries.
Beyond Earth
Red shift is a phenomenon in which the light from an object moving away from an observer is shifted towards longer wavelengths, typically seen in astronomy as an indication of the expansion of the universe.
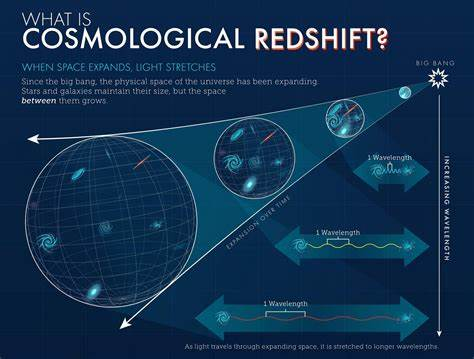
Big Bang: The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the observable universe's earliest known periods. It suggests that the universe expanded from a high-density state, evolving into its current state over billions of years.
Evidence: Red Shift and CMBR
Cosmic Microwave Background Radiation (CMBR) is electromagnetic radiation filling the universe, a remnant from the Big Bang, detected in all directions.
Life Cycle of Star
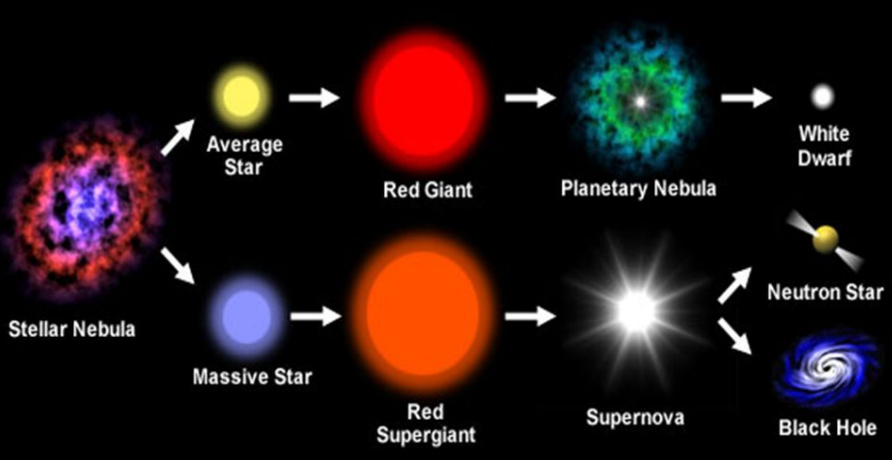
Dust and gas clouds present in a galaxy
Gravitational attraction causes cloud to become denser
Temperature and pressure increase
Fusion of hydrogen to form helium, releasing energy
Energy opposes gravity, forming a star
Star runs out of gas, collapses
Massive star collapses, produces supernova
Supernova becomes neutron star or black hole
Average star collapses, forms white dwarf
Radiation emission is the process by which energy in the form of waves or particles is released from a source, such as radioactive materials or electromagnetic sources.
Satellites are objects placed into orbit around the Earth or other celestial bodies to relay information, provide navigation, conduct research, or for other purposes.
They can be natural, like moons, or artificial, like communication or weather satellites.
Polar Orbit
Used for surveillance and weather forecasting
Orbits over poles at low height, ~90mins period
Covers entire earth quickly, good for scanning large areas
Geostationary Orbit
Used for communications
Orbits over equator, 24hrs period
Appears fixed from Earth, same angular speed
Allows fixed satellite dishes for uninterrupted data transfer
Planetary Orbits
Gravitational force causes constant change in direction
Speed is constant, velocity changes
Closer orbit to sun increases gravitational attraction
Acceleration increases, orbital speed rises
Temperature
Balance between absorbed and emitted radiation determines body temperature
Earth's temperature affected by greenhouse gases
Increase in greenhouse gases leads to global warming
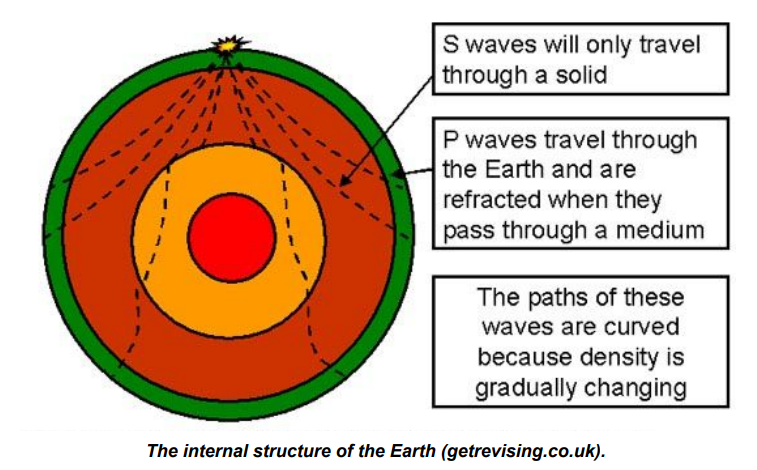
Earth’s Core
P waves pass through solids and liquids, S waves only through solids
Absence of S waves on opposite side of Earth suggests liquid core
Deep Water
SONAR used to map ocean floor
Higher frequency waves reflect subtle differences, lower frequency waves penetrate deeper
